Distributive justice focuses on the fair allocation of resources, benefits, and burdens across members of a society to ensure equity and social stability. It addresses issues of economic inequality, access to opportunities, and the criteria used to determine what people deserve based on merit, need, or equality. Explore the rest of the article to understand how distributive justice shapes social policies and impacts your daily life.
Table of Comparison
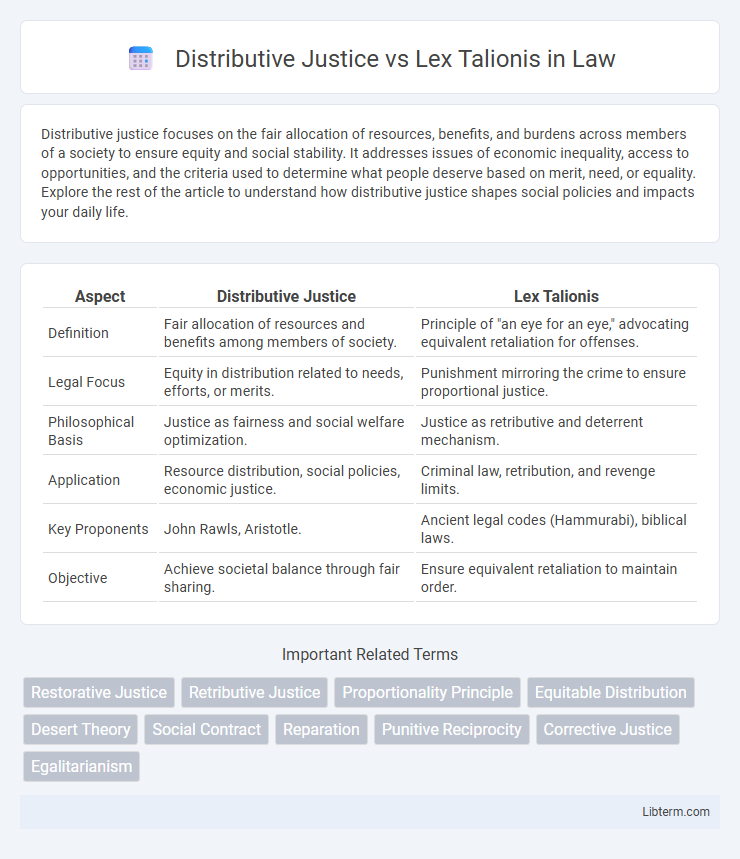
| Aspect | Distributive Justice | Lex Talionis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fair allocation of resources and benefits among members of society. | Principle of "an eye for an eye," advocating equivalent retaliation for offenses. |
| Legal Focus | Equity in distribution related to needs, efforts, or merits. | Punishment mirroring the crime to ensure proportional justice. |
| Philosophical Basis | Justice as fairness and social welfare optimization. | Justice as retributive and deterrent mechanism. |
| Application | Resource distribution, social policies, economic justice. | Criminal law, retribution, and revenge limits. |
| Key Proponents | John Rawls, Aristotle. | Ancient legal codes (Hammurabi), biblical laws. |
| Objective | Achieve societal balance through fair sharing. | Ensure equivalent retaliation to maintain order. |
Introduction to Distributive Justice and Lex Talionis
Distributive justice concerns the fair allocation of resources, opportunities, and responsibilities within a society, emphasizing equity and equality based on individual needs and contributions. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, is a principle rooted in retributive justice, advocating for punishment equivalent to the offense committed, often summarized as "an eye for an eye." Both frameworks address justice but differ fundamentally in focus: distributive justice prioritizes societal balance and fairness, while Lex Talionis centers on proportional punishment and deterrence.
Defining Distributive Justice
Distributive justice refers to the equitable allocation of resources and benefits within a society, prioritizing fairness based on individual needs, contributions, or social roles. It seeks to ensure that wealth, opportunities, and privileges are distributed in a way that promotes social welfare and reduces inequality. Unlike Lex Talionis, which emphasizes retributive justice through proportional punishment, distributive justice centers on the just organization of societal goods.
Understanding Lex Talionis (Law of Retaliation)
Lex Talionis, known as the Law of Retaliation, is a principle of justice emphasizing a proportionate response to wrongdoing, often encapsulated by the phrase "an eye for an eye." This concept seeks to ensure that punishment directly corresponds to the offense, preventing excessive or unjust penalties. Understanding Lex Talionis involves recognizing its foundational role in ancient legal systems as a mechanism to maintain social order and balance through equitable retribution.
Historical Contexts of Both Concepts
Distributive justice, rooted in ancient Greek philosophy, emphasizes the fair allocation of resources based on merit, need, or equality, evolving through thinkers like Aristotle and modern political theorists. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, originates from ancient Mesopotamian and Hebrew legal codes, epitomized by the principle "an eye for an eye," aiming to impose proportionate punishment to maintain social order. Historical contexts reveal distributive justice as a framework for societal balance in wealth and power, whereas Lex Talionis functions primarily as a mechanism for retributive justice and legal deterrence.
Core Philosophical Principles Compared
Distributive justice centers on the fair allocation of resources based on equity, need, or merit, emphasizing societal welfare and balanced opportunities. Lex Talionis, rooted in the principle of "an eye for an eye," focuses on proportional retribution, ensuring punishment mirrors the offense to maintain moral order. While distributive justice prioritizes collective fairness and social harmony, lex talionis emphasizes individual accountability and exact reciprocity in justice.
Ethical Implications in Modern Society
Distributive justice emphasizes equitable allocation of resources based on fairness and need, promoting social stability and reducing inequality in modern societies. Lex Talionis, or the principle of retributive justice, advocates proportional retaliation, which can perpetuate cycles of violence and hinder restorative justice efforts. Ethical implications revolve around balancing fairness in punishment with societal rehabilitation and the prevention of harm, challenging legal systems to integrate empathy with accountability.
Application in Legal Systems
Distributive justice in legal systems ensures equitable allocation of resources and rights based on fairness, often influencing social welfare laws and affirmative action policies. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, applies retributive justice principles, emphasizing proportional punishment such as "an eye for an eye," commonly seen in criminal law and traditional legal codes. Modern legal frameworks increasingly balance these concepts by protecting individual rights while enforcing penalties proportional to offenses.
Strengths and Critiques of Distributive Justice
Distributive justice emphasizes fair allocation of resources based on need, merit, or equality, promoting social cohesion and reducing inequality. Strengths include fostering societal stability and addressing systemic disparities, though critiques highlight challenges in defining fairness and potential conflicts with individual incentives. Unlike Lex Talionis, which focuses on retributive justice through proportional punishment, distributive justice prioritizes equitable outcomes and social welfare.
Strengths and Critiques of Lex Talionis
Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, emphasizes proportional justice by ensuring the punishment mirrors the offense, which upholds fairness and deters excessive penalties. Its strength lies in providing clear, objective standards for retributive justice, promoting accountability and social order. However, critiques highlight its potential rigidity, neglecting context and rehabilitation, and risks perpetuating cycles of violence rather than fostering restorative justice principles.
Contemporary Relevance and Future Perspectives
Distributive Justice emphasizes equitable allocation of resources based on need or contribution, shaping modern social policies and welfare systems that address inequality and social cohesion. Lex Talionis, or the law of retaliation, influences contemporary criminal justice debates by invoking proportional punishment principles but faces criticism for potentially perpetuating cycles of violence rather than restorative outcomes. Future perspectives suggest integrating distributive justice frameworks with restorative justice models to promote societal harmony and reduce recidivism, reflecting a shift toward more compassionate and effective justice approaches.
Distributive Justice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com