Understanding your condition is crucial for effective management and treatment. Accurate diagnosis and personalized care plans help improve outcomes and enhance quality of life. Discover how to take control and support your health by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
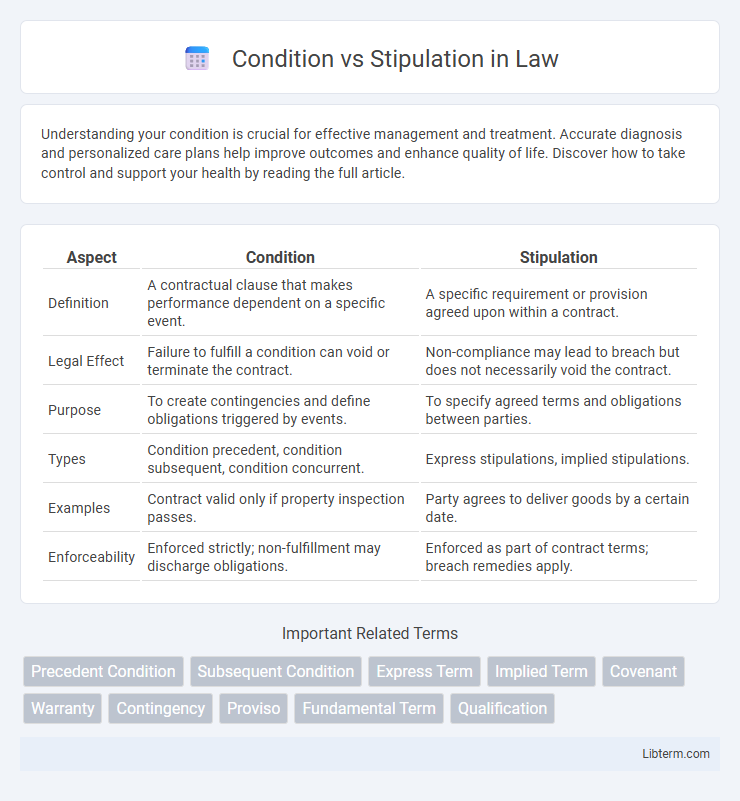
| Aspect | Condition | Stipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A contractual clause that makes performance dependent on a specific event. | A specific requirement or provision agreed upon within a contract. |
| Legal Effect | Failure to fulfill a condition can void or terminate the contract. | Non-compliance may lead to breach but does not necessarily void the contract. |
| Purpose | To create contingencies and define obligations triggered by events. | To specify agreed terms and obligations between parties. |
| Types | Condition precedent, condition subsequent, condition concurrent. | Express stipulations, implied stipulations. |
| Examples | Contract valid only if property inspection passes. | Party agrees to deliver goods by a certain date. |
| Enforceability | Enforced strictly; non-fulfillment may discharge obligations. | Enforced as part of contract terms; breach remedies apply. |
Introduction to Conditions and Stipulations
Conditions and stipulations define specific requirements within agreements that affect the parties' obligations. A condition is a future event or action that must occur before a contract becomes effective or a duty is triggered, while a stipulation refers to agreed-upon terms or provisions explicitly outlined in the contract. Understanding the distinction between conditions and stipulations is essential for interpreting contractual responsibilities and ensuring compliance.
Defining Condition in Legal and Contractual Terms
A defining condition in legal and contractual terms refers to a specific requirement or event that must occur before a party is obligated to perform a contractual duty. Unlike stipulations, which are agreed-upon provisions or requirements within an agreement, conditions serve as prerequisite triggers that activate or nullify contractual rights and obligations. Understanding conditions is essential for interpreting contract enforceability and determining parties' responsibilities under legal frameworks.
Understanding Stipulation: Meaning and Usage
A stipulation is a specific agreement or requirement explicitly stated within a contract or legal document, often used to outline obligations or concessions agreed upon by the parties involved. Unlike conditions, which can trigger rights or obligations when certain events occur, stipulations serve as clearly defined terms that must be adhered to during the execution of an agreement. Understanding stipulations helps ensure compliance and clarity in contractual obligations, preventing disputes and facilitating smooth enforcement.
Key Differences Between Condition and Stipulation
A condition is a fundamental requirement in a contract that must be met for the contract to be enforceable or to create an obligation, while a stipulation refers to specific terms or provisions agreed upon by the parties that detail rights or duties within the contract. Key differences include that conditions often affect the existence or performance of the contract itself, whereas stipulations usually govern the manner or method of carrying out contractual obligations. Conditions typically trigger or terminate obligations based on an event, whereas stipulations outline agreed specifics without necessarily affecting the contract's validity.
Legal Implications of Conditions in Agreements
Conditions in agreements serve as pivotal legal triggers that either activate or nullify contractual obligations, ensuring parties meet specific prerequisites for performance. Failure to satisfy a condition generally allows non-breaching parties to withhold performance or terminate the contract without liability, underscoring its critical role in risk allocation. Stipulations, by contrast, often represent agreed-upon provisions rather than conditional triggers, having less direct impact on the enforceability of the contract terms.
Role of Stipulations in Contractual Obligations
Stipulations serve as specific provisions within contracts that outline precise obligations or requirements parties must fulfill, often detailing the manner, time, or quality of performance. They function to clarify and enforce nuanced aspects of the agreement, ensuring compliance and reducing ambiguity. Unlike conditions that affect the contract's existence or enforceability, stipulations primarily govern the execution of contractual duties.
Examples of Condition vs Stipulation in Real Contracts
A condition in a contract might be a buyer's obligation to secure financing before the sale is finalized, triggering contract performance only if the financing is approved. A stipulation often appears as a clause requiring a tenant to maintain the property in good condition throughout the lease term, serving as a specific contractual requirement rather than a contingency. Real estate purchase agreements commonly include conditions like inspections and appraisals, whereas employment contracts frequently contain stipulations such as confidentiality and non-compete clauses.
Enforceability: Condition vs Stipulation
Conditions impose specific requirements that must be met for a contract to become enforceable or for certain obligations to apply, ensuring legal certainty. Stipulations are contractual provisions that outline specific promises or obligations, generally enforceable if clearly stated and agreed upon by parties. Enforceability of conditions tends to depend on strict compliance, while stipulations allow some flexibility based on intent and circumstances.
Common Misconceptions About Condition and Stipulation
Conditions and stipulations are often confused, but they play distinct roles in contracts; a condition is a fundamental requirement that must be met for the contract to be enforceable, while a stipulation is a specific term or provision agreed upon by the parties. A common misconception is that all stipulations are conditions, leading to misunderstandings about contract enforcement and remedies. Misinterpreting a stipulation as a condition can result in unnecessary contract termination or disputes over performance obligations.
Summary: Choosing Between Condition and Stipulation
Choosing between condition and stipulation hinges on their legal implications and enforceability; conditions typically dictate the occurrence of a specific event that must happen for a contract to be valid, while stipulations are agreed-upon provisions or requirements within the contract itself. Conditions often impact the contract's existence or performance, making them crucial in risk allocation and contract fulfillment. Stipulations tend to clarify obligations, rights, or duties, ensuring detailed compliance without necessarily affecting the contract's validity.
Condition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com