Compensation plays a critical role in attracting and retaining top talent by offering competitive salaries and benefits that reflect an employee's skills and contributions. Understanding various compensation models helps you make informed decisions that align with company goals and employee satisfaction. Explore the detailed insights in the rest of this article to optimize your compensation strategies effectively.
Table of Comparison
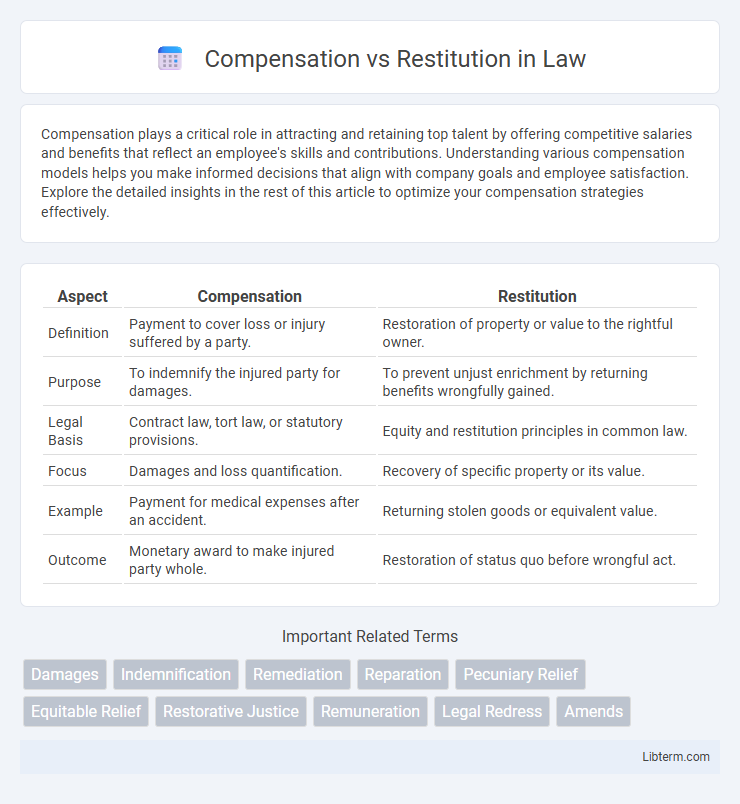
| Aspect | Compensation | Restitution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Payment to cover loss or injury suffered by a party. | Restoration of property or value to the rightful owner. |
| Purpose | To indemnify the injured party for damages. | To prevent unjust enrichment by returning benefits wrongfully gained. |
| Legal Basis | Contract law, tort law, or statutory provisions. | Equity and restitution principles in common law. |
| Focus | Damages and loss quantification. | Recovery of specific property or its value. |
| Example | Payment for medical expenses after an accident. | Returning stolen goods or equivalent value. |
| Outcome | Monetary award to make injured party whole. | Restoration of status quo before wrongful act. |
Understanding Compensation and Restitution
Compensation involves providing monetary payment to cover a loss or injury as agreed upon or mandated by law, ensuring the injured party is financially restored. Restitution specifically aims to restore the injured party to their original position before the harm occurred, often requiring the return of property or its value. Both concepts function within legal frameworks but differ in scope: compensation often addresses broader damages, while restitution focuses on reversing unjust enrichment or loss.
Key Differences Between Compensation and Restitution
Compensation involves providing monetary payment to cover losses or damages suffered by a party, often linked to contractual or legal obligations. Restitution focuses on restoring the injured party to their original position by returning the exact benefit or property gained unjustly by the other party. The key difference lies in compensation awarding a sum reflecting loss, while restitution aims to prevent unjust enrichment by recovering specific assets or benefits.
Legal Definitions: Compensation vs Restitution
Compensation refers to the monetary payment awarded to cover loss, injury, or suffering caused by another party's actions, often linked to breach of contract or tort claims. Restitution involves restoring the injured party to the original position before the wrongful act occurred, emphasizing the return of unjust gains rather than monetary damages. Legal definitions distinguish compensation as a remedy for damages incurred, while restitution aims to prevent unjust enrichment by recovering specific benefits improperly obtained.
Historical Origins of Both Concepts
Compensation originates from Roman law principles, where obligations to make amends for loss or damage were formalized through monetary payment. Restitution has its roots in ancient legal systems such as Lex Aquilia, emphasizing the restoration of the injured party to their original position before harm occurred. Both concepts evolved distinctly, with compensation focusing on financial redress and restitution on reversing unjust enrichment.
When is Compensation Awarded?
Compensation is awarded when a plaintiff suffers quantifiable losses due to the defendant's actions, aiming to make the injured party financially whole. It covers damages such as medical expenses, lost wages, and property repair costs, reflecting the actual harm incurred. Courts determine compensation based on evidence proving the extent of the injury and monetary impact on the victim.
When is Restitution Applicable?
Restitution is applicable when one party has been unjustly enriched at the expense of another, requiring the return of benefits or the value of those benefits to prevent unfair gain. It is often used in cases involving breach of contract, torts, or mistakes that result in one party receiving something to which they are not entitled. Compensation, by contrast, addresses the monetary equivalent for losses or damages suffered, rather than recovery of specific benefits.
Examples of Compensation Cases
Compensation cases often involve scenarios where an employee receives payment for lost wages due to workplace injury or illness, ensuring financial stability during recovery. Another example includes customers obtaining monetary reimbursement from businesses for defective products or unsatisfactory services under consumer protection laws. In personal injury claims, compensation covers medical expenses, pain, and suffering, highlighting the legal system's role in balancing losses with appropriate financial redress.
Examples of Restitution in Practice
Restitution involves restoring the victim to their original position by returning stolen property or repaying the value of damages, such as a thief returning stolen goods or a contractor compensating for shoddy work. Courts often order restitution in criminal cases to repay victims for financial losses caused by fraud, embezzlement, or property damage. Unlike compensation, which broadly covers economic and non-economic losses, restitution specifically targets the recovery of the victim's actual losses through direct reimbursement or asset return.
Impact on Victims and Offenders
Compensation provides victims with monetary reimbursement for losses or damages incurred, aiding in their financial recovery and emotional closure. Restitution, often court-ordered, requires offenders to directly repay victims, promoting offender accountability and fostering a sense of justice. Both approaches impact victims by addressing harm repair while influencing offenders through responsibility acceptance and potential behavior rehabilitation.
Choosing the Right Remedy: Compensation or Restitution
Choosing the right remedy between compensation and restitution depends on the nature of the loss and the desired outcome. Compensation aims to provide monetary damages to cover the harm suffered, often measured by the actual loss or injury, while restitution focuses on restoring the injured party to their original position by returning property or benefits unjustly gained by the defendant. Understanding whether the goal is to financially indemnify the plaintiff or to prevent unjust enrichment guides the appropriate selection of remedy in legal disputes.
Compensation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com