An interim remedy provides temporary relief or protection during ongoing legal proceedings to prevent harm or preserve rights. It safeguards your interests until a final judgment is reached, ensuring fairness and continuity in the process. Explore the article to learn how interim remedies can impact your case and when to seek them.
Table of Comparison
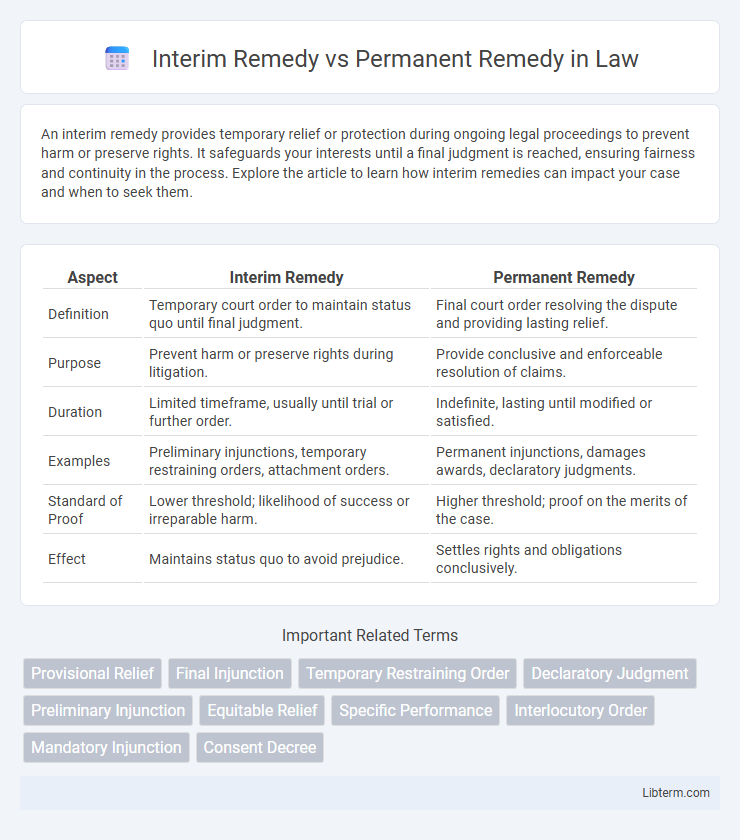
| Aspect | Interim Remedy | Permanent Remedy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary court order to maintain status quo until final judgment. | Final court order resolving the dispute and providing lasting relief. |
| Purpose | Prevent harm or preserve rights during litigation. | Provide conclusive and enforceable resolution of claims. |
| Duration | Limited timeframe, usually until trial or further order. | Indefinite, lasting until modified or satisfied. |
| Examples | Preliminary injunctions, temporary restraining orders, attachment orders. | Permanent injunctions, damages awards, declaratory judgments. |
| Standard of Proof | Lower threshold; likelihood of success or irreparable harm. | Higher threshold; proof on the merits of the case. |
| Effect | Maintains status quo to avoid prejudice. | Settles rights and obligations conclusively. |
Introduction to Interim and Permanent Remedies
Interim remedies serve as temporary measures to preserve the status quo or prevent harm before a final decision is made, often including injunctions or restraining orders. Permanent remedies provide a final resolution after the court's judgment, such as damages awards or specific performance, ensuring lasting enforcement of rights. Understanding the distinct roles and applications of interim and permanent remedies is essential for effective legal strategy and dispute resolution.
Definitions: Interim Remedy vs Permanent Remedy
Interim remedy refers to a temporary court order or relief granted to maintain the status quo or prevent harm during ongoing litigation, ensuring immediate protection before a final decision. Permanent remedy, on the other hand, is the final court judgment or enforcement that resolves the dispute definitively and provides lasting relief or compensation. Understanding the distinction between these remedies is crucial for legal strategy and effective dispute resolution.
Legal Framework Governing Remedies
The legal framework governing remedies distinguishes interim remedies as temporary court orders designed to preserve the status quo or prevent harm during litigation, such as injunctions or temporary restraining orders. Permanent remedies, including damages or specific performance, are final judicial decisions that resolve the dispute after full trial and adjudication. Statutory provisions and case law outline the criteria and procedures for granting both interim and permanent remedies, ensuring due process and balancing parties' rights.
Key Differences Between Interim and Permanent Remedies
Interim remedies provide temporary relief to preserve the status quo or prevent harm during ongoing litigation, while permanent remedies offer conclusive solutions after a final judgment. Interim remedies, such as preliminary injunctions or temporary restraining orders, are time-limited and subject to modification, whereas permanent remedies include final injunctions, monetary damages, or specific performance that resolve the dispute permanently. The key differences lie in their duration, purpose, and enforceability, with interim remedies addressing immediate needs and permanent remedies delivering lasting resolution.
Common Types of Interim Remedies
Common types of interim remedies include injunctive relief, which prevents parties from taking specific actions during litigation, and interlocutory orders granting temporary possession or custody of property. Other frequent interim remedies involve orders for the preservation of evidence, freezing assets to prevent dissipation, and interim maintenance payments in family law cases. These urgent measures aim to maintain the status quo and protect parties' interests until a permanent remedy is adjudicated.
Common Types of Permanent Remedies
Common types of permanent remedies include injunctions, specific performance, and damages, each aimed at providing a lasting solution to legal disputes. Injunctions compel a party to do or refrain from doing a specific act, while specific performance mandates the fulfillment of contractual obligations. Damages compensate the injured party financially for losses suffered, establishing a definitive resolution beyond temporary relief offered by interim remedies.
Criteria for Granting Interim Remedies
Interim remedies are granted based on the urgency to prevent irreparable harm or preserve the status quo pending a final decision, requiring a strong likelihood of success on the merits and the balance of hardships favoring the applicant. Courts assess whether monetary damages are insufficient and if the delay in granting relief would cause substantial prejudice. Permanent remedies, in contrast, are awarded after a full trial or hearing and address long-term resolution of the dispute.
When Are Permanent Remedies Appropriate?
Permanent remedies are appropriate when a legal violation causes ongoing or irreversible harm that cannot be adequately addressed by temporary measures. Courts award permanent remedies after a full trial and when it is clear that monetary damages are insufficient to resolve the dispute. Situations such as property disputes, intellectual property infringements, or repeated contract breaches often require permanent injunctive relief or specific performance to prevent future harm.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Remedy
Interim remedies provide swift, temporary relief to prevent harm or preserve the status quo during legal disputes, offering advantages such as immediate enforcement and reduced risk of irreparable damage. Limitations include their provisional nature, requiring further legal proceedings to establish final judgment, and potential misuse if granted without sufficient evidence. Permanent remedies deliver conclusive resolution and enforceable rights after thorough evaluation, ensuring lasting justice but often involving lengthy litigation and higher costs, which delay relief and may cause prolonged uncertainty.
Practical Considerations in Seeking Legal Remedies
Interim remedies provide temporary relief to preserve the status quo or prevent harm while a legal dispute is ongoing, often requiring urgent court approval and a demonstration of immediate risk or irreparable injury. Permanent remedies, in contrast, aim to fully resolve the legal issue with enforceable judgments such as damages or injunctions after a thorough trial or adjudication process. Practitioners must assess factors like evidentiary requirements, timing, and the likelihood of success to strategically pursue interim relief as a precursor to securing a permanent remedy.
Interim Remedy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com