A Petition for Reconsideration allows you to formally request a review of a previous decision or ruling, emphasizing errors or new evidence that may impact the outcome. This legal tool can be essential in correcting misunderstandings and ensuring fair judgment in your case. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to properly file a Petition for Reconsideration and strengthen your chances of success.
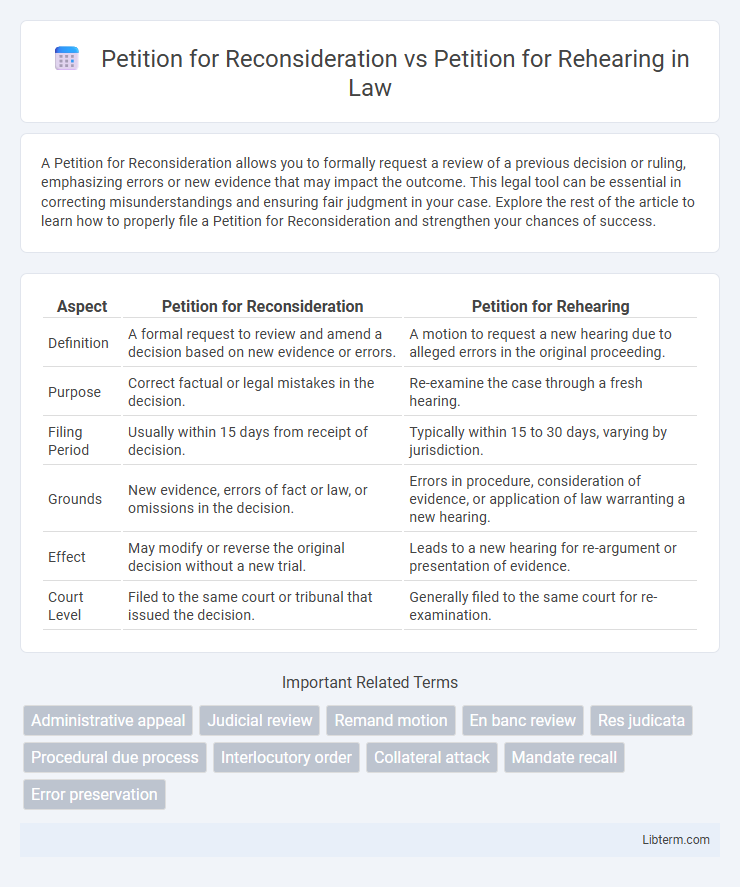
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Petition for Reconsideration | Petition for Rehearing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A formal request to review and amend a decision based on new evidence or errors. | A motion to request a new hearing due to alleged errors in the original proceeding. |
| Purpose | Correct factual or legal mistakes in the decision. | Re-examine the case through a fresh hearing. |
| Filing Period | Usually within 15 days from receipt of decision. | Typically within 15 to 30 days, varying by jurisdiction. |
| Grounds | New evidence, errors of fact or law, or omissions in the decision. | Errors in procedure, consideration of evidence, or application of law warranting a new hearing. |
| Effect | May modify or reverse the original decision without a new trial. | Leads to a new hearing for re-argument or presentation of evidence. |
| Court Level | Filed to the same court or tribunal that issued the decision. | Generally filed to the same court for re-examination. |
Introduction to Legal Petitions
Petition for Reconsideration and Petition for Rehearing are legal remedies used to challenge court decisions, each serving distinct procedural purposes. Petition for Reconsideration typically requests a court to review its judgment due to errors of fact or law, while Petition for Rehearing seeks another hearing to address new evidence or legal arguments. Understanding these petitions is crucial for effective case strategy and ensuring proper judicial review.
Defining Petition for Reconsideration
A Petition for Reconsideration is a formal request filed to a court or administrative agency seeking a review and possible modification of a decision based on overlooked facts or legal errors. This petition aims to correct substantive mistakes or present new evidence without initiating a full appeal process. It primarily serves to prompt the decision-maker to re-evaluate the original ruling within the same adjudicative body.
Understanding Petition for Rehearing
A Petition for Rehearing requests a court to review its decision due to overlooked facts, misapplication of law, or errors in judgment, emphasizing correction within the same case. Unlike a Petition for Reconsideration, which may be filed in administrative or legal contexts to challenge a prior ruling based on new evidence or changes in circumstances, the Petition for Rehearing specifically targets the finality of a court's judgment. Understanding this distinction is crucial for effective legal strategy and timely filing.
Key Differences Between the Two Petitions
A Petition for Reconsideration challenges a court's decision by asserting that the court overlooked or misapprehended facts or law, emphasizing errors in the original judgment. In contrast, a Petition for Rehearing requests the same court to review its ruling again, typically due to new evidence or a significant legal question not previously considered. The key difference lies in their purpose: reconsideration targets legal or factual errors in the decision, while rehearing seeks a second evaluation of the case without necessarily identifying errors.
Legal Grounds for Filing Each Petition
Petition for Reconsideration challenges a court's decision based on alleged errors of law, fact, or new evidence that could change the outcome, emphasizing substantive legal grounds. Petition for Rehearing focuses on correcting judicial oversights or misapprehensions in a prior ruling, concentrating on procedural or factual clarifications rather than introducing new legal arguments. Both petitions serve the purpose of seeking modification or reversal of a decision but differ in their legal basis and scope of review under procedural rules.
Procedural Requirements and Deadlines
Petition for Reconsideration requires filing within a specified period, often 15 days from receipt of the decision, and must present new evidence or arguments that were not previously considered. Petition for Rehearing demands a stricter adherence to procedural rules, typically filed within 10 days after the decision, focusing on errors of law or factual mistakes in the court's judgment. Both petitions must comply with court-specific formatting and submission guidelines to avoid dismissal.
Common Scenarios for Use
Petition for Reconsideration is commonly used when a party believes the court overlooked or misappreciated facts or legal principles in its decision. Petition for Rehearing is typically filed when new evidence emerges or significant legal errors are identified after the original judgment. Both petitions serve to request the same court to review its decision but differ in the scope and timing of issues addressed.
Potential Outcomes and Court Responses
A Petition for Reconsideration requests the court to review its decision due to an error or overlooked facts, often leading to modification or reversal of the judgment. A Petition for Rehearing challenges the court's ruling, focusing on legal or factual errors, and can result in the court reaffirming, amending, or vacating its original decision. Courts may grant, deny, or schedule oral arguments for both petitions, with outcomes significantly impacting the progression or finality of the case.
Strategic Considerations for Litigants
A Petition for Reconsideration typically challenges a court's ruling based on overlooked facts or legal errors, making it crucial for litigants to demonstrate clear grounds for revision to increase success chances. A Petition for Rehearing focuses on persuading the same court to reexamine issues, often relying on changes in law or new evidence, requiring a strategic assessment of timing and the strength of newly presented material. Litigants must weigh factors like court receptivity, procedural rules, and potential impact on case outcomes when choosing between reconsideration or rehearing to optimize litigation strategy.
Conclusion: Choosing the Appropriate Petition
Choosing between a Petition for Reconsideration and a Petition for Rehearing depends on the specific legal context and procedural rules governing the case. A Petition for Reconsideration typically challenges the court's factual findings or legal interpretations, seeking to correct errors without introducing new evidence. In contrast, a Petition for Rehearing focuses on addressing overlooked issues or arguments raised during the original hearing, making it essential to evaluate which petition aligns with the grounds and relief sought for effective legal remedy.
Petition for Reconsideration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com