Recklessness involves acting with a disregard for potential consequences, often leading to harmful outcomes. Understanding the legal and psychological aspects of recklessness can help you recognize risky behavior and prevent dangerous situations. Explore the rest of this article to learn how recklessness impacts decisions and what you can do to stay safe.
Table of Comparison
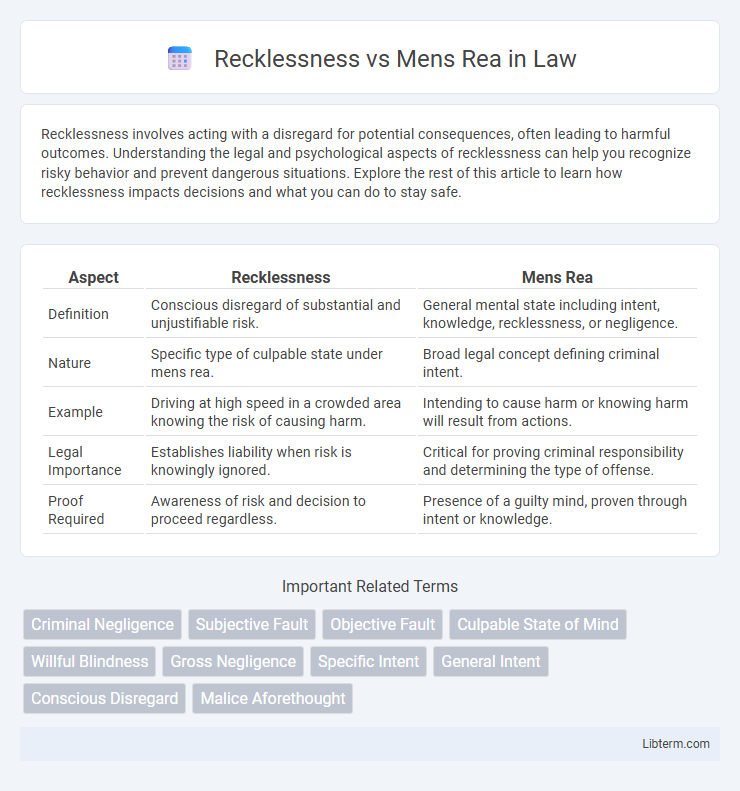
| Aspect | Recklessness | Mens Rea |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conscious disregard of substantial and unjustifiable risk. | General mental state including intent, knowledge, recklessness, or negligence. |
| Nature | Specific type of culpable state under mens rea. | Broad legal concept defining criminal intent. |
| Example | Driving at high speed in a crowded area knowing the risk of causing harm. | Intending to cause harm or knowing harm will result from actions. |
| Legal Importance | Establishes liability when risk is knowingly ignored. | Critical for proving criminal responsibility and determining the type of offense. |
| Proof Required | Awareness of risk and decision to proceed regardless. | Presence of a guilty mind, proven through intent or knowledge. |
Introduction to Recklessness and Mens Rea
Recklessness involves conscious disregard of a substantial and unjustifiable risk, where the individual is aware of the risk but proceeds anyway. Mens rea represents the mental state or intention behind a criminal act, encompassing various levels such as intention, knowledge, recklessness, and negligence. Understanding the distinction between recklessness and other forms of mens rea is crucial for determining culpability in criminal law.
Defining Recklessness in Criminal Law
Recklessness in criminal law refers to a conscious disregard of a substantial and unjustifiable risk that a particular result will occur or that a certain circumstance exists, distinguishing it from mens rea, which involves intentional or knowing behavior. The Model Penal Code defines recklessness as the defendant's awareness of the risk and their decision to proceed anyway, reflecting a culpable mental state less blameworthy than intent but more so than negligence. Courts analyze whether the risk was substantial and whether the defendant's disregard deviated grossly from the standard of conduct a law-abiding person would observe, establishing recklessness as a key element in numerous criminal offenses.
The Concept of Mens Rea Explained
Mens rea, a fundamental principle in criminal law, refers to the mental state or intent behind a defendant's actions, distinguishing intentional wrongdoing from accidental harm. Recklessness involves conscious disregard of a substantial risk, while mens rea requires purposeful or knowing intent to commit a crime. Understanding mens rea helps determine criminal liability by assessing whether the defendant had the necessary guilty mind at the time of the offense.
Types of Mens Rea: Comparing Levels of Culpability
Types of mens rea include intention, knowledge, recklessness, and negligence, each reflecting a different level of culpability in criminal law. Intent involves a purposeful act to bring about a specific result, while knowledge denotes awareness that a particular outcome is virtually certain. Recklessness occurs when a person consciously disregards a substantial and unjustifiable risk, representing a lower degree of culpability than intention or knowledge but higher than negligence.
Key Differences Between Recklessness and Mens Rea
Recklessness involves consciously disregarding a substantial and unjustifiable risk, whereas mens rea refers to the overall mental state or intent behind committing a crime. Recklessness is a specific type of mens rea, emphasizing awareness of risk without intent to cause harm, while mens rea encompasses a broader range of intentions, including purpose, knowledge, and negligence. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for determining culpability and applying appropriate legal standards in criminal cases.
Legal Standards for Establishing Recklessness
Legal standards for establishing recklessness require proving that the defendant consciously disregarded a substantial and unjustifiable risk, demonstrating a gross deviation from the standard of care a reasonable person would observe. Courts assess whether the individual had actual awareness of the risk or if the risk was so obvious that the defendant must have been aware. This subjective test distinguishes recklessness from negligence by emphasizing the defendant's state of mind and intentional risk-taking behavior.
Notable Case Law Illustrating Mens Rea
In R v Cunningham (1957), mens rea was established as the defendant recklessly caused gas to escape, highlighting the subjective awareness of risk requirement in criminal liability. R v G (2003) clarified recklessness by assessing whether the defendant foresaw the risk and unjustifiably took it, refining mens rea standards for offences like arson. These cases underscore mens rea as a crucial mental element distinguishing reckless actions from intentional wrongdoing in criminal law.
Impact on Criminal Responsibility and Sentencing
Recklessness involves conscious disregard of a substantial risk, while mens rea refers to the intent or knowledge of wrongdoing required for criminal liability. The presence of mens rea usually leads to harsher sentencing due to the offender's purposeful conduct, whereas recklessness may result in lesser penalties reflecting a lower degree of culpability. Courts assess these mental states to determine the severity of punishment, significantly impacting criminal responsibility and sentencing outcomes.
Challenges in Proving Recklessness vs Mens Rea
Proving recklessness involves demonstrating that the defendant consciously disregarded a substantial and unjustifiable risk, which can be difficult due to its subjective nature and variability in interpretation across jurisdictions. Mens rea, or the "guilty mind," requires establishing specific intent or knowledge of wrongdoing, often demanding concrete evidence of the defendant's mental state at the time of the offense. Challenges arise because recklessness hinges on a lower level of culpability than intent, making it harder to distinguish from negligence, while mens rea necessitates more direct proof of purposeful action or awareness.
Conclusion: The Importance of Mental State in Criminal Justice
The distinction between recklessness and mens rea is crucial in criminal justice, as it determines the defendant's level of culpability based on their mental state. Mens rea signifies intentional or knowing wrongdoing, whereas recklessness involves conscious disregard of substantial risks, impacting sentencing and legal outcomes. Understanding these mental states ensures fair punishment and accurate attribution of criminal liability.
Recklessness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com