Constitutional law establishes the framework for government authority and protects individual rights by interpreting the constitution's provisions. It addresses the balance of power among branches of government and safeguards fundamental freedoms critical to a democratic society. Explore the following article to deepen your understanding of how constitutional law impacts your daily life and legal protections.
Table of Comparison
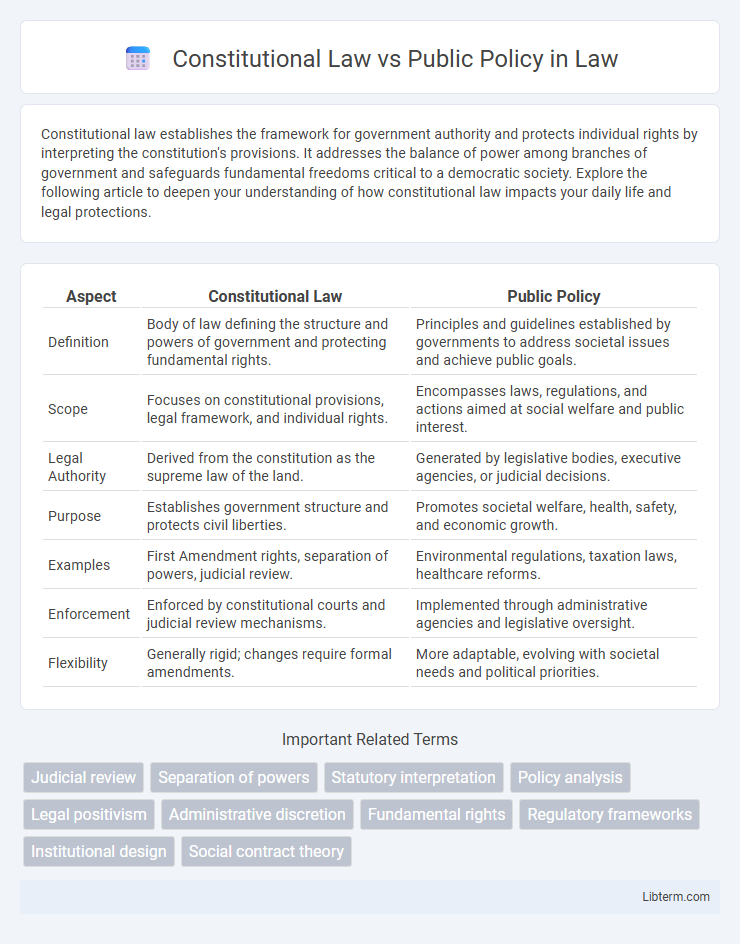
| Aspect | Constitutional Law | Public Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Body of law defining the structure and powers of government and protecting fundamental rights. | Principles and guidelines established by governments to address societal issues and achieve public goals. |
| Scope | Focuses on constitutional provisions, legal framework, and individual rights. | Encompasses laws, regulations, and actions aimed at social welfare and public interest. |
| Legal Authority | Derived from the constitution as the supreme law of the land. | Generated by legislative bodies, executive agencies, or judicial decisions. |
| Purpose | Establishes government structure and protects civil liberties. | Promotes societal welfare, health, safety, and economic growth. |
| Examples | First Amendment rights, separation of powers, judicial review. | Environmental regulations, taxation laws, healthcare reforms. |
| Enforcement | Enforced by constitutional courts and judicial review mechanisms. | Implemented through administrative agencies and legislative oversight. |
| Flexibility | Generally rigid; changes require formal amendments. | More adaptable, evolving with societal needs and political priorities. |
Introduction: Defining Constitutional Law and Public Policy
Constitutional law establishes the fundamental principles and framework governing the structure, powers, and limitations of government institutions, rooted in a nation's constitution. Public policy comprises the strategies and decisions crafted by governmental entities to address societal issues and promote the public good. Understanding the distinction between constitutional law and public policy is essential for analyzing how legal principles guide policymaking within regulatory and institutional boundaries.
Historical Foundations of Constitutional Law
The historical foundations of constitutional law trace back to landmark documents such as the Magna Carta (1215), which established the principle of limited government and protection of individual rights. The evolution continued through the English Bill of Rights (1689) and the U.S. Constitution (1787), embedding concepts of separation of powers, federalism, and judicial review. These foundational charters shaped constitutional law by codifying legal frameworks that balance governmental authority and individual freedoms, distinct from the more flexible and policy-driven nature of public policy.
Evolution and Purpose of Public Policy
Public policy has evolved from a framework aimed at addressing societal needs to a dynamic tool influencing legal interpretations within constitutional law. Its purpose is to promote the common good, guide governmental decision-making, and fill gaps where constitutional provisions may be ambiguous. This evolution underscores public policy's critical role in shaping laws that reflect contemporary values while ensuring constitutional principles are upheld.
Key Differences Between Constitutional Law and Public Policy
Constitutional law primarily deals with the interpretation and application of a country's constitution, establishing the fundamental legal framework and protecting individual rights against government actions. Public policy involves the principles and strategies formulated by governmental or institutional bodies to address societal issues and guide decision-making processes. The key difference lies in constitutional law's binding, legal authority derived from constitutional text, whereas public policy is more flexible, reflecting political, social, and economic objectives without necessarily having the force of law.
Constitutional Frameworks Shaping Public Policy
Constitutional frameworks establish the foundational principles and legal structures that guide public policy formulation, ensuring policies align with constitutional mandates such as separation of powers and protection of fundamental rights. Judicial review mechanisms empower courts to evaluate public policies against constitutional provisions, reinforcing accountability and legality in governance. This interplay between constitutional law and public policy ensures that legislative and executive actions adhere to constitutional norms, shaping sustainable and rights-based public policies.
Judicial Interpretation vs Policy-Making Authority
Judicial interpretation in constitutional law involves courts analyzing and applying constitutional provisions to specific cases, ensuring legal consistency and protecting fundamental rights. Public policy authority lies primarily with legislative and executive branches, which design and implement policies reflecting societal goals and priorities. The balance between judicial interpretation and policy-making authority maintains constitutional governance by preventing overreach while allowing adaptive policy responses.
Conflict and Harmonization: When Law Meets Policy
Constitutional law establishes the fundamental legal framework and principles governing a nation, while public policy directs governmental actions aimed at societal goals. Conflict arises when policy initiatives challenge constitutional rights or exceed legal boundaries, prompting judicial review to ensure compliance. Harmonization occurs through interpretative strategies that balance policy objectives with constitutional mandates, preserving rule of law and democratic legitimacy.
Case Studies: Constitutional Challenges to Public Policy
Case studies in constitutional law often examine challenges where public policies are contested on grounds of fundamental rights violations or constitutional overreach. Landmark cases such as *Brown v. Board of Education* highlight the judiciary's role in overturning discriminatory public policies that conflict with constitutional guarantees of equality. These legal battles underscore the tension between government authority in policymaking and the enforcement of constitutional protections to safeguard individual rights.
The Role of Government Institutions in Law and Policy
Government institutions play a crucial role in shaping constitutional law and public policy by interpreting, implementing, and enforcing legal frameworks that uphold democratic principles. Courts, legislatures, and executive agencies collaborate to ensure that laws align with constitutional mandates while addressing societal needs through policy initiatives. The dynamic interaction of these institutions maintains the balance of power and protects citizens' rights within the legal and policy landscape.
Future Trends: Constitutional Law’s Influence on Public Policy
Future trends reveal Constitutional Law increasingly shaping public policy through judicial interpretations that expand individual rights and government powers. Emerging challenges such as digital privacy, climate change, and healthcare reform prompt constitutional scrutiny, driving policy adaptations grounded in constitutional principles. This dynamic interaction reinforces Constitutional Law as a foundational framework guiding the evolution of public policy in response to societal needs.
Constitutional Law Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com