Asyndeton is a rhetorical device that omits conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise and impactful statement. It enhances the rhythm and urgency of a sentence, making your message more memorable and engaging. Discover how mastering asyndeton can elevate your writing by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
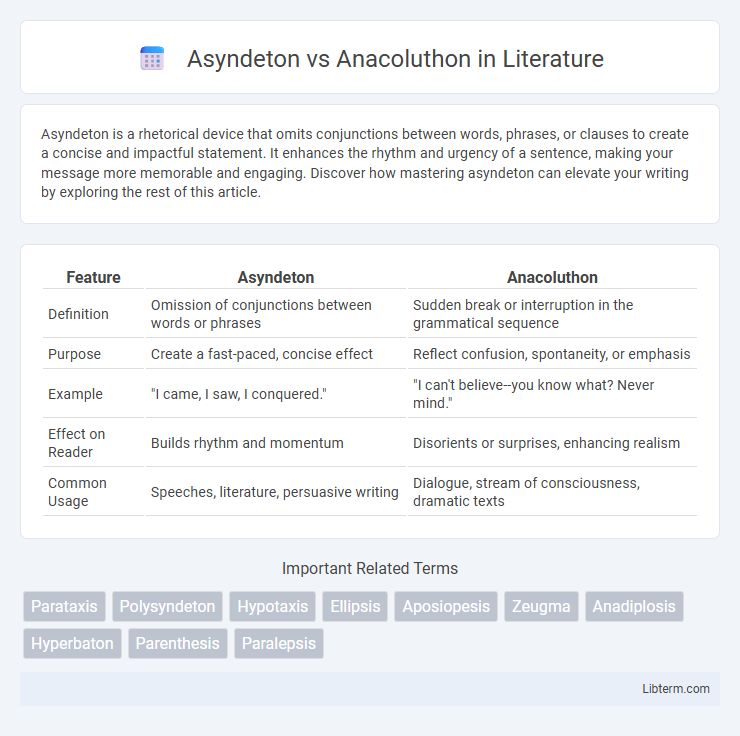
| Feature | Asyndeton | Anacoluthon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Omission of conjunctions between words or phrases | Sudden break or interruption in the grammatical sequence |
| Purpose | Create a fast-paced, concise effect | Reflect confusion, spontaneity, or emphasis |
| Example | "I came, I saw, I conquered." | "I can't believe--you know what? Never mind." |
| Effect on Reader | Builds rhythm and momentum | Disorients or surprises, enhancing realism |
| Common Usage | Speeches, literature, persuasive writing | Dialogue, stream of consciousness, dramatic texts |
Introduction to Asyndeton and Anacoluthon
Asyndeton is a rhetorical device characterized by the deliberate omission of conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses to create a concise, impactful effect. Anacoluthon involves a sudden break in the syntactical structure of a sentence, causing an unexpected shift or interruption in the flow of thought. Both techniques enhance literary and rhetorical expression by manipulating sentence structure to engage readers and emphasize specific ideas.
Defining Asyndeton: Meaning and Usage
Asyndeton is a rhetorical device characterized by the deliberate omission of conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses, creating a concise and impactful expression. This technique enhances the rhythm and pace of a sentence, often used to evoke urgency or emphasize enumeration in literary and persuasive contexts. Writers employ asyndeton to deliver messages with clarity and intensity, making statements more memorable and dynamic.
What Is Anacoluthon? A Clear Explanation
Anacoluthon is a rhetorical device characterized by a sudden break in the grammatical structure of a sentence, leaving it unfinished or disrupted, which creates a sense of confusion or spontaneity in speech or writing. It contrasts with asyndeton, which is the omission of conjunctions between clauses for a concise, impactful effect. Anacoluthon is often used to reflect natural thought processes, emphasize emotional intensity, or mimic interrupted dialogue.
Key Differences Between Asyndeton and Anacoluthon
Asyndeton is a rhetorical device characterized by the omission of conjunctions between related clauses or items, creating a concise and impactful effect, while anacoluthon involves a sudden break or interruption in the grammatical structure of a sentence, leading to a shift or incomplete thought. The key difference lies in their syntactic function: asyndeton maintains grammatical parallelism without conjunctions, enhancing rhythm and emphasis, whereas anacoluthon disrupts syntax, reflecting spontaneity or confusion in speech. Examples of asyndeton include Julius Caesar's "I came, I saw, I conquered," whereas anacoluthon appears in phrases like "I can't believe--well, never mind," illustrating the structural discontinuity.
Grammatical Structures: How They Differ
Asyndeton features the deliberate omission of conjunctions between closely related clauses, creating a fast-paced and impactful rhythm by linking phrases directly. Anacoluthon involves a sudden break or shift in the grammatical structure within a sentence, resulting in an unexpected and often disjointed expression where the initial clause does not logically connect to the following one. The key grammatical difference lies in asyndeton's consistent coordination without conjunctions, while anacoluthon disrupts syntactic continuity, producing an incomplete or fragmented sentence structure.
Effects on Tone and Style
Asyndeton enhances tone by creating a brisk, urgent rhythm through the deliberate omission of conjunctions, fostering a sense of speed and intensity in writing. Anacoluthon disrupts expected syntactic flow, generating a tone of confusion or spontaneity that emphasizes emotional instability or stream-of-consciousness style. Together, these devices shape stylistic impact by manipulating sentence structure to evoke specific psychological or emotional responses in the reader.
Examples of Asyndeton in Literature
Asyndeton is a literary device characterized by the omission of conjunctions between words, phrases, or clauses, as seen in Julius Caesar's famous line, "I came, I saw, I conquered." This technique creates a rapid, impactful rhythm that enhances the emotional intensity of a passage. Contrarily, anacoluthon involves a disruption in the syntactic flow, often reflecting a speaker's hesitation or shift in thought, rather than the deliberate brevity found in asyndeton.
Anacoluthon in Famous Texts
Anacoluthon, characterized by a sudden break in grammatical structure within a sentence, serves to convey urgency, confusion, or emphasis in famous texts such as James Joyce's "Ulysses" and Shakespeare's "Hamlet." Unlike asyndeton, which omits conjunctions for stylistic brevity, anacoluthon disrupts expected syntax to reflect a character's inner turmoil or fragmented thought process. This rhetorical device enriches literary works by mirroring natural speech patterns and highlighting psychological complexity.
Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls
Asyndeton and anacoluthon are often confused due to their disruption of traditional sentence structure, but asyndeton involves the deliberate omission of conjunctions to create a concise, impactful rhythm, whereas anacoluthon results from a sudden break in sentence syntax, often reflecting a speaker's interrupted or shifting thought. A common misconception is that both devices serve purely stylistic purposes, while anacoluthon can also signal confusion or emotional intensity, potentially leading to misinterpretation if overused or misunderstood. Writers should avoid the pitfall of employing anacoluthon without clear intent, as it may confuse readers, whereas asyndeton requires careful balance to maintain clarity without sacrificing the intended rhetorical effect.
When to Use Asyndeton vs Anacoluthon
Asyndeton is best used to create a fast-paced, dramatic effect by intentionally omitting conjunctions, making lists or phrases feel more urgent and impactful. Anacoluthon occurs when a sentence abruptly breaks its grammatical structure, often to mimic natural speech or highlight emotional intensity, but should be used sparingly to avoid confusing the reader. Choose asyndeton for concise emphasis and rhythm in polished writing, while anacoluthon suits informal contexts or creative works where disruption of syntax serves a stylistic purpose.
Asyndeton Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com