Understanding the legality of a contract is essential to ensure that agreements are enforceable and protect your rights under the law. A valid contract must include offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual consent without any illegal activities involved. Explore the rest of this article to learn more about the key elements that determine whether your contract is legally binding.
Table of Comparison
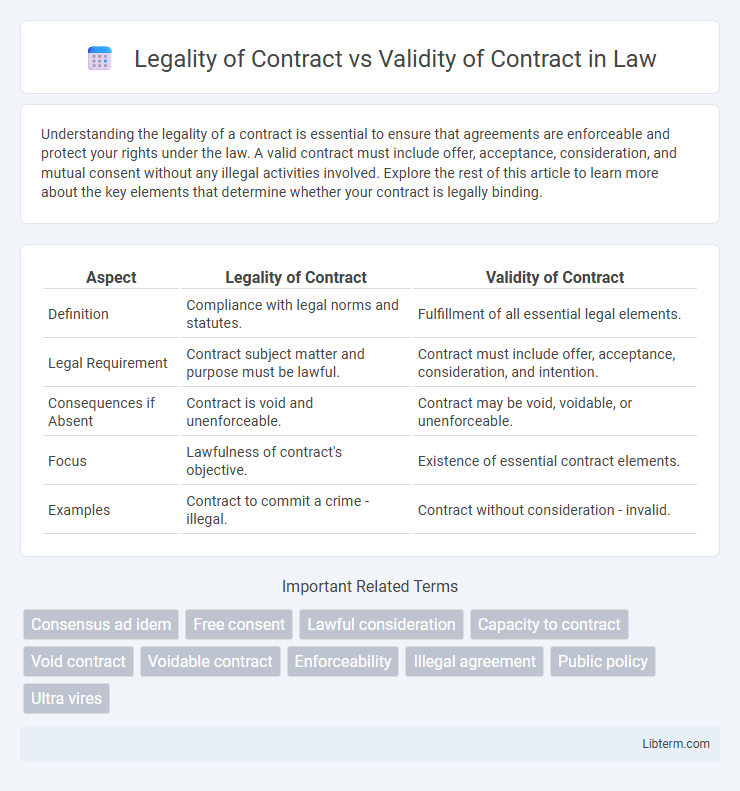
| Aspect | Legality of Contract | Validity of Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Compliance with legal norms and statutes. | Fulfillment of all essential legal elements. |
| Legal Requirement | Contract subject matter and purpose must be lawful. | Contract must include offer, acceptance, consideration, and intention. |
| Consequences if Absent | Contract is void and unenforceable. | Contract may be void, voidable, or unenforceable. |
| Focus | Lawfulness of contract's objective. | Existence of essential contract elements. |
| Examples | Contract to commit a crime - illegal. | Contract without consideration - invalid. |
Introduction to Contract Law
The legality of a contract refers to whether the contract's subject matter and terms comply with the law and public policy, ensuring it is not for illegal activities. Validity of a contract involves meeting essential elements such as offer, acceptance, consideration, legal capacity, and mutual consent, which confirms the contract is enforceable by law. In contract law, a contract must be both legal and valid to be binding and enforceable in a court of law.
Defining Legality of a Contract
Legality of a contract refers to the requirement that the agreement's purpose and terms comply with existing laws and public policy, ensuring the contract is not for illegal activities. A contract lacking legality is void and unenforceable regardless of its formation or the parties' intentions. Thus, legality is a fundamental criterion for a contract's enforceability, distinguishing it from mere validity, which also considers factors like consent and capacity.
Understanding Validity in Contracts
Understanding the validity of a contract involves assessing whether all essential elements such as offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual consent are present and legally enforceable. A valid contract must comply with legal requirements, ensuring it is not only agreed upon but also legally binding and capable of being executed in a court of law. While the legality of a contract refers to the requirement that the contract's purpose and terms must not violate any laws, validity ensures the contract is properly formed and effective in creating legal obligations.
Legal Requirements for a Valid Contract
A valid contract must fulfill essential legal requirements including offer, acceptance, mutual consent, consideration, capacity, and lawful purpose to be enforceable in a court of law. The legality of a contract pertains specifically to whether the contract's object or purpose is lawful, as contracts formed for illegal activities are void and unenforceable. Ensuring both the validity and legality of a contract guarantees that the agreement is binding and compliant with statutory regulations.
Elements Affecting Contract Legality
Contract legality hinges on compliance with laws and public policy, requiring the subject matter and terms to be lawful. Factors affecting legality include the purpose of the contract, the legality of the object, and the capacity of the parties involved. Validity depends on essential elements like offer, acceptance, consideration, and genuine consent, but a valid contract can still be illegal if it violates statutory requirements or involves unlawful activities.
Key Differences: Legality vs Validity
Legality of contract refers to whether the contract's subject matter and terms comply with laws and public policy, making it lawful to enforce. Validity of contract involves essential elements like offer, acceptance, consideration, and capacity that ensure the agreement is legally binding. A contract can be valid but not legal if its purpose violates the law, whereas legality is a component of overall contract validity but does not alone guarantee enforceability.
Consequences of Illegal Contracts
Illegal contracts lack legal enforceability and typically result in nullification, preventing either party from seeking judicial remedies. Consequences of illegal contracts include penalties, restitution requirements, and potential criminal charges depending on the jurisdiction and nature of the illegality. Courts refuse to uphold illegal agreements, aiming to deter unlawful conduct and preserve public policy.
Situations Rendering Contracts Invalid
Situations rendering contracts invalid often involve the absence of legality or essential elements such as consent, capacity, and lawful object. Contracts lacking a legal purpose, involving fraud, coercion, mistake, or illegality, are deemed void or voidable. These factors must be scrutinized to determine the distinction between mere legality issues and the overall validity of a contract under contract law.
Real-World Examples: Legal vs Valid Contracts
A contract can be legally binding yet invalid if essential elements like mutual consent or consideration are missing, such as a contract signed under duress being legally enforceable but voidable. Conversely, a valid contract may fail legality if it involves illegal activities, like a contract for the sale of prohibited drugs, which is automatically void despite meeting all validity criteria. Real-world examples include employment contracts that are valid and legal versus agreements involving fraud, which, while structured as contracts, are invalid due to illegality.
Ensuring Both Legality and Validity in Agreements
Ensuring both legality and validity in contracts involves confirming that the agreement complies with statutory laws and possesses all essential elements such as offer, acceptance, consideration, and mutual consent. A legally enforceable contract must not only meet these foundational criteria but also avoid any illegal subject matter or prohibited activities. Careful drafting and thorough review safeguard against void or voidable agreements, securing enforceability in legal disputes.
Legality of Contract Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com