Flashback is a powerful literary device that transports readers or viewers to a previous moment in time, enriching the narrative by revealing crucial backstory and character motivations. This technique enhances emotional depth and provides context, making the present storyline more compelling and understandable. Explore the rest of the article to learn how flashbacks can elevate your storytelling skills effectively.
Table of Comparison
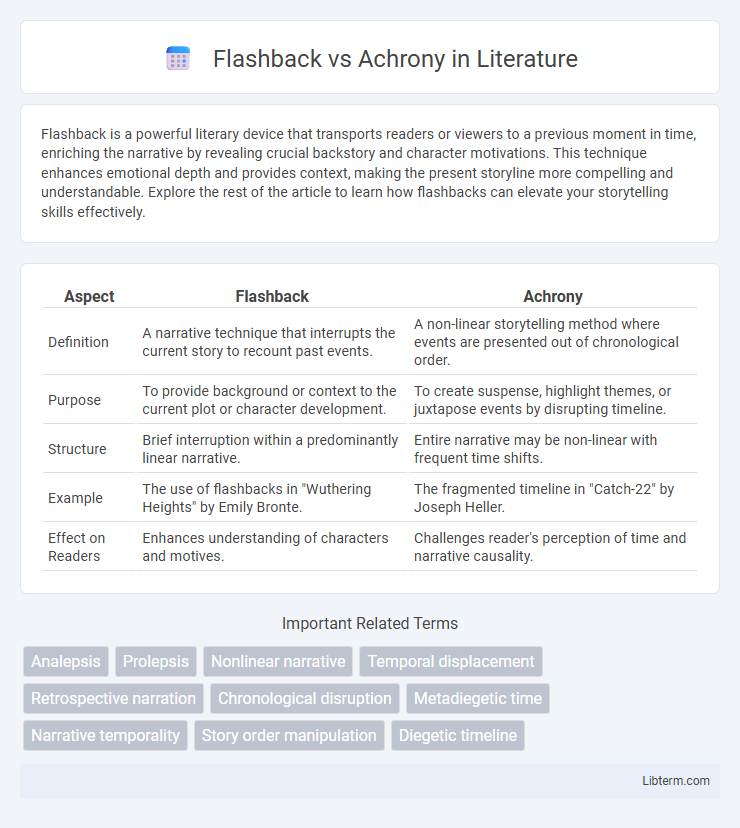
| Aspect | Flashback | Achrony |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A narrative technique that interrupts the current story to recount past events. | A non-linear storytelling method where events are presented out of chronological order. |
| Purpose | To provide background or context to the current plot or character development. | To create suspense, highlight themes, or juxtapose events by disrupting timeline. |
| Structure | Brief interruption within a predominantly linear narrative. | Entire narrative may be non-linear with frequent time shifts. |
| Example | The use of flashbacks in "Wuthering Heights" by Emily Bronte. | The fragmented timeline in "Catch-22" by Joseph Heller. |
| Effect on Readers | Enhances understanding of characters and motives. | Challenges reader's perception of time and narrative causality. |
Understanding Flashback and Achrony: Definitions
Flashback refers to a narrative technique where the chronological order is interrupted to revisit past events, enhancing plot depth and character development. Achrony is a broader concept involving non-linear time structures in storytelling, where events are presented out of temporal sequence without strict adherence to past, present, or future timelines. Understanding flashback and achrony involves recognizing that flashback is a specific instance of achrony used to provide background or context within a predominantly linear narrative framework.
Key Differences Between Flashback and Achrony
Flashback involves re-experiencing or recalling past events within a narrative, often used to provide backstory or character motivation, while achrony refers to a non-linear timeline where events are presented out of chronological order without necessarily linking directly to memory or reflection. Flashbacks typically interrupt the present action to reveal past moments, creating a temporal shift grounded in memory, whereas achrony disrupts the conventional temporal sequence to challenge readers' or viewers' perception of time. Key differences include flashback's reliance on past event insertion versus achrony's broader restructuring of narrative time that may include flashforwards, simultaneous times, or fragmented temporal order.
The Role of Flashbacks in Narrative Structure
Flashbacks play a crucial role in narrative structure by providing essential background information that deepens character development and enhances plot complexity. Unlike achrony, which presents events out of chronological order without clear temporal markers, flashbacks are deliberate interruptions in the present timeline to reveal past events that influence the current storyline. This strategic use of flashbacks enriches the audience's understanding of motivations and conflicts, creating a layered and immersive narrative experience.
Types of Achrony in Storytelling
Achrony in storytelling comprises several types, including anachrony, analepsis, and prolepsis, which manipulate the narrative timeline to alter the chronological order of events. Anachrony broadly refers to disruptions in temporal sequence, with analepsis representing flashbacks that revisit past events and prolepsis indicating flashforwards projecting future occurrences. These techniques enhance narrative complexity and character development by providing background context or foreshadowing outcomes distinct from the linear progression seen in flashbacks alone.
Examples of Flashback Usage in Literature and Film
Flashback is a narrative technique that interrupts the chronological sequence to depict events from the past, enriching character backgrounds and plot development. Classic examples include F. Scott Fitzgerald's *The Great Gatsby*, where Gatsby's past is revealed through Nick's flashbacks, and the film *The Godfather Part II*, which interweaves Michael Corleone's present with Vito Corleone's past. These flashbacks provide essential context and deepen audience understanding by revealing motivations and history otherwise inaccessible through linear storytelling.
Achrony in Modern Narratives: Trends and Techniques
Achrony in modern narratives breaks linear time sequences, blending past, present, and future to create complex story structures that challenge traditional chronology. This technique enhances thematic depth and character development through non-linear storytelling, often integrating multiple time layers simultaneously. Emerging trends emphasize immersive experiences using achrony in digital media, interactive games, and experimental films, pushing boundaries of audience engagement and narrative innovation.
Functions and Purposes of Flashbacks
Flashbacks serve to provide critical background information, reveal characters' motivations, and deepen the narrative by showing past events that influence the present storyline. Unlike achrony, which involves a non-linear timeline with disrupted chronological order for stylistic effect, flashbacks specifically function to clarify plot details and enhance emotional resonance. Their purpose is to enrich character development and contextualize current events without abandoning the overall narrative flow.
How Achrony Shapes Reader and Viewer Experience
Achrony disrupts traditional chronological narrative, compelling readers and viewers to actively piece together events and timelines, which deepens engagement and cognitive involvement. This non-linear storytelling enhances emotional resonance by revealing character motives and plot twists at strategically impactful moments rather than sequentially. Compared to flashbacks, achrony transforms passive consumption into an interactive mental exercise, fostering a more immersive and memorable experience.
Advantages and Challenges of Using Flashbacks vs. Achrony
Flashbacks enhance narrative depth by providing direct insights into past events, which can clarify character motivations and enrich plot complexity, but they may interrupt the story's chronological flow and confuse the audience if overused. Achrony offers a non-linear approach that creates suspense and engages viewers by revealing information out of sequence, though it demands careful structuring to avoid narrative fragmentation or disorientation. Both techniques require balancing clarity and intrigue, with flashbacks excelling in emotional retrospection and achrony in innovative storytelling.
Choosing the Right Technique: Flashback or Achrony?
Choosing between flashback and achrony depends on the narrative goals and thematic focus of the story. Flashbacks provide clear, chronological insights into past events, enhancing character development and plot comprehension. Achrony, characterized by non-linear storytelling, offers a fragmented or cyclical experience that can deepen mystery and engage audiences by revealing information out of sequence.
Flashback Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com