A petition for quo warranto challenges an individual's legal right to hold a public office or corporate position, ensuring accountability in governance and corporate leadership. This legal remedy prevents unauthorized usurpation of authority by requiring the respondent to show by what warrant they hold the office. Explore the rest of the article to understand how quo warranto petitions safeguard your rights and maintain lawful leadership.
Table of Comparison
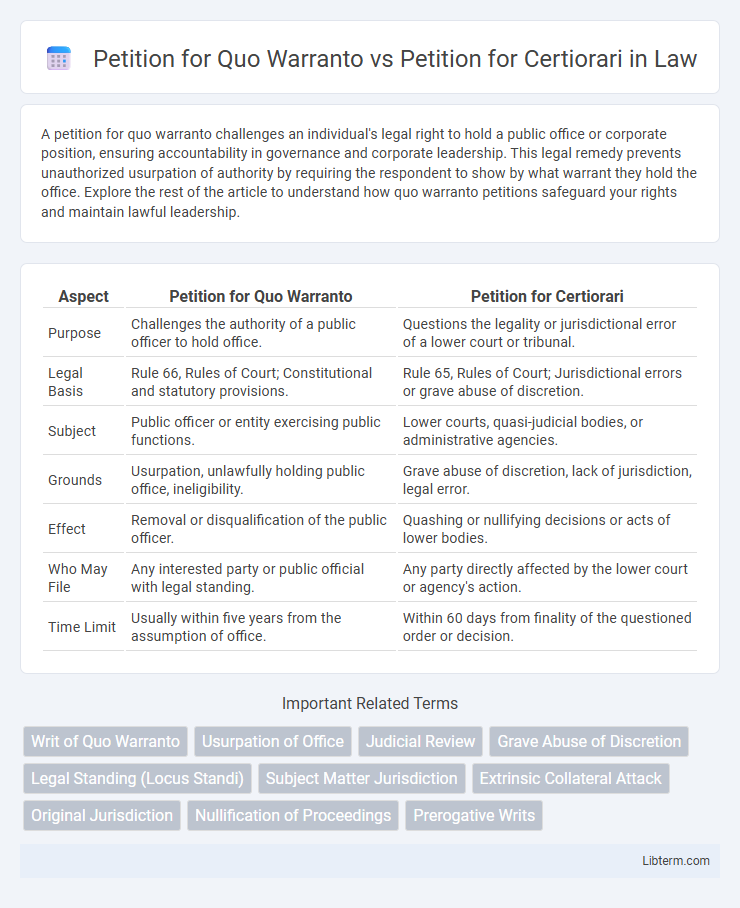
| Aspect | Petition for Quo Warranto | Petition for Certiorari |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Challenges the authority of a public officer to hold office. | Questions the legality or jurisdictional error of a lower court or tribunal. |
| Legal Basis | Rule 66, Rules of Court; Constitutional and statutory provisions. | Rule 65, Rules of Court; Jurisdictional errors or grave abuse of discretion. |
| Subject | Public officer or entity exercising public functions. | Lower courts, quasi-judicial bodies, or administrative agencies. |
| Grounds | Usurpation, unlawfully holding public office, ineligibility. | Grave abuse of discretion, lack of jurisdiction, legal error. |
| Effect | Removal or disqualification of the public officer. | Quashing or nullifying decisions or acts of lower bodies. |
| Who May File | Any interested party or public official with legal standing. | Any party directly affected by the lower court or agency's action. |
| Time Limit | Usually within five years from the assumption of office. | Within 60 days from finality of the questioned order or decision. |
Overview of Quo Warranto and Certiorari Petitions
Petition for Quo Warranto is a legal action questioning an individual's right to hold a public office or exercise a franchise, challenging the legitimacy of their authority. Petition for Certiorari is a judicial review procedure requesting a higher court to examine and correct errors of jurisdiction or legal procedures made by a lower court or tribunal. Quo Warranto focuses on the authority or legal right to hold office, whereas Certiorari targets the review of judicial or quasi-judicial actions for legal errors.
Legal Definitions: Quo Warranto vs Certiorari
Petition for Quo Warranto challenges a person's legal right to hold a public office or exercise a franchise, questioning the authority under which they are occupying the position. Petition for Certiorari seeks judicial review to correct errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion committed by a lower court or tribunal. Quo Warranto targets the legitimacy of office claims, while Certiorari addresses procedural and jurisdictional errors in administrative or judicial actions.
Historical Background and Evolution
The Petition for Quo Warranto traces its origins to English common law, designed as a legal action to challenge the authority by which a person holds public office or exercises power, evolving from the 14th century to protect public interest against unauthorized holders. The Petition for Certiorari developed later as an extraordinary remedy to request higher courts to review and correct errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse in lower courts or administrative bodies, grounded in principles of judicial supervision and due process. Both petitions have undergone significant adaptations in Philippine jurisprudence, reflecting the integration of procedural safeguards and the protection of constitutional rights against unlawful exercises of authority.
Grounds for Filing Quo Warranto
Petition for Quo Warranto is filed to challenge the authority of a person holding a public office whose right to hold the position is questioned due to lack of legal qualification, appointment, or excessive assumption of power. Grounds for filing Quo Warranto include usurpation of public office, ineligibility, or failure to meet the required qualifications prescribed by law. This differs from Petition for Certiorari, which focuses on correcting errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion by a tribunal or government agency.
Grounds for Filing Certiorari
The grounds for filing a Petition for Certiorari include errors of jurisdiction, grave abuse of discretion, and lack of due process committed by a lower court or quasi-judicial body. This remedy is pursued when there is no appeal or any other plain, speedy, and adequate remedy available. Certiorari seeks to annul or modify the decision that is null and void due to jurisdictional errors or grave abuse, distinguishing it from Quo Warranto which questions the right to hold public office.
Jurisdiction and Proper Forum
A Petition for Quo Warranto challenges a person's legal right to hold a public office, filed directly with the Court of Appeals or the Supreme Court, which holds original jurisdiction over such cases. In contrast, a Petition for Certiorari questions the legality of a decision or order by an inferior court or tribunal, typically filed with a higher court exercising supervisory jurisdiction. Jurisdiction in Quo Warranto centers on the right to office, while Certiorari addresses jurisdictional errors or grave abuse of discretion in the lower tribunal's rulings.
Parties Eligible to File Each Petition
A Petition for Quo Warranto can be filed only by the Attorney General or a private citizen acting under his authority to challenge a person's illegal claim to public office or franchise. In contrast, a Petition for Certiorari may be filed by any party who is aggrieved by a decision, order, or proceedings of a judicial or quasi-judicial body. The eligibility to file a Quo Warranto is stricter because it aims to protect public interest against usurpation of public functions, whereas Certiorari serves as a remedy for individual due process violations.
Procedures and Requirements for Filing
A Petition for Quo Warranto challenges a person's legal right to hold a public office and requires verifying the petitioner's legal standing, the respondent's authority, and the lack of a legal basis for holding the position. Filing involves submitting the petition to the proper court, accompanied by affidavits and evidence demonstrating the usurpation or unlawful holding of office, typically within a prescribed period after the contested act. A Petition for Certiorari, on the other hand, seeks judicial review of a lower court's or government agency's decision due to grave abuse of discretion, requiring verified pleadings, a clear statement of errors, and strict adherence to procedural deadlines for filing in the Supreme Court or Court of Appeals.
Effects and Consequences of Each Petition
Petition for Quo Warranto nullifies an individual's usurpation of public office, leading to removal from the position if the claim is proven valid; its effect is to uphold the lawful exercise of official functions. Petition for Certiorari annuls the proceedings or decisions of a lower court or tribunal deemed unlawful or with grave abuse of discretion, restoring proper jurisdiction and legal order. The key consequence of Quo Warranto is the forfeiture of office, whereas Certiorari primarily corrects judicial errors without affecting the officeholder's status.
Key Differences and Practical Implications
Petition for Quo Warranto challenges an individual's right to hold a public office, focusing on the legality of their claim or authority, while Petition for Certiorari seeks to review and correct errors of jurisdiction or grave abuse of discretion by lower courts or governmental bodies. Quo Warranto involves initiation by the government or interested parties questioning authority legitimacy, contrasting with Certiorari's role in judicial review to uphold rule of law and prevent arbitrary actions. Practically, Quo Warranto serves to protect public office integrity, and Certiorari ensures procedural fairness and legal consistency in administrative or judicial decisions.
Petition for Quo Warranto Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com