Adaptation is the process by which organisms adjust to changes in their environment to enhance survival and reproduction. This biological mechanism involves genetic, physiological, and behavioral modifications that improve the fit between species and their surroundings. Discover how adaptation shapes life and why understanding it is essential for your knowledge of evolution in the full article.
Table of Comparison
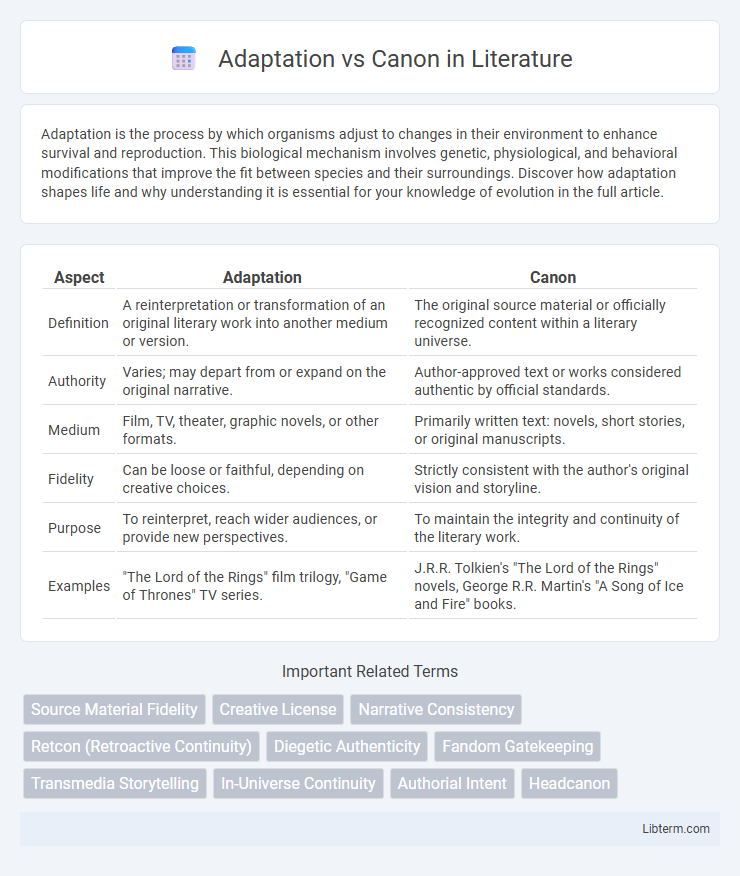
| Aspect | Adaptation | Canon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A reinterpretation or transformation of an original literary work into another medium or version. | The original source material or officially recognized content within a literary universe. |
| Authority | Varies; may depart from or expand on the original narrative. | Author-approved text or works considered authentic by official standards. |
| Medium | Film, TV, theater, graphic novels, or other formats. | Primarily written text: novels, short stories, or original manuscripts. |
| Fidelity | Can be loose or faithful, depending on creative choices. | Strictly consistent with the author's original vision and storyline. |
| Purpose | To reinterpret, reach wider audiences, or provide new perspectives. | To maintain the integrity and continuity of the literary work. |
| Examples | "The Lord of the Rings" film trilogy, "Game of Thrones" TV series. | J.R.R. Tolkien's "The Lord of the Rings" novels, George R.R. Martin's "A Song of Ice and Fire" books. |
Understanding Adaptation and Canon
Adaptation refers to the process of transforming an original work, such as a book or film, into a new format, often involving creative changes to fit the new medium's constraints and audience expectations. Canon represents the original, authoritative source material that defines the official storyline, characters, and world-building elements within a fictional universe. Understanding the distinction between adaptation and canon is essential for analyzing how narrative elements evolve and how fan interpretations relate to the source material.
The Origins of Canon in Storytelling
The origins of canon in storytelling trace back to ancient oral traditions where certain narratives were preserved and transmitted as authoritative versions within cultural or religious communities. Canon establishes a fixed reference point that distinguishes between core texts and derivative adaptations, ensuring continuity and coherence in the collective memory of a story. Adaptations, while creatively transformative, often negotiate with canonical elements to either reinforce or reinterpret the foundational narrative.
Why Adaptations Differ from the Original Canon
Adaptations differ from the original canon due to creative interpretation, audience expectations, and medium constraints. Changes in plot, character development, or setting often cater to new formats like film or television, which require pacing and visual storytelling adjustments. Licensing rights and target demographic shifts also influence deviations in adapted works.
Challenges in Balancing Fidelity and Creativity
Adaptation vs canon presents challenges in balancing fidelity and creativity where maintaining the original story's core elements often restricts innovative interpretations. Creators must navigate preserving character integrity and plot accuracy while injecting fresh perspectives that resonate with modern audiences. Striking this equilibrium requires careful consideration of fan expectations, narrative coherence, and artistic expression to avoid alienating loyal followers or stifling creative potential.
The Role of Audience Expectations
Audience expectations significantly influence the tension between adaptation and canon, as fans often anticipate fidelity to the original source material while craving innovative storytelling. Adaptations must balance preserving iconic elements of the canon with creative liberties that resonate with contemporary audiences. Understanding these expectations enhances the adaptation's reception and cultural impact, ensuring it honors the original work's essence without alienating fans.
Adaptation: Reinterpreting the Source Material
Adaptation involves reinterpreting the source material by transforming its themes, characters, and plot to fit new contexts or mediums, often broadening its appeal or relevance. This dynamic process allows creative freedom to explore different narrative perspectives while maintaining a connection to the original work's essence. Adaptations can result in innovative storytelling that resonates with contemporary audiences without being constrained by strict adherence to the canon.
Canon’s Influence on Franchise Continuity
Canon serves as the authoritative foundation that maintains coherence and consistency across a franchise, ensuring character development, plot points, and world-building remain intact. Adaptations often introduce variations or reinterpretations, but adherence to canon preserves narrative integrity and continuity, which is crucial for long-term fan engagement and franchise expansion. The influence of canon dictates which elements adaptations must follow, reinforcing established lore and preventing contradictions within the franchise universe.
Notable Examples of Adaptation Divergence
Notable examples of adaptation divergence include Ridley Scott's *Blade Runner*, which significantly altered Philip K. Dick's *Do Androids Dream of Electric Sheep?* by emphasizing dystopian aesthetics and philosophical questions about identity over the novel's plot details. The *Game of Thrones* TV series diverged from George R.R. Martin's *A Song of Ice and Fire* by introducing original character arcs and an accelerated ending due to the source material's incomplete status. Similarly, Peter Jackson's *The Lord of the Rings* films condense and rearrange key events from J.R.R. Tolkien's books to enhance cinematic pacing and visual storytelling, resulting in notable plot and character changes.
The Debate: Purist vs. Revisionist Viewpoints
The debate between purist and revisionist viewpoints centers on fidelity to the source material versus creative reinterpretation in adaptations, with purists emphasizing strict adherence to canonical elements from original works. Revisionists argue for innovative changes that reflect contemporary contexts, often altering characters, settings, or plotlines to resonate with new audiences. This ongoing discourse highlights the tension between preserving literary integrity and embracing artistic evolution in adaptation practice.
Future Trends in Adaptation and Canon
Future trends in adaptation show a growing emphasis on interactive and immersive technologies such as virtual reality and augmented reality, reshaping canonical narratives into multidimensional experiences. The canon of literature and media will increasingly integrate cross-platform storytelling, blending traditional texts with digital formats to engage diverse audiences. Adaptations are expected to prioritize inclusivity and cultural reinterpretation, challenging and expanding established canonical boundaries to reflect contemporary societal values.
Adaptation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com