Consent is a crucial aspect of personal autonomy and legal agreements, ensuring all parties willingly agree to terms or actions without coercion. Understanding the nuances of consent can protect your rights and foster trust in relationships or professional dealings. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to establish, recognize, and respect effective consent in various contexts.
Table of Comparison
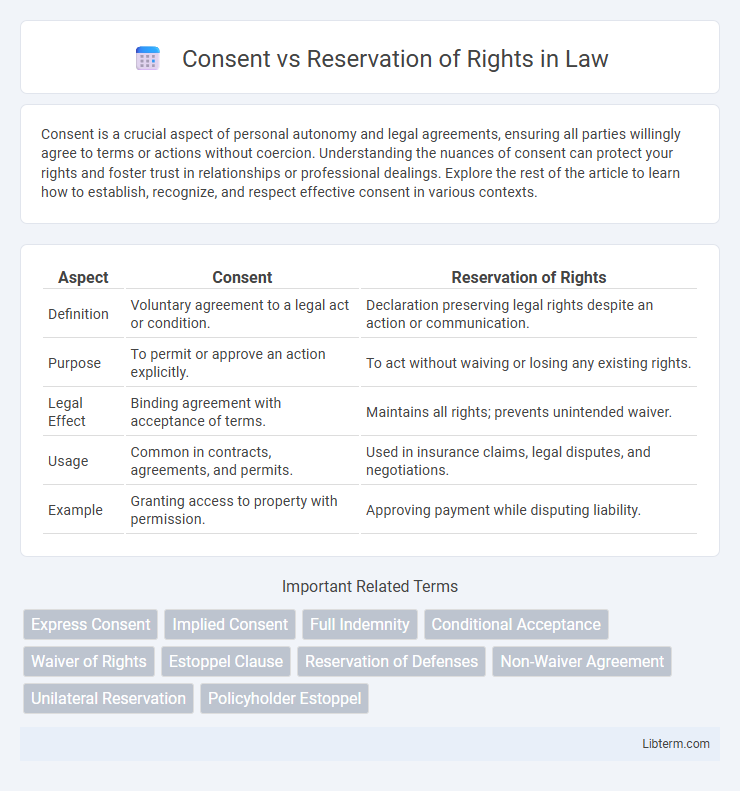
| Aspect | Consent | Reservation of Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Voluntary agreement to a legal act or condition. | Declaration preserving legal rights despite an action or communication. |
| Purpose | To permit or approve an action explicitly. | To act without waiving or losing any existing rights. |
| Legal Effect | Binding agreement with acceptance of terms. | Maintains all rights; prevents unintended waiver. |
| Usage | Common in contracts, agreements, and permits. | Used in insurance claims, legal disputes, and negotiations. |
| Example | Granting access to property with permission. | Approving payment while disputing liability. |
Introduction to Consent and Reservation of Rights
Consent refers to the explicit approval given by a party acknowledging specific actions or terms, often formalized in legal or insurance contexts to waive certain protections or objections. Reservation of rights occurs when a party agrees to proceed under a contract or claim but explicitly retains the right to contest or deny liability later. Understanding these concepts is crucial in insurance law, where insurers may consent to defend a claim while reserving their rights to deny coverage subsequently.
Defining Consent in Legal and Business Contexts
Consent in legal and business contexts refers to the voluntary agreement by a party to a proposed action or contract, demonstrating clear, informed approval without coercion. It establishes a foundation for valid contracts, ensuring all parties acknowledge and accept specific terms and conditions. Distinguishing consent from reservation of rights is crucial as consent implies agreement, while reservation of rights protects a party's future claims or defenses.
Understanding Reservation of Rights
Reservation of Rights is a legal tool used by insurers to acknowledge a claim while maintaining the right to later deny coverage based on specific policy provisions or investigations. This approach protects the insurer from waiving coverage defenses prematurely, allowing thorough claim evaluation without admitting full liability. Understanding the precise language and implications of a Reservation of Rights letter is crucial for policyholders to effectively navigate disputes and coverage issues.
Key Differences Between Consent and Reservation of Rights
Consent involves a party agreeing to a specific action or condition, often waiving certain rights, whereas Reservation of Rights means a party agrees to proceed while explicitly preserving the ability to assert claims or defenses later. Consent typically results in a clear relinquishment of certain legal options, while Reservation of Rights maintains those options for future enforcement. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in legal and insurance contexts to ensure that agreeing to terms does not unintentionally forfeit important protections.
Importance of Clear Communication in Agreements
Clear communication in agreements is crucial to distinguish between consent and reservation of rights, ensuring all parties understand their obligations and limitations. Explicitly stating whether a party consents to certain terms or reserves their rights prevents misunderstandings and potential legal disputes. Precise language in contracts enhances enforceability and safeguards parties' interests by delineating consent from conditional acceptance.
Legal Consequences of Consent vs Reservation of Rights
Consent legally confirms agreement to specific terms or conditions, potentially waiving certain rights and limiting future claims related to the consented action. Reservation of rights explicitly preserves an individual's or entity's ability to enforce rights or raise defenses despite agreeing to interim actions, thus avoiding unintended waiver. Understanding the legal consequences is critical, as consenting without reservation can lead to binding acceptance, whereas reserving rights maintains legal flexibility and protects against adverse outcomes.
Common Scenarios Illustrating Both Concepts
In insurance claims, consent occurs when the insurer agrees to a course of action, such as repairs or settlements, knowing the terms and implications, whereas reservation of rights allows the insurer to proceed with claim investigation or payment while preserving the right to deny coverage later. Common scenarios include an insurer consenting to a policyholder's choice of repair shop, contrasted with reserving rights due to suspected policy exclusions or potential fraud. Courts often evaluate these actions to determine if the insurer waived defenses or properly preserved them under state insurance laws.
Best Practices for Documentation and Notification
Documenting consent and reservation of rights requires clear, concise written communication that explicitly states the scope of consent or the specific rights being reserved to avoid future legal disputes. Notifications should be delivered through verifiable methods such as certified mail or email with read receipts to ensure acknowledgment and date-stamping for evidence. Maintaining detailed records of all correspondence, including the context and responses, supports transparency and strengthens the enforceability of consent and reservation clauses.
Risks and Challenges in Managing Consent and Rights Reservations
Managing consent alongside reservation of rights presents challenges such as ambiguity in contract interpretation, which can lead to disputes over the scope of authorized actions and retained rights. Risks include unintentionally waiving key legal protections while attempting to cooperate, thereby undermining future claims or defenses. Clear documentation and precise language are essential to mitigate misunderstandings and protect all parties involved.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Your Situation
Selecting between consent and reservation of rights depends on the specific circumstances of your legal or insurance matter, as consent confirms agreement while reservation of rights protects future claims. Evaluating your risk tolerance, potential liabilities, and the implications of admitting or denying responsibility is critical for informed decision-making. Consulting with legal counsel ensures the chosen approach aligns with your best interests and safeguards your rights effectively.
Consent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com