A ruling is an official decision made by a court or legal authority that resolves a specific issue or dispute. It establishes a precedent that can influence future cases and provides clarity on the interpretation and application of laws. Discover how different types of rulings impact your legal rights and the justice system in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
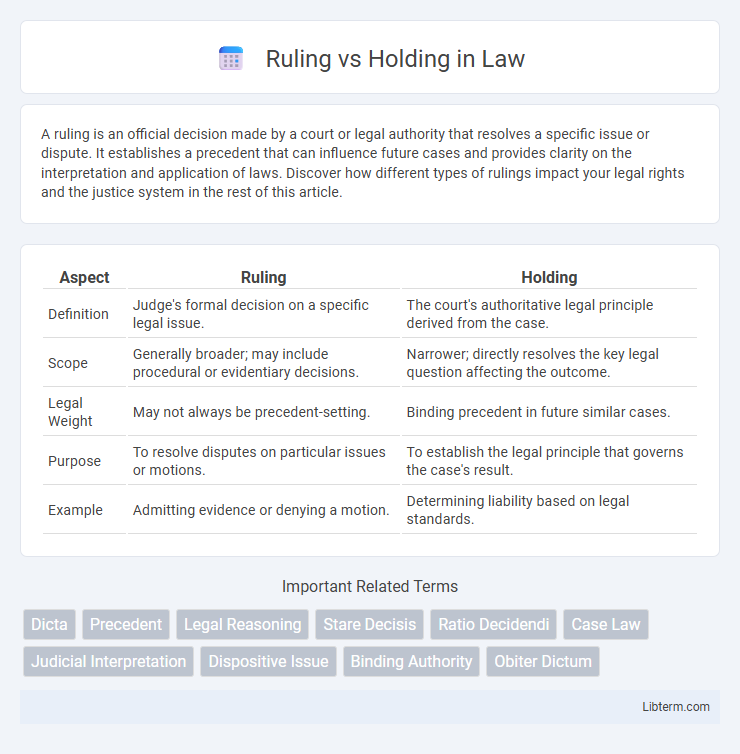
| Aspect | Ruling | Holding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Judge's formal decision on a specific legal issue. | The court's authoritative legal principle derived from the case. |
| Scope | Generally broader; may include procedural or evidentiary decisions. | Narrower; directly resolves the key legal question affecting the outcome. |
| Legal Weight | May not always be precedent-setting. | Binding precedent in future similar cases. |
| Purpose | To resolve disputes on particular issues or motions. | To establish the legal principle that governs the case's result. |
| Example | Admitting evidence or denying a motion. | Determining liability based on legal standards. |
Definition of Ruling and Holding
A ruling is a judge's official decision on a specific legal issue during the course of a trial or hearing, often determining the admissibility of evidence or procedural matters. A holding refers to the court's essential legal principle or ruling on the substantive issue, forming the binding precedent for future cases. While a ruling addresses immediate case management, a holding defines the law applied to the facts.
Key Differences Between Ruling and Holding
A ruling refers to a judge's decision on a specific legal matter or procedural issue within a case, often addressing motions or objections. Holding, however, denotes the court's authoritative legal principle derived from the case's facts that serves as precedent for future cases. Key differences include that rulings resolve individual case disputes and may be narrow or isolated, while holdings establish binding law that guides subsequent judicial decisions.
Legal Significance of a Ruling
A ruling determines how specific legal issues or motions are resolved during a case, directly impacting the procedural progress and influencing trial outcomes. It establishes authoritative guidance on the application of law within the case's context, shaping judicial discretion and case management. The legal significance of a ruling lies in its immediate effect on case strategy and its potential to set precedent for similar procedural questions in future litigation.
The Role of Holding in Judicial Decisions
Holding defines the court's essential legal principle directly resolving the dispute, serving as binding precedent for future cases. Unlike the broader ruling that may include dicta or commentary, holding specifies the authoritative interpretation of law applied to the facts, shaping judicial consistency and predictability. Courts rely on holdings to establish legal standards and guide lower courts' decisions, ensuring coherent application of legal doctrines.
How Courts Use Rulings vs Holdings
Courts use rulings to address immediate procedural or evidentiary issues within a case, providing decisions that may not set precedent. Holdings represent the court's authoritative legal determinations on the substantive issues, establishing binding precedent for future cases. Understanding the distinction allows legal professionals to identify which parts of a judicial decision shape binding legal principles versus those resolving specific case matters.
Examples Illustrating Ruling and Holding
A ruling determines the admissibility or procedure during a trial, such as a judge allowing evidence to be presented, while a holding is the court's legal principle derived from the decision, like the Supreme Court's ruling in Brown v. Board of Education declaring racial segregation unconstitutional. For example, when a judge excludes hearsay evidence, that is a ruling; when an appellate court interprets a statute to clarify its application, that forms a holding. These distinctions guide future cases by separating procedural decisions from binding legal principles.
The Impact of Holdings on Legal Precedent
Holdings in court decisions establish binding legal principles that lower courts must follow, directly shaping legal precedent and ensuring consistency in judicial outcomes. Unlike rulings, which may involve procedural or evidentiary determinations, holdings address substantive issues of law, creating authoritative guidance for future cases. The durable impact of holdings strengthens the predictability and stability of the legal system by defining how laws are interpreted and applied over time.
Common Misconceptions about Ruling and Holding
Many confuse a ruling with a holding, mistakenly believing they carry the same legal weight; a ruling refers to a judge's decision on procedural or evidentiary issues during trial, while a holding constitutes the court's final legal principle resolving the case's substantive issue. Misconceptions often arise because rulings can be interlocutory and non-precedential, whereas holdings are binding legal determinations forming precedent in future cases. Clarifying this distinction is crucial for accurate legal analysis and understanding the binding effect of judicial decisions.
Why Distinguishing Ruling from Holding Matters
Distinguishing ruling from holding matters because rulings address procedural or jurisdictional issues, while holdings establish the legal principles that guide future cases. Precise identification of holdings ensures accurate precedent application, preventing misinterpretation of a court's decision. This clarity supports consistent legal reasoning and effective advocacy in subsequent litigation.
Practical Implications for Legal Professionals
Rulings determine the outcome of specific motions or issues during a case and guide trial management, while holdings establish binding legal principles from the court's final decision that shape future case law. Legal professionals must distinguish rulings to effectively navigate procedural matters and adhere to holdings to develop case strategies and craft persuasive arguments grounded in precedent. Mastery of this distinction enhances courtroom efficiency and ensures accurate application of authoritative legal standards.
Ruling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com