A covenant is a legally binding agreement between two or more parties outlining specific promises or obligations to be fulfilled. It often restricts certain actions or ensures particular standards within contracts, property dealings, or business arrangements. Explore the full article to understand how covenants impact your rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
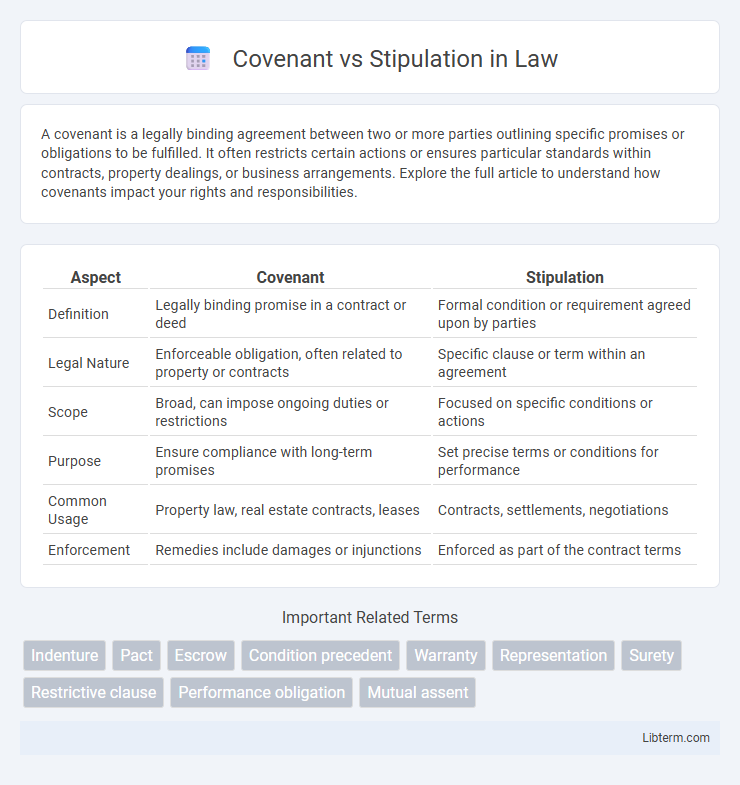
| Aspect | Covenant | Stipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legally binding promise in a contract or deed | Formal condition or requirement agreed upon by parties |
| Legal Nature | Enforceable obligation, often related to property or contracts | Specific clause or term within an agreement |
| Scope | Broad, can impose ongoing duties or restrictions | Focused on specific conditions or actions |
| Purpose | Ensure compliance with long-term promises | Set precise terms or conditions for performance |
| Common Usage | Property law, real estate contracts, leases | Contracts, settlements, negotiations |
| Enforcement | Remedies include damages or injunctions | Enforced as part of the contract terms |
Introduction to Covenants and Stipulations
Covenants are legally binding promises included in contracts that require parties to perform or refrain from specific actions, often seen in real estate and business agreements. Stipulations refer to conditions or requirements agreed upon by parties during litigation or contract negotiations, ensuring mutual consent on procedural or substantive issues. Both covenants and stipulations play critical roles in defining obligations and expectations, enhancing clarity and enforceability in legal arrangements.
Definition of Covenant
A covenant is a legally binding agreement or promise between parties, often used in real estate to impose restrictions or obligations on property use. It differs from a stipulation, which is typically a condition or requirement agreed upon within a contract or legal proceeding. Covenants ensure long-term compliance with specific terms, while stipulations often address procedural or situational matters.
Definition of Stipulation
A stipulation is a formal agreement or condition set forth between parties in a legal contract or negotiation, often specifying particular terms or obligations that must be met. Unlike a covenant, which generally refers to a solemn promise or restriction attached to property or contracts, a stipulation is typically a negotiated clause that clarifies or defines responsibilities without implied ongoing duties. Stipulations serve to streamline dispute resolution by explicitly stating agreed-upon facts or procedural rules within litigation or contractual frameworks.
Key Differences Between Covenant and Stipulation
Covenants are legally binding agreements or promises outlined in contracts, often addressing long-term obligations and rights between parties, whereas stipulations are specific conditions or requirements set within legal proceedings or contracts to clarify or limit certain actions. Covenants typically involve ongoing duties, such as restrictions on property use, while stipulations usually resolve procedural matters or agree on facts to facilitate smoother litigation or contract enforcement. The key difference lies in covenants establishing broad, enforceable promises, whereas stipulations function as precise terms agreed upon to streamline legal or contractual processes.
Legal Implications of Covenants
Covenants in legal contexts impose binding obligations on parties that affect property use, enforceable through damages or specific performance. Unlike general stipulations, covenants often run with the land, meaning they bind subsequent owners and can impact property value and rights over time. Breach of a covenant can lead to injunctions or monetary compensation, underscoring its significant legal implications in real estate and contract law.
Legal Implications of Stipulations
Stipulations in legal contexts serve as binding agreements between parties that outline specific facts or procedures to avoid disputes during litigation, reducing court time and expenses. Their legal implications include waiving the right to contest agreed-upon matters, which can affect case outcomes and limit evidentiary challenges. Carefully drafted stipulations ensure enforceability while protecting parties' interests by clearly defining the scope and terms to prevent unintended concessions.
Common Uses in Contracts
Covenants in contracts typically refer to promises or obligations parties agree to perform or refrain from, commonly found in real estate leases and loan agreements to ensure specific behaviors or conditions. Stipulations are agreed-upon terms or conditions that must be met within various legal agreements, frequently used in litigation settlements and commercial contracts to define precise responsibilities or outcomes. The key distinction lies in covenants often involving ongoing performance obligations, while stipulations generally address specific procedural or conditional requirements.
Examples of Covenants vs Stipulations
Covenants often include contractual promises such as a homeowner's agreement to maintain property aesthetics or a tenant's commitment to timely rent payment, ensuring long-term obligations and rights. Stipulations typically appear in legal settlements or court cases, where parties agree to specific conditions like postponing trial dates or waiving certain claims to facilitate dispute resolution. Examples highlight that covenants emphasize ongoing duties within agreements, while stipulations address discrete procedural or condition-based arrangements in legal contexts.
Choosing Between Covenant and Stipulation
Choosing between a covenant and a stipulation depends on the desired legal enforceability and scope within real estate or contractual agreements. Covenants typically impose broader, long-term obligations or restrictions on property use that run with the land, making them binding on future owners. Stipulations are more specific, often temporary conditions agreed upon by parties to resolve disputes or outline precise contractual duties, offering flexibility but less permanence.
Conclusion: Covenant vs Stipulation
Covenants and stipulations serve distinct roles in legal agreements; covenants are promises imposing obligations or restrictions on parties, often lasting for a defined or indefinite period. Stipulations specifically handle procedural or evidentiary agreements between parties during litigation or contract execution, typically limited in scope and duration. Understanding the difference clarifies enforceability and the nature of obligations created within contracts or legal processes.
Covenant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com