Replevin is a legal remedy that allows you to recover personal property wrongfully taken or withheld by another party. It is commonly used in disputes involving possession rather than ownership, enabling the rightful owner to regain control through a court order. Discover how replevin can protect your property rights by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
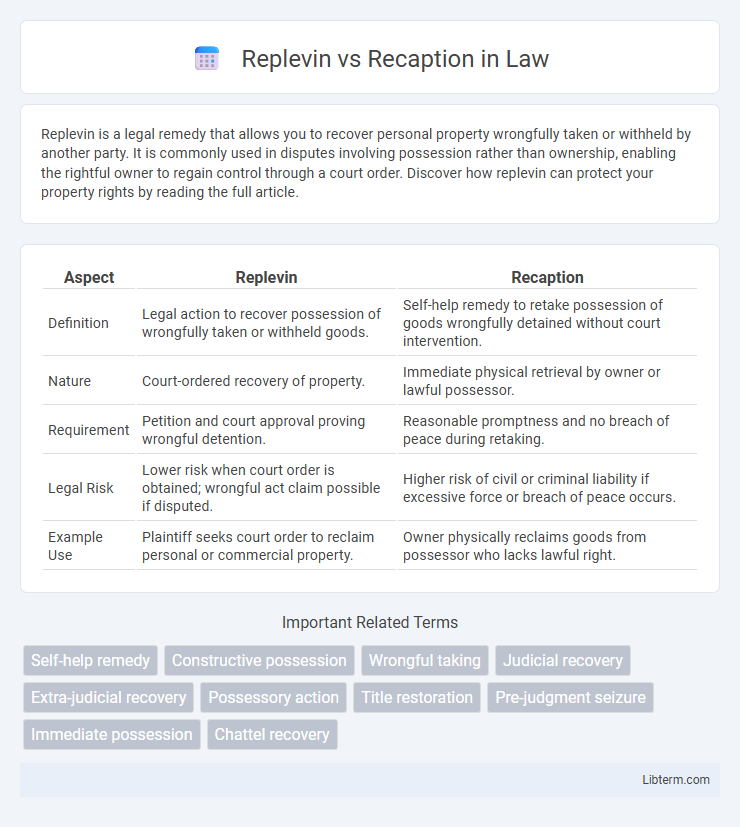
| Aspect | Replevin | Recaption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal action to recover possession of wrongfully taken or withheld goods. | Self-help remedy to retake possession of goods wrongfully detained without court intervention. |
| Nature | Court-ordered recovery of property. | Immediate physical retrieval by owner or lawful possessor. |
| Requirement | Petition and court approval proving wrongful detention. | Reasonable promptness and no breach of peace during retaking. |
| Legal Risk | Lower risk when court order is obtained; wrongful act claim possible if disputed. | Higher risk of civil or criminal liability if excessive force or breach of peace occurs. |
| Example Use | Plaintiff seeks court order to reclaim personal or commercial property. | Owner physically reclaims goods from possessor who lacks lawful right. |
Introduction to Replevin and Recaption
Replevin is a legal process that allows a person to recover personal property wrongfully taken or detained, often involving a lawsuit to regain possession before the final ownership is determined. Recaption refers to the act of reclaiming property that was previously taken or lost, typically through self-help measures without immediate court intervention. Both concepts address the retrieval of goods but differ in procedural approach and legal requirements.
Definition of Replevin
Replevin is a legal remedy that allows a person to recover goods or personal property wrongfully taken or detained from their rightful possession. It involves a court order for the return of the specific items rather than compensation for their value. Recaption, on the other hand, refers to the act of reclaiming property taken unlawfully without resorting to formal legal proceedings.
Definition of Recaption
Recaption refers to the lawful retrieval of property by a seller or owner when the buyer defaults on the payment or violates the terms of the contract, allowing the original possessor to reclaim possession without legal action. This process is distinct from replevin, where the owner must seek a court order to recover wrongfully taken or withheld property. Recaption emphasizes the seller's right to retake possession directly under specific contractual or statutory conditions.
Legal Basis for Replevin
Replevin is grounded in property law and allows a claimant to recover personal property unlawfully taken or detained, based on the legal right of possession. The legal basis for replevin involves proving ownership or superior right to possession and demonstrating wrongful detention by the opposing party. Unlike recaption, which often refers to reclaiming stolen goods without judicial involvement, replevin requires a court order for the recovery of property.
Legal Basis for Recaption
Recaption is legally based on unjust enrichment principles allowing a person to reclaim goods wrongfully taken or withheld without formal legal proceedings. Unlike replevin, which requires a court order to recover specific personal property, recaption provides immediate self-help rights rooted in property law and common law traditions. Statutory provisions governing recaption vary but typically emphasize the necessity of peaceable repossession to avoid civil liability.
Key Differences Between Replevin and Recaption
Replevin involves a legal action to recover possession of wrongfully taken or detained personal property, often requiring a court order, while recaption refers to the immediate, self-help recovery of property without formal legal proceedings. The key difference lies in replevin's reliance on judicial intervention to enforce property rights versus recaption's direct repossession approach. Replevin provides a lawful remedy ensuring due process, whereas recaption risks legal consequences if the self-help is deemed unlawful or excessive.
Procedural Requirements
Replevin requires filing a formal complaint to recover specific personal property wrongfully taken, often involving a bond to secure the defendant's interest pending the dispute resolution. Recaption involves the immediate, self-help recovery of goods unlawfully taken without the need for prior court approval, but must be executed promptly and without breaching peace. Courts strictly enforce procedural safeguards in replevin to protect due process, whereas recaption must adhere to common law limitations to avoid liability for trespass or conversion.
Remedies and Relief Provided
Replevin allows a party to recover possession of wrongfully taken or detained personal property, providing a remedy aimed at the return of the specific item rather than monetary compensation. Recaption, often a self-help remedy, involves reclaiming property through immediate physical reentry without court intervention, typically used in situations where wrongful possession is clear and prompt action is necessary. The relief in replevin is judicially ordered return of property, while recaption relies on the owner's direct action to regain possession, often limiting legal disputes but risking possible escalation.
Practical Examples and Case Studies
Replevin involves a legal action to recover specific personal property wrongfully taken or detained, as seen in cases where a tenant withholds a leased vehicle, prompting the owner to file suit to reclaim it. Recaption occurs when an item is retrieved without legal proceedings, such as a creditor repossessing collateral voluntarily returned or repossessed without court intervention after default. Practical case studies highlight that replevin suits often arise in disputes over possession requiring judicial authority, while recaption is favored for efficient recovery when the party has lawful entitlement and physical retrieval is feasible.
Conclusion: Choosing the Appropriate Remedy
Replevin provides a legal method to recover specific personal property wrongfully taken or detained, emphasizing possession restoration without determining ownership. Recaption serves as a self-help remedy allowing the immediate repossession of property taken unlawfully, but it risks legal disputes if not properly justified. When selecting the appropriate remedy, parties must assess the urgency, legality of self-help options, and long-term enforcement goals to minimize liability and ensure rightful possession.
Replevin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com