An indictment is a formal charge issued by a grand jury accusing an individual of a criminal offense, serving as a critical step in the legal process. It outlines specific allegations and enables the case to proceed to trial, ensuring that prosecutors have sufficient evidence to warrant prosecution. Discover how indictments affect your legal rights and the judicial system in the full article.
Table of Comparison
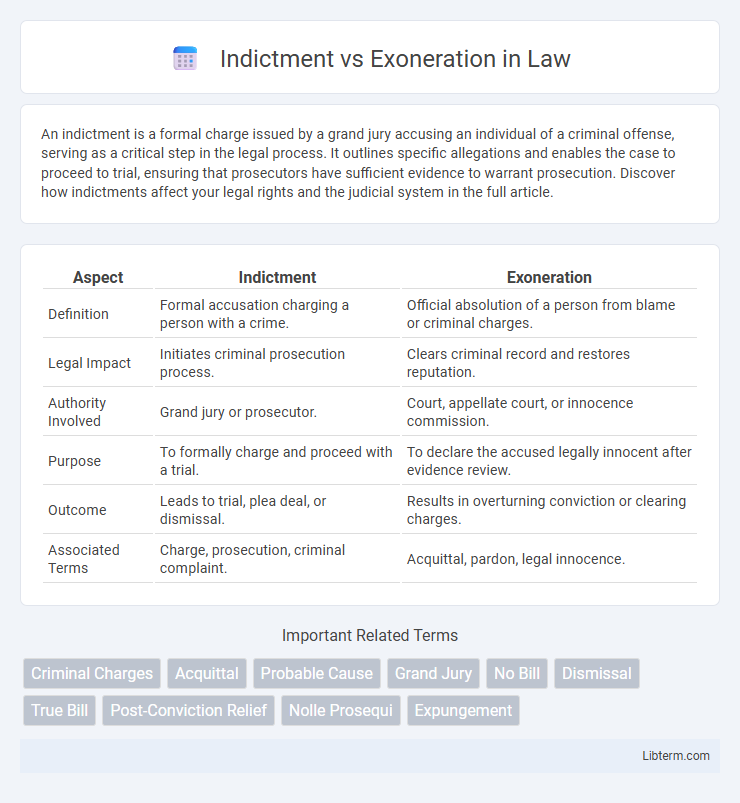
| Aspect | Indictment | Exoneration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal accusation charging a person with a crime. | Official absolution of a person from blame or criminal charges. |
| Legal Impact | Initiates criminal prosecution process. | Clears criminal record and restores reputation. |
| Authority Involved | Grand jury or prosecutor. | Court, appellate court, or innocence commission. |
| Purpose | To formally charge and proceed with a trial. | To declare the accused legally innocent after evidence review. |
| Outcome | Leads to trial, plea deal, or dismissal. | Results in overturning conviction or clearing charges. |
| Associated Terms | Charge, prosecution, criminal complaint. | Acquittal, pardon, legal innocence. |
Understanding Indictment: Definition and Process
An indictment is a formal accusation issued by a grand jury asserting that sufficient evidence exists to charge an individual with a criminal offense. The indictment process involves the presentation of evidence to the grand jury, which evaluates whether probable cause justifies proceeding to trial. Understanding the indictment is crucial as it marks the transition from investigation to prosecution in the criminal justice system.
What Does Exoneration Really Mean?
Exoneration means officially clearing an individual from blame or criminal charges, often after new evidence proves their innocence or highlights procedural errors in their prosecution. Unlike an indictment, which formally accuses someone of a crime, exoneration restores the individual's legal status and reputation by overturning wrongful convictions. This legal process is critical in justice reform, emphasizing the importance of accurate evidence and fair trials.
Key Differences Between Indictment and Exoneration
An indictment is a formal charge or accusation issued by a grand jury stating there is sufficient evidence to prosecute a person for a crime. Exoneration occurs when an individual previously charged or convicted is officially cleared of guilt, often due to new evidence proving innocence. The key difference lies in indictment initiating legal proceedings against a suspect, while exoneration completely absolves them from any criminal liability.
The Legal Path from Indictment to Trial
The legal path from indictment to trial involves a formal charge by a grand jury indicating that sufficient evidence exists to pursue criminal prosecution. Following indictment, pre-trial processes such as arraignment, motions, and discovery take place to prepare the defense and prosecution. Exoneration can occur if evidence emerges disproving guilt, often after a trial or through post-conviction review, leading to the clearance of the accused's record.
Grounds for Exoneration: Common Causes
Grounds for exoneration commonly include wrongful convictions due to new DNA evidence, prosecutorial misconduct, false confessions, and ineffective legal representation. These causes highlight systemic failures where later investigations or appeals reveal that the original evidence was flawed or the legal process was compromised. Understanding these factors is critical to ensuring justice, preventing wrongful imprisonment, and reforming the criminal justice system.
Impact of Indictment on the Accused
An indictment significantly impacts the accused by initiating formal criminal charges, often leading to immediate reputational damage and emotional distress. It restricts personal freedoms through potential bail conditions or pretrial detention and complicates employment opportunities due to the public nature of the charges. The legal process following an indictment requires substantial financial resources for defense, heightening the overall burden on the accused even before any determination of guilt or innocence.
Life After Exoneration: Challenges and Opportunities
Life after exoneration presents significant challenges, including social reintegration, psychological recovery, and securing employment due to stigmatization and gaps in criminal records. Exonerees often face limited access to compensation despite wrongful imprisonment, impacting financial stability and long-term well-being. Despite these obstacles, many pursue advocacy, education, and legal reform initiatives, transforming their experiences into opportunities for social justice advancement and policy change.
High-Profile Cases: Indictment vs Exoneration in the Media
High-profile cases often see intense media scrutiny during indictment phases, shaping public opinion before trials commence. Indictments in these cases signal formal charges but do not denote guilt, whereas exonerations highlight the clearing of accused individuals, significantly impacting reputations and legal precedents. Media coverage of these contrasting legal outcomes underscores the tension between public perception and judicial process in criminal justice.
Legal Rights During Indictment and After Exoneration
Legal rights during indictment include the right to remain silent, the right to legal counsel, and the right to a fair trial, ensuring protection from self-incrimination and unlawful detention. After exoneration, individuals are entitled to the restoration of their reputation, potential compensation for wrongful conviction, and access to legal mechanisms to clear their criminal record. Understanding these rights is crucial for safeguarding justice and upholding due process throughout the criminal justice system.
Preventing Wrongful Indictments and Ensuring Justice
Preventing wrongful indictments requires rigorous evidence review, adherence to legal standards, and implementation of advanced forensic technologies to minimize errors in the criminal justice process. Ensuring justice involves transparency in investigative procedures, continuous training for law enforcement, and safeguarding defendants' rights through effective legal representation. Strengthening these measures reduces the risk of miscarriages of justice and upholds the integrity of the judicial system while enabling rightful exoneration of the innocent.
Indictment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com