Rhyme enhances poetry by creating rhythm and musicality that captivates the reader's attention. It helps to emphasize important themes and makes verses more memorable. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mastering rhyme can elevate your writing skills.
Table of Comparison
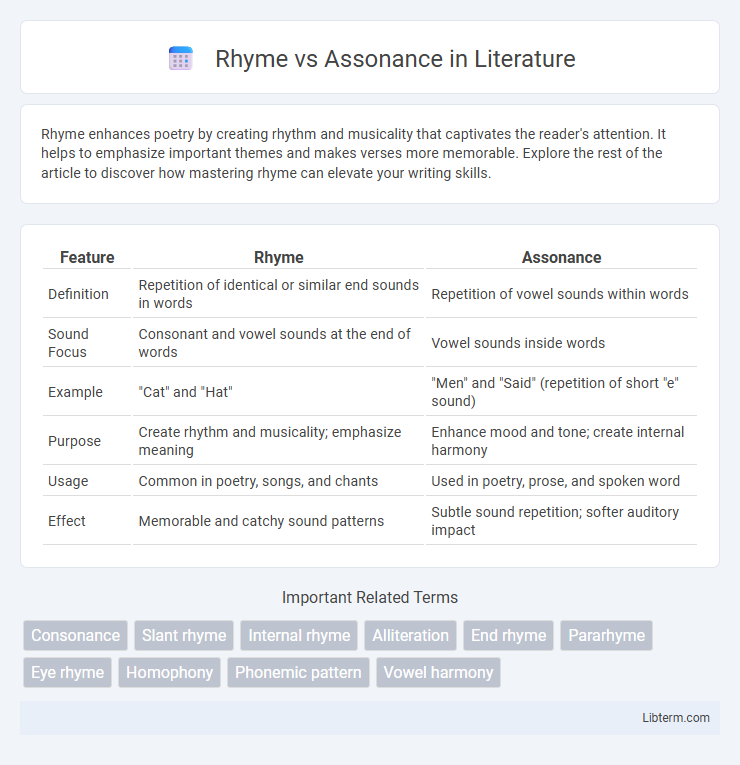
| Feature | Rhyme | Assonance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetition of identical or similar end sounds in words | Repetition of vowel sounds within words |
| Sound Focus | Consonant and vowel sounds at the end of words | Vowel sounds inside words |
| Example | "Cat" and "Hat" | "Men" and "Said" (repetition of short "e" sound) |
| Purpose | Create rhythm and musicality; emphasize meaning | Enhance mood and tone; create internal harmony |
| Usage | Common in poetry, songs, and chants | Used in poetry, prose, and spoken word |
| Effect | Memorable and catchy sound patterns | Subtle sound repetition; softer auditory impact |
Understanding Rhyme: Definition and Types
Rhyme is the repetition of similar sounding words, typically at the end of lines in poetry, creating a musical effect and enhancing memorability. Common types of rhyme include perfect rhyme, where the final stressed syllables sound identical (e.g., "cat" and "hat"), and slant rhyme, which involves a close but imperfect sound match (e.g., "shape" and "keep"). Understanding these types helps poets craft rhythm and mood, distinguishing rhyme from assonance that only repeats vowel sounds within words.
What Is Assonance? A Clear Explanation
Assonance is the repetition of vowel sounds within closely placed words to create internal rhyming and enhance musicality in poetry and prose. Unlike rhyme, which involves matching sounds at the end of words, assonance focuses on the similarity of vowel sounds regardless of consonants. This technique enriches language by adding rhythm and mood without the predictability of traditional rhyme schemes.
Key Differences Between Rhyme and Assonance
Rhyme involves the repetition of identical or similar sounds at the end of words, typically in the final syllables, creating a sense of rhythm and musicality in poetry and lyrics. Assonance refers to the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, regardless of their consonant sounds, enhancing the internal harmony of a line without relying on rhyme schemes. Key differences include rhyme's focus on matching end sounds and assonance's use of vowel repetition within lines, both serving distinct purposes in poetic structure and auditory effect.
The Role of Rhyme in Poetry and Lyrics
Rhyme serves as a fundamental tool in poetry and lyrics by creating musicality, enhancing memorability, and establishing structural patterns that guide the audience's emotional response. It reinforces thematic unity and emphasizes key ideas through sound repetition at line endings, often contributing to a poem's rhythmic flow and lyrical appeal. Unlike assonance, which relies on vowel sound repetition within words, rhyme involves precise phonetic matching, making it essential for crafting catchy, resonant verses.
How Assonance Enhances Literary Expression
Assonance enhances literary expression by creating internal vowel sound repetition that adds musicality and rhythm without relying on exact word matches, unlike rhyme which depends on matching end sounds. This technique deepens emotional resonance and mood by subtly linking words through sound patterns, enriching imagery and thematic cohesion. Writers use assonance to evoke feelings and emphasize key ideas, making their language more engaging and memorable.
Examples of Rhyme in Classic and Modern Works
Rhyme features prominently in both classic and modern poetry, enriching texts with melodic resonance and reinforcing thematic elements. In classic literature, Shakespeare's sonnets employ end rhymes like "day" and "way" to enhance lyrical quality, while modern works such as Robert Frost's "Stopping by Woods on a Snowy Evening" use rhymes like "deep" and "keep" to build rhythm and mood. These examples illustrate rhyme's enduring role in structuring verse and deepening emotional impact across literary eras.
Famous Uses of Assonance in Literature
Assonance, the repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words, enhances musicality and emotional impact in literature. Edgar Allan Poe's "The Raven" famously employs assonance with the long "o" sound in phrases like "Once upon a midnight dreary," creating a haunting atmosphere. Similarly, Dylan Thomas's "Do not go gentle into that good night" uses assonance to intensify the poem's urgent, emotional plea.
When to Use Rhyme vs Assonance in Writing
Use rhyme in writing to create musicality and memorability, especially in poetry and songwriting where structured patterns enhance rhythm and emphasis. Employ assonance to subtly unify lines and evoke mood without the predictability of rhyme, making it ideal for prose or free verse that values natural flow. Rhyme suits formal or lyrical works aiming for auditory impact, while assonance supports nuanced sound texture and emotional resonance.
The Impact on Mood and Tone: Rhyme vs Assonance
Rhyme creates a sense of harmony and closure, often producing a rhythmic and memorable mood that reinforces a poem's tone. Assonance focuses on vowel sound repetition, crafting a subtler, more fluid atmosphere that can evoke introspection or emotional complexity. The distinct auditory patterns of rhyme and assonance influence the overall impact on mood, shaping how readers emotionally connect with the text.
Tips for Incorporating Rhyme and Assonance Effectively
Incorporate rhyme and assonance by placing rhyming words at line ends to enhance musicality and using assonance within lines for subtle internal harmony. Employ varied rhyme schemes like ABAB or AABB to maintain reader interest and experiment with vowel repetition to create mood or emphasis. Balance these devices to avoid predictability while enriching the lyrical quality of your writing.
Rhyme Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com