Extortion is a criminal act involving the coercion of someone through threats, often demanding money, property, or services in exchange for refraining from harmful actions. It violates personal rights and carries severe legal consequences across various jurisdictions. Explore the article to understand how extortion works and how you can protect yourself effectively.
Table of Comparison
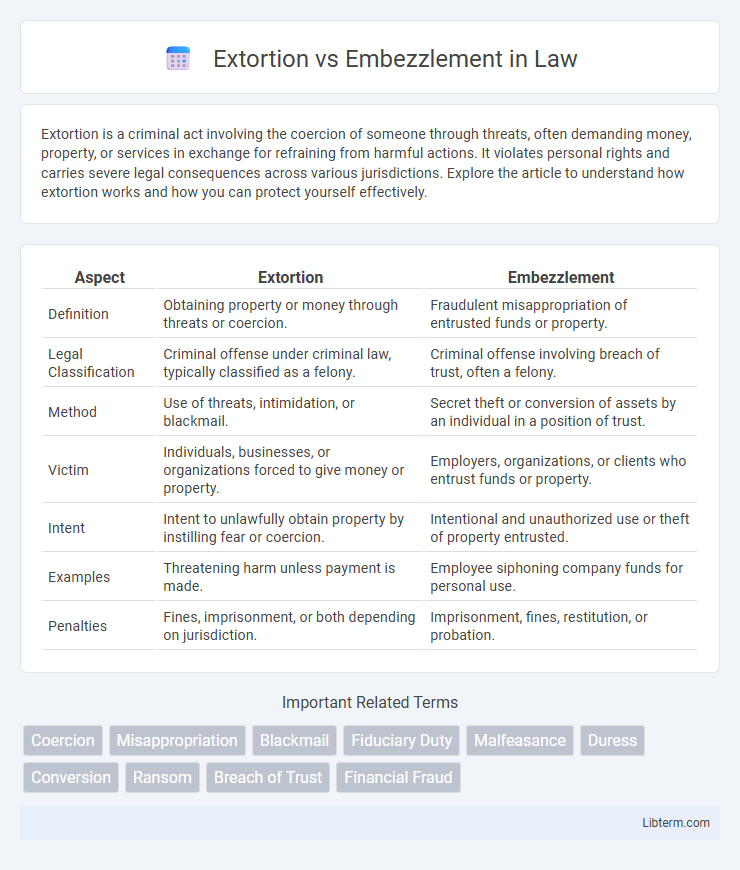
| Aspect | Extortion | Embezzlement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Obtaining property or money through threats or coercion. | Fraudulent misappropriation of entrusted funds or property. |
| Legal Classification | Criminal offense under criminal law, typically classified as a felony. | Criminal offense involving breach of trust, often a felony. |
| Method | Use of threats, intimidation, or blackmail. | Secret theft or conversion of assets by an individual in a position of trust. |
| Victim | Individuals, businesses, or organizations forced to give money or property. | Employers, organizations, or clients who entrust funds or property. |
| Intent | Intent to unlawfully obtain property by instilling fear or coercion. | Intentional and unauthorized use or theft of property entrusted. |
| Examples | Threatening harm unless payment is made. | Employee siphoning company funds for personal use. |
| Penalties | Fines, imprisonment, or both depending on jurisdiction. | Imprisonment, fines, restitution, or probation. |
Introduction to Extortion and Embezzlement
Extortion involves unlawfully obtaining money, property, or services from a person through coercion, threats, or force, typically leveraging fear to compel compliance. Embezzlement refers to the fraudulent appropriation of funds or assets by a person entrusted with their care, often occurring in professional or fiduciary relationships. Both crimes involve financial deceit but differ in their methods: extortion relies on intimidation, while embezzlement depends on betrayal of trust.
Defining Extortion: Key Elements
Extortion involves obtaining money, property, or services from a person or institution through coercion, threats, or intimidation, distinguishing it as a crime involving fear and duress. The key elements of extortion include the use of wrongful threats, the victim's compelled consent, and the perpetrator's intent to gain unlawfully. In contrast, embezzlement is the fraudulent appropriation of assets by a person entrusted with them, lacking the element of coercion present in extortion.
Defining Embezzlement: Key Elements
Embezzlement involves the fraudulent appropriation of property or funds entrusted to an individual's care, often occurring in employment or fiduciary relationships. Key elements include the lawful possession of assets, intent to steal or convert those assets for personal use, and a breach of trust or duty. Unlike extortion, embezzlement does not require coercion or threats but hinges on the misuse of entrusted resources.
Legal Differences Between Extortion and Embezzlement
Extortion involves obtaining money, property, or services from a person or institution through coercion, threats, or force, whereas embezzlement is the fraudulent taking of property or money by a person in a position of trust, such as an employee or fiduciary. The key legal difference lies in the method of obtaining assets: extortion employs intimidation or threats, while embezzlement involves deceit or breach of fiduciary duty without direct threats. Penalties for extortion often include criminal charges related to violent or coercive acts, whereas embezzlement is prosecuted as a financial crime emphasizing breach of trust and misappropriation of funds.
Methods and Tactics Used in Extortion
Extortion involves coercing victims through threats, intimidation, or blackmail to obtain money, property, or services, often leveraging fear or harm. Methods include demanding payments under threat of violence, exposing damaging information, or exploiting vulnerabilities to enforce compliance. Unlike embezzlement, which entails the illicit misappropriation of funds by someone entrusted with them, extortion relies on overt pressure tactics to compel victims into surrendering assets.
Common Scenarios of Embezzlement
Embezzlement commonly occurs in workplaces where employees manipulate financial records or divert company funds for personal use, often involving cash, checks, or electronic transfers. Typical scenarios include accountants inflating expenses, managers creating fake vendors for false payments, and employees stealing petty cash or inventory for resale. These acts usually exploit trust and access to financial systems, differentiating embezzlement from extortion, which involves coercion or threats to obtain money or property.
Impact on Victims: Extortion vs Embezzlement
Extortion causes victims severe psychological distress and financial loss through threats or coercion, often leading to long-term fear and trauma. Embezzlement results in substantial monetary damage as trusted insiders illegally siphon funds, undermining organizational trust and stability. Both crimes severely disrupt victims' financial security, but extortion uniquely inflicts emotional harm alongside economic consequences.
Penalties and Legal Consequences
Extortion typically carries severe penalties including substantial fines, imprisonment ranging from several years to decades, and restitution orders due to its coercive nature and threat of harm. Embezzlement penalties vary based on the amount stolen but often involve significant fines, imprisonment, probation, and mandatory restitution to victims. Both crimes result in permanent criminal records that impact future employment opportunities and civil rights such as voting and firearm possession.
Famous Cases of Extortion and Embezzlement
Famous cases of extortion include the FBI's conviction of Whitey Bulger, who used threats and intimidation to control criminal enterprises. Embezzlement scandals often involve high-profile figures like Bernie Madoff, whose Ponzi scheme defrauded investors of billions. Both crimes showcase the abuse of trust and power for financial gain, highlighting legal and ethical violations in corporate and criminal settings.
Prevention Strategies and Legal Remedies
Effective prevention strategies for extortion include robust internal controls, employee training on recognizing coercive tactics, and implementing secure communication channels to detect threats early. Embezzlement prevention relies on strict financial oversight, segregation of duties, and regular audits to identify unauthorized transactions promptly. Legal remedies differ as extortion often involves criminal prosecution with penalties such as imprisonment, while embezzlement cases may lead to restitution orders, fines, and criminal charges depending on the severity and jurisdiction.
Extortion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com