Certiorari is a legal process whereby a higher court reviews the decision of a lower court to determine if there were errors in the application of the law. The Supreme Court often uses certiorari to select cases of significant public or constitutional importance for review. Explore the rest of this article to understand how certiorari impacts your legal rights and the judicial system.
Table of Comparison
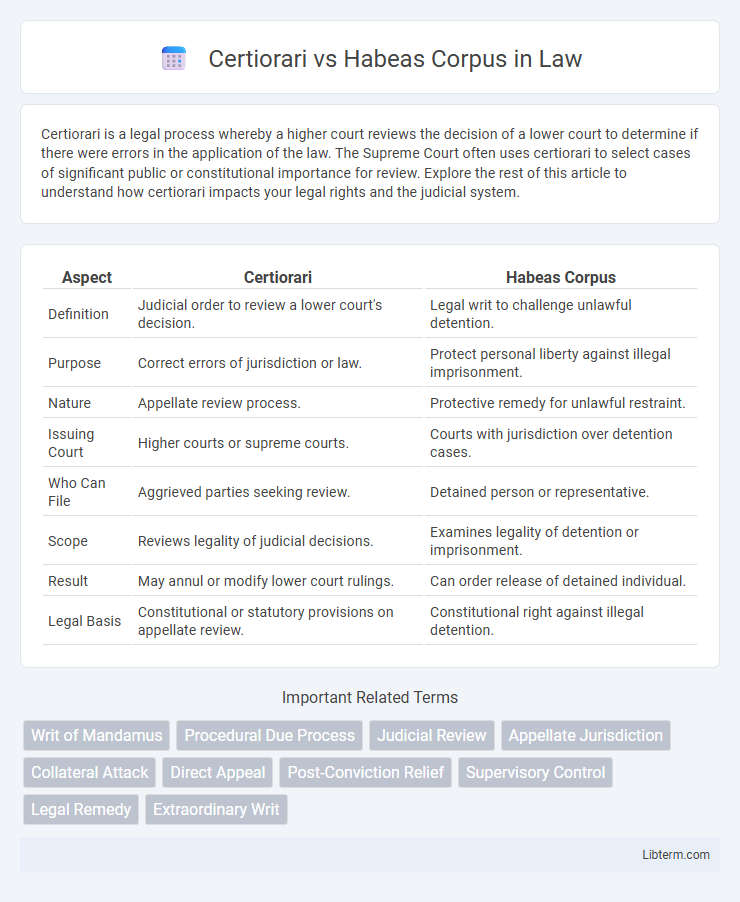
| Aspect | Certiorari | Habeas Corpus |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judicial order to review a lower court's decision. | Legal writ to challenge unlawful detention. |
| Purpose | Correct errors of jurisdiction or law. | Protect personal liberty against illegal imprisonment. |
| Nature | Appellate review process. | Protective remedy for unlawful restraint. |
| Issuing Court | Higher courts or supreme courts. | Courts with jurisdiction over detention cases. |
| Who Can File | Aggrieved parties seeking review. | Detained person or representative. |
| Scope | Reviews legality of judicial decisions. | Examines legality of detention or imprisonment. |
| Result | May annul or modify lower court rulings. | Can order release of detained individual. |
| Legal Basis | Constitutional or statutory provisions on appellate review. | Constitutional right against illegal detention. |
Introduction to Certiorari and Habeas Corpus
Certiorari is a legal mechanism used by higher courts to review and potentially overturn decisions made by lower courts, ensuring the correct application of law and judicial procedures. Habeas corpus is a constitutional safeguard that protects individual freedom by allowing detainees to challenge unlawful imprisonment before a court. Both writs serve distinct functions within the judicial system, with certiorari focusing on appellate review and habeas corpus emphasizing protection against illegal detention.
Definition of Certiorari
Certiorari is a legal process through which a higher court reviews the decision of a lower court to ensure the proper application of law and legal principles. This writ is typically issued by appellate courts, such as the Supreme Court, to correct errors or clarify legal interpretations. Unlike habeas corpus, which challenges unlawful detention, certiorari focuses on reviewing judicial rulings for procedural or substantive correctness.
Definition of Habeas Corpus
Habeas Corpus is a legal writ demanding that a detained person be brought before a court to determine if their imprisonment or detention is lawful. It serves as a fundamental protection against illegal detention and ensures individual freedom by requiring prompt judicial review. Unlike Certiorari, which is a court order to review decisions of lower courts, Habeas Corpus directly challenges the legality of a person's physical restraint.
Historical Background of Both Writs
Certiorari originated in English common law as a means for higher courts to review decisions of lower courts, evolving during the medieval period to ensure legal errors were corrected. Habeas Corpus traces back to the Habeas Corpus Act of 1679 in England, designed to protect individual freedom by preventing unlawful detention. Both writs have become fundamental in modern legal systems, safeguarding judicial oversight and personal liberty.
Legal Basis and Statutory Provisions
Certiorari is grounded in Article 8, Section 21 of the 1987 Philippine Constitution, allowing the Supreme Court to review cases for grave abuse of discretion amounting to lack or excess of jurisdiction, primarily governed by Rule 65 of the Rules of Court. Habeas Corpus is constitutionally mandated under Article 3, Section 15 to safeguard individual liberty against unlawful detention, with its procedural framework outlined in Rule 102 of the Rules of Court. Both remedies serve distinct legal purposes: Certiorari corrects errors of jurisdiction by lower courts or tribunals, while Habeas Corpus challenges the legality of a person's detention or restraint.
Purpose and Scope of Certiorari
Certiorari serves primarily to review decisions of lower courts or administrative bodies to ensure legal correctness and prevent jurisdictional errors, focusing on cases with significant public importance or constitutional questions. Its scope is discretionary, allowing higher courts to control the appeal process and maintain uniformity in the application of law. Habeas Corpus, by contrast, is a remedy against unlawful detention, safeguarding an individual's liberty by questioning the legality of their imprisonment rather than addressing broader judicial errors.
Purpose and Scope of Habeas Corpus
Habeas Corpus serves as a fundamental legal remedy designed to protect individual liberty by challenging unlawful detention or imprisonment, ensuring that a person's right to freedom is not violated without due process. Its scope is specifically focused on the legality of the detention itself, compelling authorities to justify the basis for incarceration before a court. In contrast, Certiorari is a discretionary judicial review mechanism primarily used to review the decisions of lower courts or administrative bodies for jurisdictional errors or grave abuse of discretion.
Key Differences: Certiorari vs Habeas Corpus
Certiorari is a judicial review process wherein a higher court orders a lower court to submit the record for examination to determine if there were legal errors, primarily used in appellate procedure. Habeas Corpus is a legal action that challenges the lawfulness of a person's detention or imprisonment, aiming to protect individual freedom by requiring the custodian to justify the legality of the confinement. The key difference lies in Certiorari's focus on reviewing lower court decisions for procedural correctness, while Habeas Corpus directly addresses the legality of a person's detention.
Landmark Cases Illustrating Each Writ
The landmark case Marbury v. Madison (1803) established the writ of certiorari as a key tool for the U.S. Supreme Court to review lower court decisions, shaping judicial review. In contrast, Ex parte Milligan (1866) prominent for habeas corpus, reinforced the right to challenge unlawful detention and upheld civil liberties during wartime. These cases distinctly highlight certiorari's role in appellate jurisdiction and habeas corpus's function in protecting personal freedom.
Conclusion: Choosing the Appropriate Legal Remedy
Certiorari is an appellate remedy used to review lower court decisions for legal errors, while habeas corpus addresses unlawful detention or imprisonment, protecting an individual's personal liberty. Selecting the appropriate legal remedy depends on whether the issue involves challenging judicial rulings (certiorari) or contesting the legality of confinement (habeas corpus). Understanding the distinct functions and procedural requirements of each remedy ensures effective legal strategy and protection of rights.
Certiorari Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com