Prosecution plays a crucial role in the criminal justice system by presenting evidence to prove the defendant's guilt beyond a reasonable doubt. Effective prosecution ensures accountability and upholds the rule of law while protecting the rights of victims and society. Explore the full article to understand how prosecution shapes legal outcomes and influences justice.
Table of Comparison
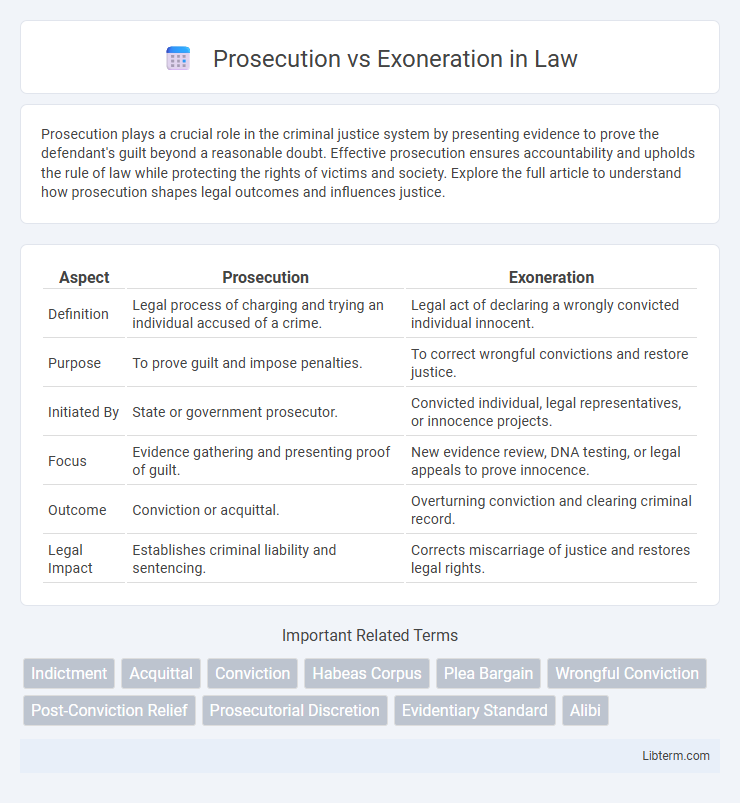
| Aspect | Prosecution | Exoneration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal process of charging and trying an individual accused of a crime. | Legal act of declaring a wrongly convicted individual innocent. |
| Purpose | To prove guilt and impose penalties. | To correct wrongful convictions and restore justice. |
| Initiated By | State or government prosecutor. | Convicted individual, legal representatives, or innocence projects. |
| Focus | Evidence gathering and presenting proof of guilt. | New evidence review, DNA testing, or legal appeals to prove innocence. |
| Outcome | Conviction or acquittal. | Overturning conviction and clearing criminal record. |
| Legal Impact | Establishes criminal liability and sentencing. | Corrects miscarriage of justice and restores legal rights. |
Understanding Prosecution: Definition and Process
Prosecution refers to the legal process whereby a government authority, usually represented by a public prosecutor, formally charges an individual or entity with a crime and seeks to prove their guilt in a court of law. This process involves investigation, indictment, arraignment, trial, and sentencing if the defendant is found guilty. Understanding prosecution requires knowledge of the roles of prosecutors, the rights of the accused, and the evidentiary standards necessary to establish criminal liability beyond a reasonable doubt.
What Does Exoneration Mean in the Legal System?
Exoneration in the legal system refers to the formal clearing of an individual from criminal charges or conviction, often following new evidence proving their innocence. It signifies the official recognition that the accused did not commit the crime, resulting in the reversal of wrongful convictions. This process restores the person's legal rights and can involve the release from imprisonment, expungement of records, or compensation for wrongful prosecution.
Key Differences Between Prosecution and Exoneration
Prosecution involves the legal process where the state charges and seeks to prove the guilt of an accused individual through evidence and trial procedures. Exoneration occurs when an individual previously convicted is officially cleared of guilt due to new evidence, wrongful conviction recognition, or procedural errors. Key differences include prosecution initiating criminal charges and seeking conviction, whereas exoneration overturns a conviction, restoring the individual's innocence and legal status.
The Prosecutor’s Role in Criminal Justice
The prosecutor's role in criminal justice centers on evaluating evidence to determine whether charges should be filed, ensuring that cases brought to trial have sufficient merit. Prosecutors are responsible for advocating on behalf of the state while upholding ethical standards, including the duty to disclose exculpatory evidence that may lead to exoneration. Balancing the pursuit of convictions with the protection of innocent individuals is fundamental to maintaining fairness and integrity within the criminal justice system.
Pathways Leading to Exoneration
Prosecution pathways leading to exoneration often involve the emergence of new evidence such as DNA testing, eyewitness recantations, or prosecutorial misconduct revelations. Post-conviction review processes, including appeals and innocence projects, play a critical role in identifying wrongful convictions and facilitating exonerations. Legal reforms emphasizing transparency, access to evidence, and fair trial standards contribute significantly to the increase in exoneration rates across jurisdictions.
Common Causes of Wrongful Prosecution
Wrongful prosecution often stems from eyewitness misidentification, which is a leading cause contributing to erroneous convictions due to flawed memory recall or suggestive identification procedures. False confessions, influenced by intense police interrogation tactics or psychological pressure, significantly increase the risk of prosecuting innocent individuals. Additionally, official misconduct, including evidence suppression and forensic errors, undermines justice and frequently results in the exoneration of wrongfully convicted defendants.
Impact of Exoneration on Individuals and Society
Exoneration profoundly restores the lives of wrongfully convicted individuals by clearing their criminal records and enabling access to social and economic opportunities previously denied. It also challenges systemic flaws within the justice system, prompting reforms that enhance legal accuracy and fairness on a societal level. The broader impact includes strengthening public trust in legal institutions and highlighting the critical need for rigorous evidence review and accountability.
Legal Standards for Prosecution versus Exoneration
Legal standards for prosecution require probable cause supported by sufficient evidence to initiate charges, ensuring a reasonable likelihood of conviction beyond a reasonable doubt. Exoneration relies on a higher burden of proof demonstrating actual innocence, often needing new evidence, DNA testing, or proof of procedural errors that invalidate the original conviction. Courts balance these standards to uphold justice, prioritizing the prevention of wrongful convictions while maintaining accountability for criminal conduct.
Famous Cases Highlighting Prosecution and Exoneration
The O.J. Simpson trial exemplifies prosecution challenges with overwhelming public scrutiny despite controversial evidence leading to acquittal. In contrast, the Central Park Five case underscores wrongful convictions overturned through DNA evidence and advocacy, highlighting systemic failures and eventual exoneration. The case of Steven Avery, popularized by "Making a Murderer," reveals prosecutorial misconduct and the vital role of post-conviction reviews in achieving justice.
Future Trends in Justice: Reducing Wrongful Prosecution
Emerging technologies such as AI-driven evidence analysis and blockchain for maintaining tamper-proof records are poised to revolutionize the prosecution process by minimizing errors and biases. Enhanced forensic methods combined with comprehensive data integration enable faster identification of wrongful prosecutions, facilitating more timely exonerations. Legislative reforms promoting transparency and mandatory recording of interrogations further support justice systems in reducing wrongful convictions and safeguarding civil rights.
Prosecution Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com