Haiku is a traditional Japanese poetry form consisting of three lines with a syllable pattern of 5-7-5, capturing moments of nature or emotion in a concise yet vivid way. This poetic style encourages mindfulness and deep observation, offering a unique lens to experience the world around you. Explore the nuances and beauty of haiku in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
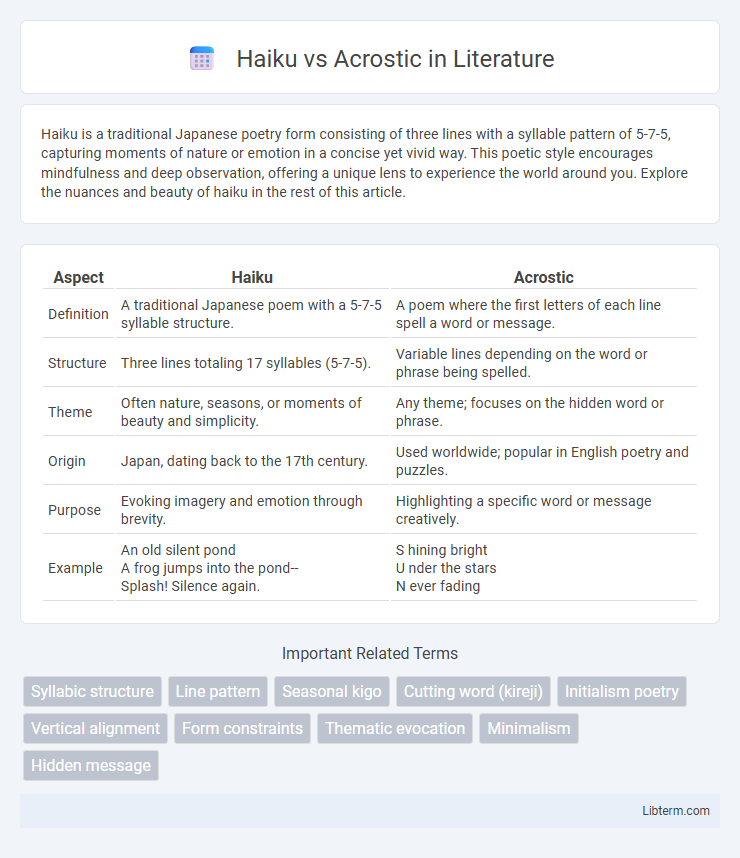
| Aspect | Haiku | Acrostic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A traditional Japanese poem with a 5-7-5 syllable structure. | A poem where the first letters of each line spell a word or message. |
| Structure | Three lines totaling 17 syllables (5-7-5). | Variable lines depending on the word or phrase being spelled. |
| Theme | Often nature, seasons, or moments of beauty and simplicity. | Any theme; focuses on the hidden word or phrase. |
| Origin | Japan, dating back to the 17th century. | Used worldwide; popular in English poetry and puzzles. |
| Purpose | Evoking imagery and emotion through brevity. | Highlighting a specific word or message creatively. |
| Example |
An old silent pond A frog jumps into the pond-- Splash! Silence again. |
S hining bright U nder the stars N ever fading |
Introduction to Haiku and Acrostic Poetry
Haiku is a traditional Japanese poetry form consisting of three lines with a syllable pattern of 5-7-5, emphasizing nature and seasonal themes. Acrostic poetry arranges the first letters of each line to spell out a word or message vertically, often used for creative expression or mnemonic devices. Both forms offer unique structures that challenge poets to convey meaning concisely and artistically.
Historical Origins and Cultural Context
Haiku originated in 17th-century Japan as a concise poetic form emphasizing nature and seasonal themes, rooted in the collaborative linked-verse tradition called renga. Acrostic poetry dates back to ancient Greece and Rome, where authors used it as a mnemonic device or to convey secret messages through initial letters of lines. These forms reflect distinct cultural contexts: Haiku embodies Zen aesthetics and simplicity, while acrostics highlight linguistic play and coded communication.
Structure and Form: Haiku Explained
Haiku is a traditional Japanese poetic form consisting of three lines with a 5-7-5 syllable structure, emphasizing simplicity and nature imagery. It follows a fixed syllabic pattern that creates a concise and evocative expression within 17 syllables. Acrostic poetry, in contrast, uses the first letters of each line to spell out a word or message and does not adhere to a specific syllable count or line structure.
Structure and Form: Acrostic Unveiled
Haiku consists of three lines with a 5-7-5 syllable pattern, emphasizing brevity and seasonal imagery. Acrostic poems feature a vertical arrangement of letters that spell out a word or message, with each line beginning with the corresponding letter. The structure of acrostics allows for creative flexibility in line length and rhythm, contrasting with haiku's strict syllabic form.
Thematic Focus: What Haikus and Acrostics Express
Haikus traditionally capture fleeting moments in nature, emphasizing sensory experiences and seasonal themes, often evoking tranquility and reflection. Acrostics focus on expressing clear, direct messages or specific ideas spelled out through the first letters of each line, making them ideal for thematic clarity and wordplay. While haikus evoke mood and imagery through concise syllabic structure, acrostics convey deliberate meanings tied to the spelled word or phrase.
Language and Word Choice Differences
Haikus rely on concise, evocative language adhering to a strict 5-7-5 syllable pattern, emphasizing imagery and seasonal references to capture a fleeting moment. Acrostic poems use words or phrases where the first letter of each line spells out a message, allowing for more flexibility in vocabulary and thematic expression. The word choice in Haikus focuses on brevity and sensory detail, while Acrostics prioritize clarity and alignment with the hidden word or phrase.
Creative Process: Writing a Haiku vs. an Acrostic
Writing a haiku requires a focus on syllable count and seasonal imagery, typically structured in three lines of 5-7-5 syllables, emphasizing simplicity and nature-inspired themes. In contrast, crafting an acrostic involves selecting a word or phrase as the poem's spine, with each line starting with a letter from that word, enabling expression through thematic or descriptive sentences. The haiku process prioritizes brevity and evocative emotion, while the acrostic encourages wordplay and structural creativity tied to the chosen keyword.
Educational Benefits for Students
Haiku poetry enhances students' understanding of syllable structure and promotes concise, vivid expression, improving their linguistic precision and creativity. Acrostic poems reinforce vocabulary retention and spelling skills by encouraging learners to connect words systematically with thematic concepts. Both forms foster critical thinking and engagement, supporting diverse learning styles through structured yet imaginative writing exercises.
Popular Examples and Notable Poets
Haiku, a traditional Japanese form known for its three-line, 5-7-5 syllable structure, boasts notable poets like Matsuo Basho, whose work exemplifies seasonal imagery and simplicity. Acrostic poetry, where the first letters of each line spell out a word or message, has been popularized by poets such as Edgar Allan Poe, especially in his poem "An Acrostic." Popular haiku often capture moments from nature, while acrostics serve as creative tools for hidden meanings or tribute poems.
Choosing Between Haiku and Acrostic Poetry
Choosing between haiku and acrostic poetry depends on the desired structure and thematic focus. Haikus follow a strict 5-7-5 syllable pattern emphasizing nature and emotion, making them ideal for concise, vivid imagery. Acrostic poems offer creative freedom, allowing the first letters of each line to spell a word or message, suitable for personalized or thematic expression.
Haiku Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com