Temporary custody grants a parent or guardian the legal right to care for a child for a limited period, often during emergencies or transitions. It ensures the child's safety and well-being while longer-term custody arrangements are determined. Explore the article to understand how temporary custody works and what it means for your family.
Table of Comparison
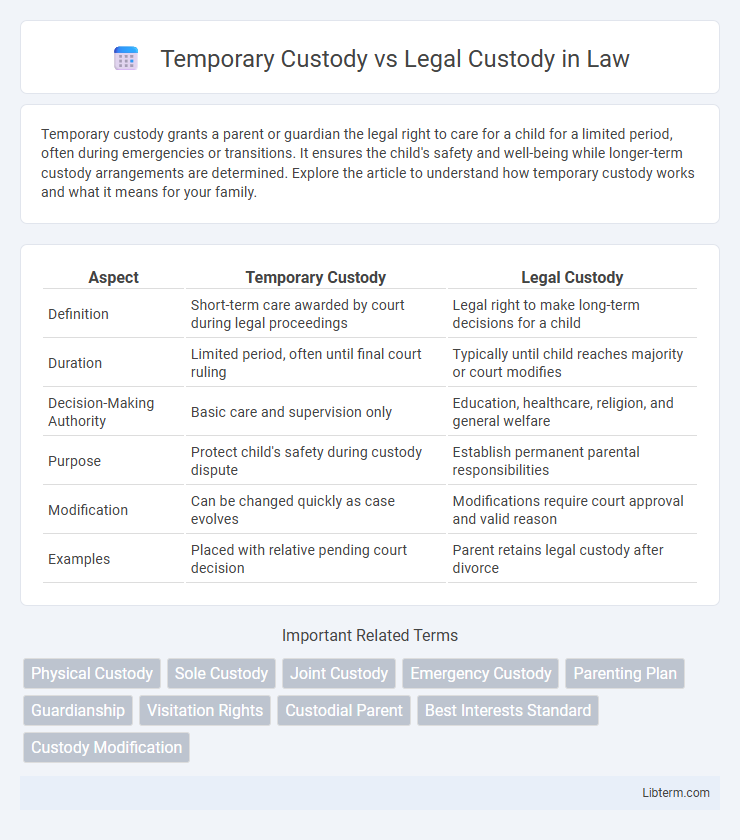
| Aspect | Temporary Custody | Legal Custody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term care awarded by court during legal proceedings | Legal right to make long-term decisions for a child |
| Duration | Limited period, often until final court ruling | Typically until child reaches majority or court modifies |
| Decision-Making Authority | Basic care and supervision only | Education, healthcare, religion, and general welfare |
| Purpose | Protect child's safety during custody dispute | Establish permanent parental responsibilities |
| Modification | Can be changed quickly as case evolves | Modifications require court approval and valid reason |
| Examples | Placed with relative pending court decision | Parent retains legal custody after divorce |
Introduction to Temporary Custody and Legal Custody
Temporary custody grants a caregiver short-term responsibility for a child's care during emergencies or transitional periods, ensuring the child's immediate safety and well-being. Legal custody refers to the court-recognized right to make significant decisions concerning a child's upbringing, including education, healthcare, and religious training. Understanding the distinctions between these custody types is vital for navigating family law and child welfare cases effectively.
Defining Temporary Custody
Temporary custody refers to the short-term care and decision-making authority granted to an individual or agency for a child during emergencies or pending a court's final decision. This form of custody is typically awarded when the child's immediate safety or well-being is at risk, ensuring protection until a permanent arrangement is established. Legal custody, in contrast, involves the long-term right to make significant decisions about the child's upbringing, including education, health care, and religion.
Understanding Legal Custody
Legal custody grants a parent or guardian the authority to make major decisions regarding a child's education, healthcare, and religious upbringing. It differs from temporary custody, which provides short-term care without transferring decision-making rights. Understanding legal custody is crucial for determining long-term parental responsibilities and rights in family law cases.
Key Differences Between Temporary and Legal Custody
Temporary custody grants a parent or guardian short-term care rights, often during emergencies or pending court decisions, without altering long-term parental responsibilities. Legal custody involves the right to make significant decisions about a child's upbringing, including education, health care, and religion, providing authority that extends beyond temporary arrangements. Key differences include duration, decision-making authority, and the intent behind the custody assignment, with legal custody offering a permanent or long-term solution compared to the provisional nature of temporary custody.
Situations Requiring Temporary Custody
Situations requiring temporary custody often arise during emergencies such as a parent's hospitalization, incarceration, or absence due to military deployment, where immediate care arrangements are necessary for the child's well-being. Temporary custody grants a caregiver the authority to make critical decisions for the child, including medical care and education, but this authority is limited in duration and scope compared to legal custody. Courts typically determine temporary custody to ensure the child's safety and stability while long-term custody arrangements are pending.
The Legal Process for Obtaining Custody
The legal process for obtaining temporary custody typically involves filing an emergency petition in family court demonstrating immediate risk or harm to the child, often requiring expedited hearings and proof of urgency. Legal custody is established through a formal court procedure where both parents' rights and responsibilities are assessed, including background checks, custody evaluations, and mediation to determine the child's best interests. Courts issue custody orders based on evidence, parental fitness, and child welfare, with temporary custody orders often reviewed or modified during ongoing legal proceedings.
Parental Rights in Temporary vs Legal Custody
Temporary custody grants a parent limited rights to care for a child for a specific period, typically during emergencies or pending court decisions, without transferring full parental rights. Legal custody involves the comprehensive right to make significant decisions about the child's upbringing, including education, healthcare, and religion. Parental rights under legal custody are extensive and enduring, while temporary custody rights are constrained and usually reinstated to the original custodian once the temporary order ends.
Factors Courts Consider in Custody Decisions
Courts weigh several factors in determining temporary custody versus legal custody, prioritizing the child's best interests through assessments of parental ability to provide stability, emotional support, and safety. Considerations include each parent's mental and physical health, history of caregiving, and the child's relationship with each parent. The court also evaluates potential risks such as abuse or neglect, aiming to promote continuity and foster the child's well-being during custody transitions.
Impacts on Child Welfare and Stability
Temporary custody grants short-term care to a guardian, often during emergencies, impacting child welfare by providing immediate stability but potentially causing emotional uncertainty. Legal custody involves long-term decision-making authority over a child's upbringing, promoting consistent care and a stable environment essential for healthy development. Differences between these custody types significantly affect a child's emotional security, access to resources, and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions on Custody Types
Temporary custody grants a parent or guardian short-term physical care of a child, usually during legal proceedings or emergencies, while legal custody involves the right to make major decisions about the child's welfare, including education, healthcare, and religious upbringing. Frequently asked questions about custody types often address differences in decision-making authority, duration of custody, and how custody arrangements affect visitation rights. Understanding the distinction between temporary and legal custody is critical for parents navigating family law disputes or seeking custody modifications.
Temporary Custody Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com