Navigating tax laws requires a clear understanding of current regulations to ensure compliance and maximize your financial benefits. Keeping up-to-date with tax deductions, credits, and filing deadlines can significantly impact your overall tax liability. Explore our detailed article to master tax laws and optimize your financial strategy.
Table of Comparison
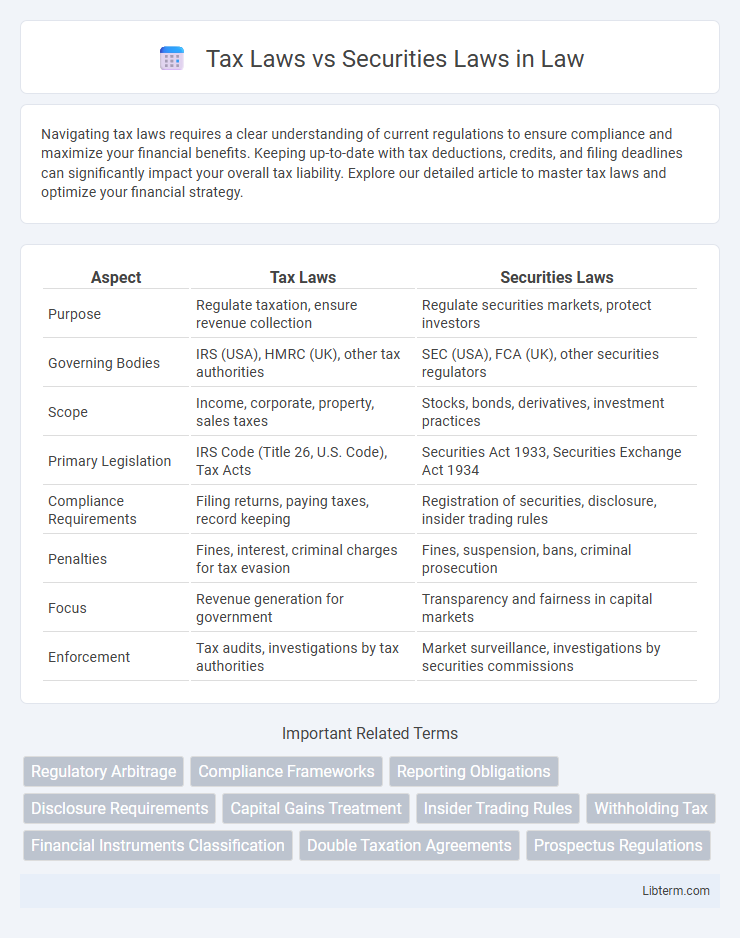
| Aspect | Tax Laws | Securities Laws |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Regulate taxation, ensure revenue collection | Regulate securities markets, protect investors |
| Governing Bodies | IRS (USA), HMRC (UK), other tax authorities | SEC (USA), FCA (UK), other securities regulators |
| Scope | Income, corporate, property, sales taxes | Stocks, bonds, derivatives, investment practices |
| Primary Legislation | IRS Code (Title 26, U.S. Code), Tax Acts | Securities Act 1933, Securities Exchange Act 1934 |
| Compliance Requirements | Filing returns, paying taxes, record keeping | Registration of securities, disclosure, insider trading rules |
| Penalties | Fines, interest, criminal charges for tax evasion | Fines, suspension, bans, criminal prosecution |
| Focus | Revenue generation for government | Transparency and fairness in capital markets |
| Enforcement | Tax audits, investigations by tax authorities | Market surveillance, investigations by securities commissions |
Introduction to Tax Laws and Securities Laws
Tax laws govern the rules and regulations related to the assessment, collection, and enforcement of taxes imposed by federal, state, and local governments. Securities laws regulate the issuance, trading, and disclosure requirements of financial instruments such as stocks and bonds to protect investors and maintain fair markets. Understanding the distinctions between tax laws and securities laws is crucial for compliance with respective obligations in corporate finance and investment activities.
Defining Tax Laws: Purpose and Scope
Tax laws regulate the collection of revenue by governments through various forms of taxation, including income, corporate, property, and sales taxes, ensuring compliance and legal obligations are met. These laws define taxable events, tax rates, deductions, credits, and enforcement mechanisms to fund public services and infrastructure. The primary purpose of tax laws is to provide a legal framework for revenue generation while maintaining fairness and economic balance within the jurisdiction.
Understanding Securities Laws: Key Objectives
Securities laws primarily aim to protect investors by ensuring transparency, fairness, and integrity in the financial markets. These regulations mandate full disclosure of material information to prevent fraud, manipulation, and insider trading within securities transactions. Unlike tax laws that govern taxation and revenue collection, securities laws focus on maintaining investor confidence and promoting efficient capital markets.
Major Regulatory Bodies: IRS vs SEC
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) administers tax laws by enforcing tax codes, collecting federal taxes, and ensuring compliance with tax regulations. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulates securities laws, overseeing securities markets to protect investors, maintain fair trading practices, and facilitate capital formation. Both agencies operate under distinct mandates, with the IRS focusing on tax enforcement and the SEC on financial market integrity.
Compliance Requirements: Tax Filings vs Securities Disclosures
Tax laws mandate strict compliance with periodic tax filings, including income, corporate, and payroll taxes, requiring accurate financial reporting and timely submission to tax authorities. Securities laws impose rigorous disclosure requirements to protect investors, necessitating transparent reporting of material information, periodic financial statements, and immediate disclosure of significant events to regulatory bodies such as the SEC. Non-compliance in tax filings can lead to penalties and audits, while failures in securities disclosures risk enforcement actions, fines, and reputational damage.
Overlapping Jurisdictions: When Tax and Securities Laws Intersect
Tax laws and securities laws intersect in areas such as capital gains reporting and the taxation of dividend income, requiring coordination between the IRS and the SEC. Overlapping jurisdictions arise prominently in initial public offerings (IPOs) and mergers, where compliance with both sets of regulations ensures accurate financial disclosures and proper tax treatment. Enforcement agencies collaborate to address fraud or misrepresentation that may violate both tax evasion statutes and securities fraud provisions.
Common Violations and Legal Consequences
Common violations under tax laws include tax evasion, underreporting income, and improper deductions, which can lead to penalties, interest charges, and criminal prosecution. Securities laws are frequently violated through insider trading, fraud, and misleading disclosures, resulting in fines, disgorgement of profits, and imprisonment. Both legal frameworks impose strict regulatory oversight to maintain market integrity and ensure fair financial reporting.
Impact on Business Operations and Investments
Tax laws influence business operations by dictating corporate tax obligations, affecting cash flow, budgeting, and financial planning, which directly impacts investment strategies and returns. Securities laws regulate the issuance, trading, and disclosure requirements of financial instruments, ensuring market transparency and protecting investors from fraud or manipulation. Compliance with both tax and securities regulations is crucial for businesses to maintain legal standing, optimize capital structure, and attract sustainable investment.
Recent Reforms and Legislative Updates
Recent reforms in tax laws emphasize enhanced reporting requirements and stricter penalties for non-compliance, aligning with global initiatives to combat tax evasion and promote transparency. Legislative updates in securities laws focus on increasing regulatory oversight, improving investor protections, and adapting to the rise of digital assets and blockchain technologies. Both areas reflect a trend towards integrating advanced monitoring systems and fostering cross-agency collaboration to address evolving financial market complexities.
Best Practices for Navigating Tax and Securities Regulations
Understanding the distinctions between tax laws and securities laws is fundamental for ensuring compliance and mitigating legal risks in financial transactions. Best practices include maintaining thorough documentation of all transactions, consulting with specialized legal and tax professionals, and implementing robust internal controls to monitor ongoing regulatory changes. Proactively aligning corporate governance policies with both IRS regulations and SEC guidelines enhances transparency and reduces the likelihood of penalties.
Tax Laws Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com