International law governs interactions between nations by establishing treaties, customs, and principles that promote global order and cooperation. It addresses issues including human rights, trade regulations, and conflict resolution to maintain peace and justice worldwide. Explore the rest of this article to understand how international law affects Your rights and obligations on the global stage.
Table of Comparison
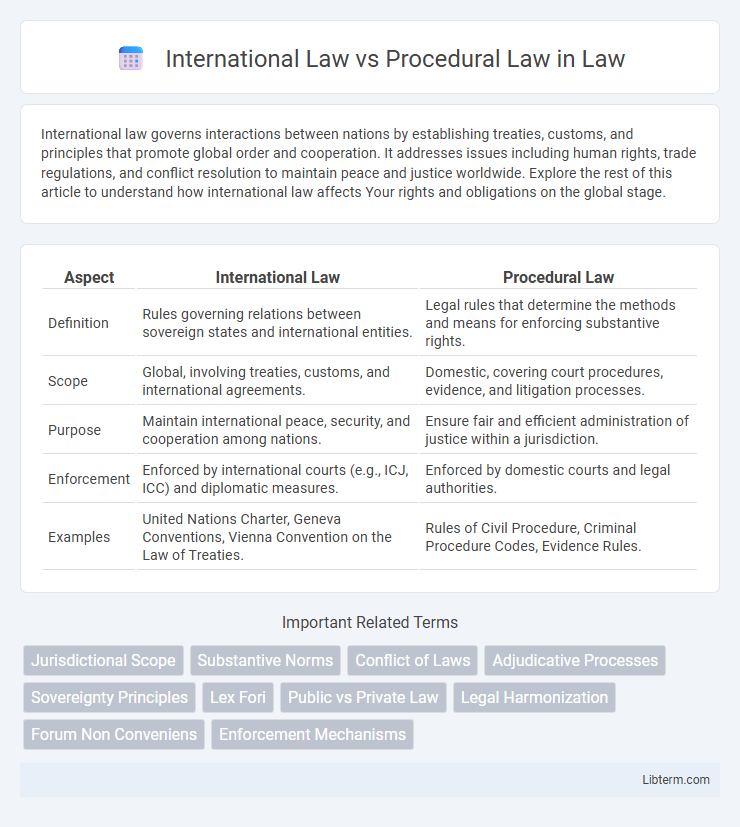
| Aspect | International Law | Procedural Law |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules governing relations between sovereign states and international entities. | Legal rules that determine the methods and means for enforcing substantive rights. |
| Scope | Global, involving treaties, customs, and international agreements. | Domestic, covering court procedures, evidence, and litigation processes. |
| Purpose | Maintain international peace, security, and cooperation among nations. | Ensure fair and efficient administration of justice within a jurisdiction. |
| Enforcement | Enforced by international courts (e.g., ICJ, ICC) and diplomatic measures. | Enforced by domestic courts and legal authorities. |
| Examples | United Nations Charter, Geneva Conventions, Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties. | Rules of Civil Procedure, Criminal Procedure Codes, Evidence Rules. |
Introduction to International Law and Procedural Law
International Law governs the legal relations and responsibilities of states and international entities, establishing norms for diplomacy, treaties, and human rights on a global scale. Procedural Law, also known as adjective law, outlines the methods and processes through which substantive laws are enforced, focusing on legal proceedings, jurisdiction, and evidence. Understanding both frameworks is crucial for navigating disputes involving international actors and ensuring the fair administration of justice across borders.
Defining International Law: Scope and Application
International Law governs the rights and responsibilities of states and international entities, addressing issues such as treaties, human rights, and conflict resolution on a global scale. It applies universally between sovereign nations and specialized agencies, establishing legal frameworks for diplomatic relations, war conduct, and environmental agreements. Procedural Law, by contrast, sets the rules for how courts and tribunals operate within individual jurisdictions, guiding the enforcement and adjudication processes rather than defining substantive global norms.
Understanding Procedural Law in Legal Systems
Procedural law governs the rules and processes by which courts hear and determine what happens in civil, lawsuit, criminal or administrative proceedings, ensuring fair application of justice. It defines the methods for enforcing rights and duties established by substantive laws, including rules of evidence, jurisdiction, and pleading. In contrast, international law regulates relations between sovereign states and international entities, focusing on agreements, treaties, and conduct beyond domestic legal procedures.
Key Differences Between International and Procedural Law
International law governs the relations and conduct between sovereign states and international entities, emphasizing treaties, customs, and principles recognized globally. Procedural law focuses on the rules and processes within a specific legal system that regulate how courts operate, including the methods for enforcing rights and adjudicating disputes. Key differences include scope, with international law addressing state interactions on a global scale, whereas procedural law manages the application of substantive law within domestic judicial systems.
Sources of International Law vs. Sources of Procedural Law
Sources of international law primarily include treaties, customary international law, general principles recognized by civilized nations, judicial decisions, and scholarly writings, as outlined in Article 38(1) of the ICJ Statute. Procedural law sources derive from domestic legal codes, court rules, statutes, and case precedents that govern the processes and methods by which courts operate. While international law sources shape the rights and obligations between states, procedural law sources regulate the conduct of legal proceedings and the enforcement of substantive law within national jurisdictions.
Jurisdictional Issues: International vs. Domestic Procedures
Jurisdictional issues in international law primarily address disputes between sovereign states and the recognition of authority beyond domestic boundaries, often governed by treaties and customary international norms. Procedural law within domestic systems dictates how courts operate internally, establishing rules for jurisdiction, evidence, and trial conduct specific to national legal frameworks. Conflicts arise when determining the applicable jurisdiction, requiring harmonization between international treaties and domestic procedural rules to ensure legal consistency and enforceability.
Enforcement Mechanisms in International and Procedural Law
Enforcement mechanisms in International Law primarily rely on diplomatic negotiations, sanctions, and resolutions by international organizations such as the United Nations, lacking a centralized enforcement authority. Procedural Law provides structured enforcement through judicial systems, including courts and tribunals, ensuring compliance with legal processes via sanctions like fines, imprisonment, or injunctions. The fundamental difference lies in International Law's voluntary state compliance versus Procedural Law's mandated enforcement within sovereign jurisdictions.
Real-world Cases Comparing Both Legal Domains
International law governs the relationships between sovereign states and international organizations, with landmark cases like the International Court of Justice's ruling on the South China Sea dispute demonstrating its role in resolving territorial conflicts. Procedural law, on the other hand, regulates the processes and methods courts follow within domestic legal systems, as seen in the United States with the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure guiding litigation steps. Comparing these domains reveals that while international law emphasizes state sovereignty and treaties, procedural law prioritizes fairness and consistency in judicial processes within national jurisdictions.
The Interplay Between International and Procedural Law
The interplay between international law and procedural law shapes how states and international actors implement legal norms during dispute resolution and cooperation frameworks. International law provides the substantive rules governing relations among states, while procedural law dictates the methods and processes for enforcing those rules in courts and tribunals. Understanding this dynamic ensures effective adjudication of cross-border disputes and promotes compliance with international obligations.
Future Trends and Challenges in Harmonizing Legal Approaches
Future trends in harmonizing International Law and Procedural Law emphasize the increasing role of digital governance frameworks and cross-border dispute resolution mechanisms, driven by globalization and technological advancements. Challenges include reconciling diverse legal traditions and ensuring consistent application of procedural standards across jurisdictions to enhance cooperation and predictability. Efforts to integrate artificial intelligence in case management and evidence evaluation will demand new procedural norms aligned with evolving international legal principles.
International Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com