Habeas corpus is a fundamental legal principle safeguarding individual freedom by preventing unlawful detention or imprisonment. It ensures that a person held in custody can promptly challenge the legality of their detention before a court. Explore the article to understand how habeas corpus protects your rights and its significance in modern law.
Table of Comparison
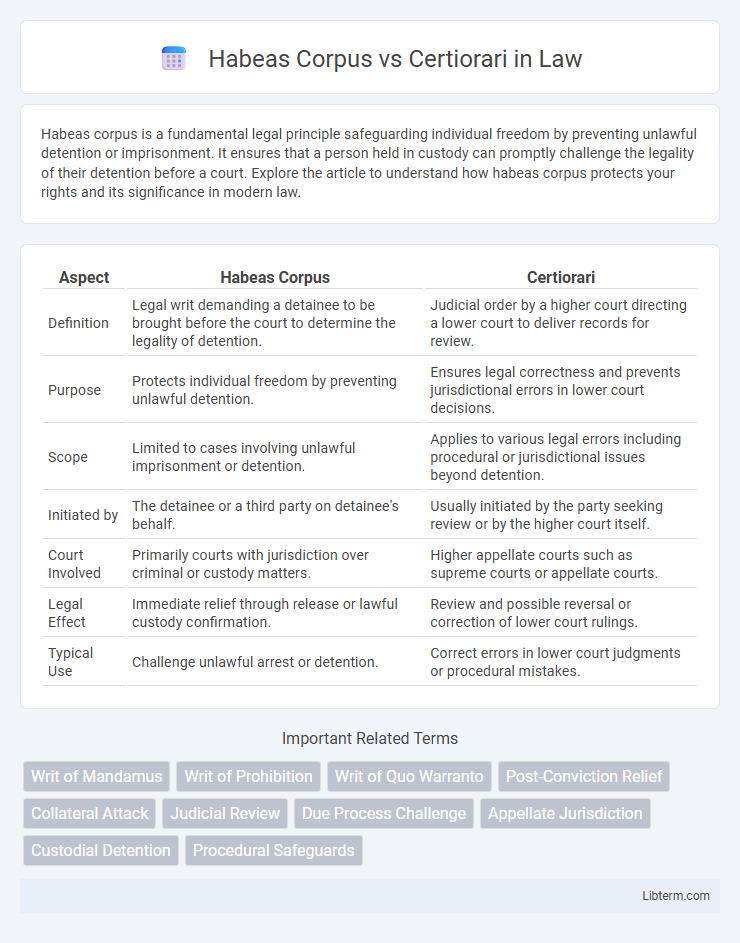
| Aspect | Habeas Corpus | Certiorari |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal writ demanding a detainee to be brought before the court to determine the legality of detention. | Judicial order by a higher court directing a lower court to deliver records for review. |
| Purpose | Protects individual freedom by preventing unlawful detention. | Ensures legal correctness and prevents jurisdictional errors in lower court decisions. |
| Scope | Limited to cases involving unlawful imprisonment or detention. | Applies to various legal errors including procedural or jurisdictional issues beyond detention. |
| Initiated by | The detainee or a third party on detainee's behalf. | Usually initiated by the party seeking review or by the higher court itself. |
| Court Involved | Primarily courts with jurisdiction over criminal or custody matters. | Higher appellate courts such as supreme courts or appellate courts. |
| Legal Effect | Immediate relief through release or lawful custody confirmation. | Review and possible reversal or correction of lower court rulings. |
| Typical Use | Challenge unlawful arrest or detention. | Correct errors in lower court judgments or procedural mistakes. |
Understanding Habeas Corpus: Definition and Purpose
Habeas Corpus is a fundamental legal principle that safeguards individual freedom by requiring authorities to justify a person's detention before a court. Its primary purpose is to prevent unlawful imprisonment and ensure that a prisoner's rights are not violated, serving as a critical check on executive and judicial power. Unlike Certiorari, which is a discretionary review by a higher court of lower court decisions, Habeas Corpus specifically addresses the legality of detention or imprisonment.
Certiorari Explained: Meaning and Application
Certiorari is a legal writ issued by a higher court to review the decision and proceedings of a lower court for errors of law or jurisdictional issues. It serves as a discretionary tool that allows appellate courts, such as the Supreme Court, to ensure uniformity in legal interpretations and correct injustices. This writ is commonly applied in cases where no plain, speedy, and adequate remedy exists, enabling the higher court to examine whether the lower court acted within its authority.
Historical Origins of Habeas Corpus and Certiorari
Habeas Corpus originated in 13th-century England as a legal mechanism to protect individual freedom by demanding a court to determine the legality of a prisoner's detention. Certiorari emerged later in common law to allow higher courts to review and clarify decisions made by lower courts, functioning as a supervisory writ. Both writs reflect the evolution of judicial safeguards, with Habeas Corpus centered on personal liberty and Certiorari focused on appellate review processes.
Key Legal Principles Behind Habeas Corpus
Habeas Corpus is a fundamental legal principle ensuring a person's right to challenge unlawful detention, mandating that authorities justify the legality of imprisonment before a court. It embodies protection against arbitrary detention by requiring immediate judicial review to safeguard individual liberty. Certiorari, in contrast, is a writ issued by higher courts to review lower court decisions for legal errors, focusing on appellate oversight rather than personal liberty protection.
Key Legal Principles Behind Certiorari
Certiorari is a discretionary judicial review mechanism allowing higher courts to examine lower court decisions for legal errors, ensuring uniformity and adherence to due process. It primarily addresses questions of law rather than fact, emphasizing the correction of jurisdictional mistakes or procedural irregularities. Habeas Corpus, in contrast, safeguards individual liberty by challenging unlawful detention through immediate judicial intervention.
Main Differences: Habeas Corpus vs Certiorari
Habeas Corpus primarily focuses on challenging unlawful detention by demanding a person's release from illegal imprisonment, ensuring protection of individual liberty. Certiorari, on the other hand, is a discretionary judicial review procedure where a higher court orders a lower court to deliver its record for examination and correction of errors. While Habeas Corpus addresses personal freedom and detention legality, Certiorari pertains to appellate jurisdiction and error correction in judicial decisions.
Legal Procedures Involved in Habeas Corpus Petitions
Habeas Corpus petitions involve a legal procedure demanding that a detainee be brought before the court to examine the lawfulness of their detention, ensuring protection against unlawful imprisonment. The process requires the petitioner to file a writ, supported by facts demonstrating illegal confinement, prompting judicial review and possible immediate release if detention lacks legal basis. Courts prioritize swift hearings in Habeas Corpus cases, emphasizing fundamental rights and procedural safeguards distinct from the appellate review process in Certiorari petitions.
Legal Procedures in Certiorari Applications
Certiorari applications involve judicial review where a higher court examines the records of a lower court to determine if legal errors affected the case outcome, primarily ensuring jurisdictional authority and procedural fairness. This legal procedure requires the petitioner to demonstrate that the lower court acted without jurisdiction, exceeded its authority, or violated due process, often by filing a formal motion supported by pertinent records. Unlike habeas corpus, which challenges unlawful detention, certiorari targets the validity of judicial or quasi-judicial decisions, emphasizing compliance with statutory and constitutional mandates.
Impact on Individual Rights and Judicial Review
Habeas Corpus protects individual liberty by allowing courts to examine the legality of a person's detention, serving as a critical safeguard against unlawful imprisonment. Certiorari empowers higher courts to review and correct errors in lower court decisions, reinforcing judicial oversight and consistency in the application of law. Both mechanisms significantly influence individual rights and judicial review, with Habeas Corpus prioritizing personal freedom and Certiorari ensuring the integrity of judicial processes.
Landmark Cases: Habeas Corpus and Certiorari in Practice
Habeas Corpus landmark cases such as *Ex parte Milligan* (1866) established the protection against unlawful detention, emphasizing the judiciary's role in safeguarding individual liberty. In contrast, certiorari cases like *Marbury v. Madison* (1803) solidified the Supreme Court's power to review lower court decisions, shaping the practice of judicial oversight. Both writs serve as crucial legal tools, with Habeas Corpus addressing personal freedom and Certiorari ensuring proper legal procedure and constitutional compliance.
Habeas Corpus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com