Dialect reflects the unique characteristics of language spoken in specific regions, revealing cultural identity and social history. Variations in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar shape the way communities communicate and connect through their distinct linguistic patterns. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how dialect influences communication and culture.
Table of Comparison
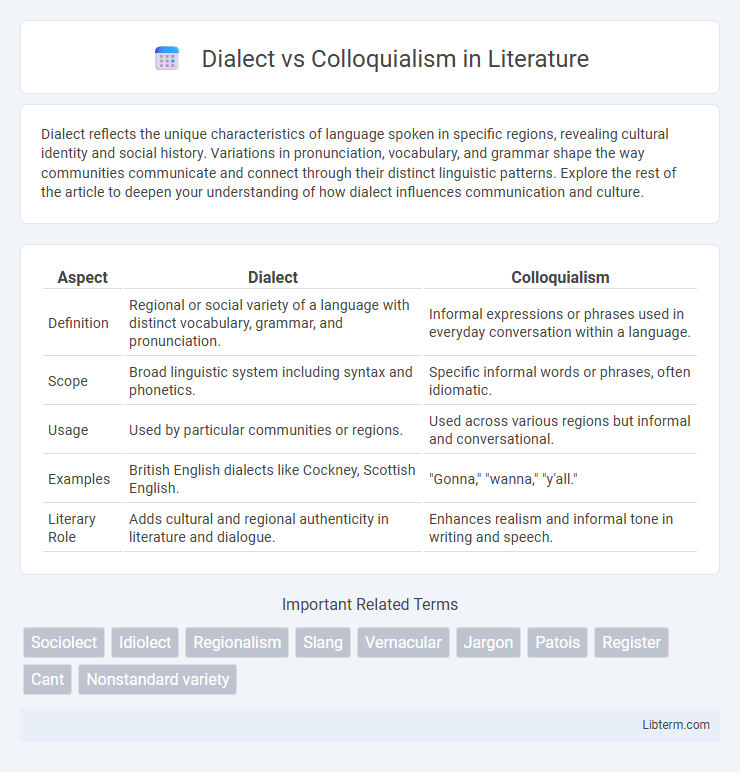
| Aspect | Dialect | Colloquialism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regional or social variety of a language with distinct vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. | Informal expressions or phrases used in everyday conversation within a language. |
| Scope | Broad linguistic system including syntax and phonetics. | Specific informal words or phrases, often idiomatic. |
| Usage | Used by particular communities or regions. | Used across various regions but informal and conversational. |
| Examples | British English dialects like Cockney, Scottish English. | "Gonna," "wanna," "y'all." |
| Literary Role | Adds cultural and regional authenticity in literature and dialogue. | Enhances realism and informal tone in writing and speech. |
Defining Dialect: Language Variation Explained
Dialect refers to a regional or social variety of a language distinguished by unique vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation patterns. It reflects language variation shaped by geographical, cultural, and social factors, representing the full linguistic system used within a particular community. Unlike colloquialism, which involves informal expressions or slang, dialect encompasses broader structural differences in language use.
What Is Colloquialism? Everyday Speech Unpacked
Colloquialism refers to informal language or expressions used in everyday speech that reflect casual conversation rather than formal writing. These phrases or words often reveal cultural nuances and regional influences but do not necessarily indicate distinct linguistic structures like a dialect does. Understanding colloquialism enhances communication by capturing the natural, familiar tone people use in daily interactions.
Key Differences Between Dialect and Colloquialism
Dialects are regional or social varieties of a language characterized by distinct vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation, while colloquialisms are informal expressions or phrases used within a dialect or language. Dialects encompass broader linguistic features and can differ significantly between communities, whereas colloquialisms are not systematic and often limited to conversational language. Key differences include scope--dialects affect the entire language system, and colloquialisms pertain mainly to informal speech patterns.
Historical Roots of Dialects in Language
Dialects originate from historical linguistic variations shaped by geographic, social, and cultural factors over centuries, reflecting regional identities and community interactions. These linguistic forms preserve archaic vocabulary, phonetic shifts, and syntax unique to specific locales, tracing back to migration patterns, invasions, and isolation. Understanding the historical roots of dialects illuminates the evolution of language diversity and its role in cultural heritage.
The Role of Colloquialisms in Communication
Colloquialisms play a vital role in communication by reflecting informal language use that fosters relatability and social bonding among speakers within specific communities. Unlike dialects, which encompass broader linguistic variations including grammar and pronunciation, colloquialisms primarily involve slang and idiomatic expressions that add color and cultural context to everyday conversations. Recognizing colloquialisms enhances understanding of local speech patterns and improves effective, natural interaction in both spoken and written communication.
Geographic Influence on Dialects and Colloquial Speech
Geographic influence significantly shapes dialects, resulting in distinct vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar tied to specific regions, such as the Southern American English dialect's unique vowel shifts. Colloquial speech varies within these dialects, reflecting local customs and social interactions, like the use of "y'all" in the Southern United States as a familiar second-person plural pronoun. Regional isolation and community interaction reinforce these linguistic features, embedding geographic identity within both dialects and colloquial expressions.
Examples of Dialects vs. Colloquialisms in English
Dialect refers to regional or social varieties of a language distinguished by vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation, such as the Cockney dialect in London with unique terms like "apples and pears" meaning stairs. Colloquialisms are informal expressions or phrases used in everyday conversation across various dialects, like "gonna" for "going to" or "wanna" for "want to." While a dialect encompasses a broader linguistic system, colloquialisms are specific informal words or phrases within those dialects or the standard language.
Cultural Significance of Dialect and Colloquialism
Dialect reflects the unique linguistic traits of a specific region or social group, preserving cultural heritage and identity through distinctive vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar. Colloquialisms capture informal, everyday language and provide insight into the values, humor, and social norms of a community. Understanding dialects and colloquialisms enriches cross-cultural communication and promotes appreciation of cultural diversity within language.
Dialect and Colloquialism in Literature and Media
Dialect and colloquialism shape authenticity and cultural identity in literature and media by reflecting regional speech patterns and informal language use. Dialects often appear in character dialogues to convey social background and geographic roots, enhancing the narrative's realism and depth. Colloquialisms add relatable, conversational tone, making characters more believable and engaging for diverse audiences.
Impact on Understanding and Miscommunication
Dialect variations often influence pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar, which can lead to challenges in comprehension between speakers from different regions. Colloquialisms, being informal expressions unique to specific groups, may cause misunderstanding when used outside their cultural context. Both dialects and colloquialisms significantly impact effective communication, increasing the risk of misinterpretation in diverse linguistic settings.
Dialect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com