A well-curated collection showcases unique items that reflect your personality and style, making your space truly distinctive. Choosing pieces with meaning and quality enhances the overall aesthetic and value of your collection. Explore the rest of the article to discover expert tips on building and maintaining a remarkable collection.
Table of Comparison
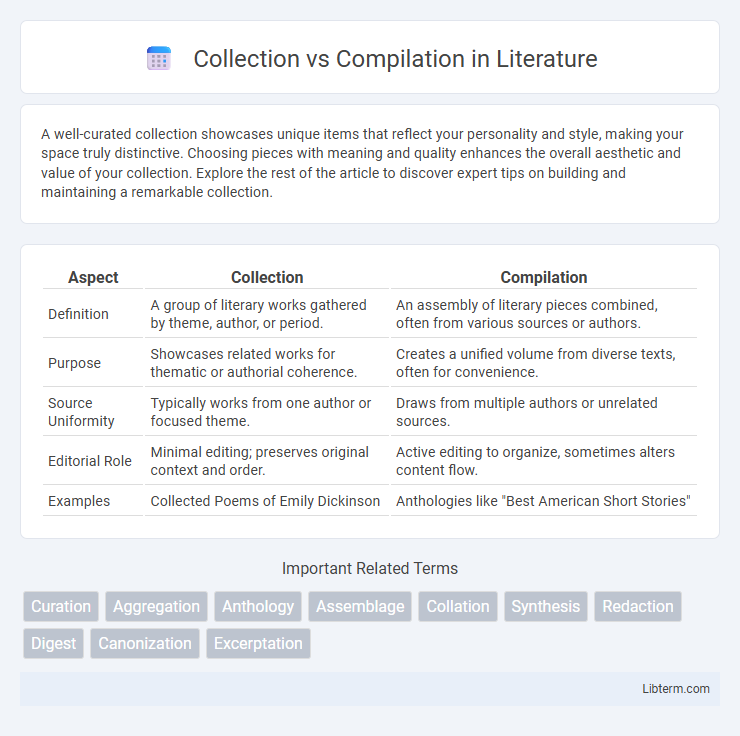
| Aspect | Collection | Compilation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A group of literary works gathered by theme, author, or period. | An assembly of literary pieces combined, often from various sources or authors. |
| Purpose | Showcases related works for thematic or authorial coherence. | Creates a unified volume from diverse texts, often for convenience. |
| Source Uniformity | Typically works from one author or focused theme. | Draws from multiple authors or unrelated sources. |
| Editorial Role | Minimal editing; preserves original context and order. | Active editing to organize, sometimes alters content flow. |
| Examples | Collected Poems of Emily Dickinson | Anthologies like "Best American Short Stories" |
Introduction to Collection and Compilation
A collection is a curated group of related works or items, typically gathered based on a shared theme or author, enhancing accessibility and organization. Compilation involves assembling various pieces, often from multiple sources, into a single volume or dataset, emphasizing completeness and variety. Both methods serve to aggregate content but differ in purpose and scope, with collections favoring thematic unity and compilations prioritizing comprehensive inclusion.
Defining Collection
A collection is a curated group of related items gathered based on specific criteria, such as theme, author, or genre, emphasizing totality and cohesion. Unlike a compilation, which often assembles disparate elements primarily for convenience or accessibility, a collection highlights intentional organization and significance of each item within the set. Defining a collection involves recognizing its purpose to represent a comprehensive scope or a thematic unity rather than just aggregation.
Understanding Compilation
Compilation refers to the process of gathering and organizing diverse pieces of content or data into a single, cohesive unit, often with a specific theme or purpose. Unlike a collection, which may simply aggregate items without modification, a compilation typically involves selecting, editing, and arranging the materials to create new value or insight. Understanding compilation is essential for industries like publishing, music, and software development, where curated assemblies enhance accessibility and usability.
Key Differences Between Collection and Compilation
A collection consists of individual works or items grouped together without significant modification, typically preserving their original form and authorship, whereas a compilation involves selecting, organizing, and sometimes editing or transforming those items into a new, unified work. Key differences lie in copyright treatment: collections protect only the selection or arrangement, while compilations can receive protection for new creative expression in the compilation process. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for determining intellectual property rights and obligations in publishing and content creation.
Purposes of Collection
The purpose of a collection is to systematically gather related items for easy access, preservation, or thematic organization, often serving educational, research, or archival needs. Collections aim to provide a cohesive grouping that facilitates study, comparison, or enjoyment by users interested in specific subjects. This contrasts with compilations, which typically focus on assembling disparate materials into a new, unified work for presentation or publication.
Purposes of Compilation
A compilation serves the purpose of organizing and presenting pre-existing works or data to create a cohesive resource, often aimed at facilitating easy access and reference. Unlike a collection, a compilation involves selecting, editing, and sometimes annotating items to highlight specific themes or insights. Compilations are critical in academic, legal, and editorial contexts where structured and comprehensive aggregation enhances understanding and usability.
Legal Implications: Collection vs Compilation
In legal contexts, a collection refers to an assembly of pre-existing works without significant originality, often lacking separate copyright protection. A compilation, however, involves the selective and creative arrangement or coordination of materials, granting it potential copyright protection as a derivative work. Courts evaluate the originality in the selection, coordination, or arrangement to determine legal rights distinguishing collections from compilations.
Real-World Examples of Collections and Compilations
Collections such as the "Harry Potter" series by J.K. Rowling group individual novels into a unified set centered on a common theme or storyline, offering a cohesive reading experience. Compilations like the "Now That's What I Call Music!" albums assemble hit songs from various artists and genres, creating a diverse but thematically linked playlist. In contrast, museum collections organize artifacts from specific historical periods or cultures, while art compilations combine diverse works from multiple creators into a single exhibition catalog.
How to Choose: Collection or Compilation?
Choosing between a collection and a compilation depends on the specific context and purpose of the content aggregation. A collection typically refers to a curated set of works or items grouped by a common theme or author, ideal for focused exploration and in-depth analysis. A compilation combines diverse materials from multiple sources to provide a broad overview or comprehensive resource, making it suitable for general reference or comparative study.
Conclusion: Collection vs Compilation
A collection consists of discrete, independently created works brought together without significant modification, while a compilation involves selecting, organizing, and often editing materials to create a new, cohesive work. Legal protections differ as collections typically maintain individual copyrights for each item, whereas compilations may enjoy copyright protection for the originality in selection and arrangement. Understanding these distinctions is essential for creators and users to navigate intellectual property rights effectively.
Collection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com