Consonance is a literary device characterized by the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the end or middle of words in close proximity, enhancing the rhythm and musicality of a text. This technique is widely used in poetry and prose to create a pleasing auditory effect and reinforce the mood or tone. Explore the rest of the article to discover how consonance can elevate your writing style.
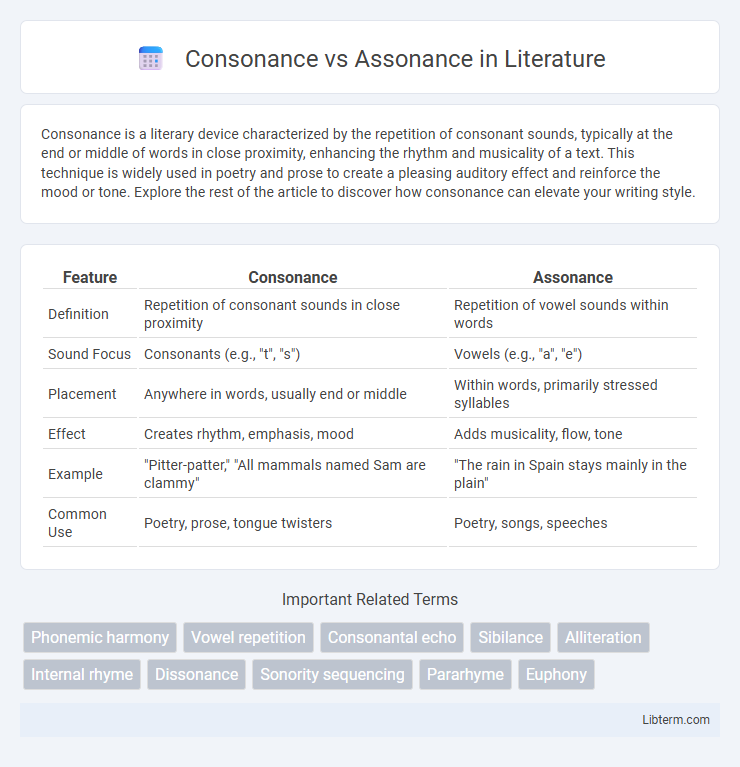
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Consonance | Assonance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetition of consonant sounds in close proximity | Repetition of vowel sounds within words |
| Sound Focus | Consonants (e.g., "t", "s") | Vowels (e.g., "a", "e") |
| Placement | Anywhere in words, usually end or middle | Within words, primarily stressed syllables |
| Effect | Creates rhythm, emphasis, mood | Adds musicality, flow, tone |
| Example | "Pitter-patter," "All mammals named Sam are clammy" | "The rain in Spain stays mainly in the plain" |
| Common Use | Poetry, prose, tongue twisters | Poetry, songs, speeches |
Introduction to Consonance and Assonance
Consonance refers to the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the end or middle of words, creating a harmonious effect in poetry and prose. Assonance involves the repetition of vowel sounds within closely placed words, enhancing the musicality and mood of the text. Both consonance and assonance serve as essential literary devices that enrich the auditory appeal and emotional impact of language.
Defining Consonance
Consonance is a literary device characterized by the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the end or middle of words in close proximity, enhancing rhythm and mood in poetry and prose. This technique differs from assonance, which involves the repetition of vowel sounds, creating a distinct auditory effect. Writers use consonance to emphasize particular words, reinforce meaning, and contribute to the overall sonic texture of the text.
Defining Assonance
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words to create internal rhyming and enhance the musical quality of language. It differs from consonance, which involves the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the beginning or end of words. Assonance often appears in poetry and prose to evoke mood and emphasize particular phrases through vowel harmony.
Key Differences Between Consonance and Assonance
Consonance involves the repetition of consonant sounds, typically at the end or middle of words, creating a harmonious effect, while assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, enhancing musicality and mood. Consonance often emphasizes crisp, sharp sounds like "t" or "k," whereas assonance focuses on softer, elongated vowel sounds such as "ee" or "oo." The key difference lies in the type of sound repeated: consonant sounds for consonance and vowel sounds for assonance, both serving distinct roles in poetry and prose to enrich auditory appeal.
Examples of Consonance in Literature
Consonance, the repetition of consonant sounds at the end or middle of words, is frequently found in literature to create rhythm and mood, such as the "p" sound in Edgar Allan Poe's "The Raven" with "weak and weary." Another example appears in Shakespeare's "Macbeth," where the repetition of the "t" sound in "All's well that ends well" enhances the lyrical quality. These instances illustrate how consonance emphasizes key themes and heightens the auditory experience of poetry and prose.
Examples of Assonance in Poetry
Assonance in poetry involves the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, creating internal rhyming and musicality, as seen in the phrase "Hear the mellow wedding bells" by Edgar Allan Poe. This technique enhances mood and tone by emphasizing particular vowel sounds like the long "e" in Poe's example, making the line more melodic and memorable. Unlike consonance, which focuses on repeated consonant sounds, assonance centers exclusively on vocalic harmony to enrich the poem's auditory experience.
Effects of Consonance in Writing
Consonance enhances writing by creating rhythm and musicality through the repetition of consonant sounds, often at the end or middle of words, which intensifies mood and tone. It reinforces key themes and emotions, making phrases more memorable and engaging for readers. Consonance also aids in unifying lines of poetry or prose, providing a subtle but powerful acoustic coherence that deepens the impact of the text.
Impact of Assonance on Tone and Mood
Assonance, the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, significantly shapes the tone and mood of a text by creating a musical or rhythmic quality that evokes specific emotions. Its use in poetry and prose can lead to a soothing, melancholic, or intense atmosphere depending on the chosen vowel sounds, such as the soft "ee" sound fostering calmness or the open "o" sound generating a somber mood. Unlike consonance, which emphasizes consonant sound repetition, assonance directly influences the emotional resonance and auditory appeal, deeply engaging the reader's emotional response.
Consonance and Assonance in Song Lyrics
Consonance in song lyrics emphasizes the repetition of consonant sounds, often enhancing the rhythm and mood by creating a sense of cohesion and musicality. Assonance highlights the repetition of vowel sounds, contributing to the melody and emotional resonance within verses. Both techniques enrich lyrical expression, making songs more memorable and engaging through sonic texture and pattern.
Tips for Using Consonance and Assonance Effectively
To use consonance effectively, emphasize repeating consonant sounds at the end or middle of words to create rhythm and enhance mood, especially in poetry and prose. Employ assonance by repeating vowel sounds within words to produce internal rhyming, which can evoke emotion and add musicality to your writing. Balancing both consonance and assonance ensures varied sound patterns, preventing monotony and enriching the auditory experience for readers.
Consonance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com