Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method used to identify, analyze, and report patterns within data, helping to uncover core themes that provide insight into participants' experiences and perspectives. This approach allows you to systematically organize and interpret complex data, revealing meaningful connections that inform your understanding of the subject. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to effectively apply thematic analysis in your research.
Table of Comparison
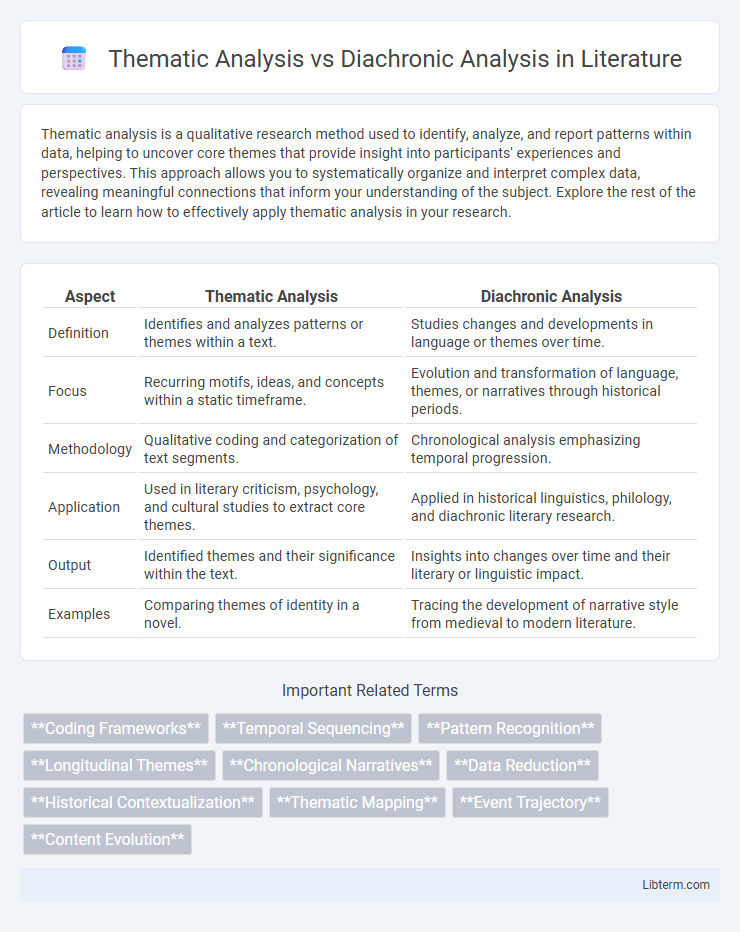
| Aspect | Thematic Analysis | Diachronic Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifies and analyzes patterns or themes within a text. | Studies changes and developments in language or themes over time. |
| Focus | Recurring motifs, ideas, and concepts within a static timeframe. | Evolution and transformation of language, themes, or narratives through historical periods. |
| Methodology | Qualitative coding and categorization of text segments. | Chronological analysis emphasizing temporal progression. |
| Application | Used in literary criticism, psychology, and cultural studies to extract core themes. | Applied in historical linguistics, philology, and diachronic literary research. |
| Output | Identified themes and their significance within the text. | Insights into changes over time and their literary or linguistic impact. |
| Examples | Comparing themes of identity in a novel. | Tracing the development of narrative style from medieval to modern literature. |
Introduction to Thematic and Diachronic Analysis
Thematic Analysis identifies and interprets patterns or themes within qualitative data, emphasizing the meaning behind recurring concepts. Diachronic Analysis examines how phenomena, language, or data evolve over time, focusing on temporal changes and historical development. Together, these methods offer complementary insights by revealing both the content structure and its progression across different periods.
Defining Thematic Analysis
Thematic Analysis is a qualitative research method used to identify, analyze, and report patterns or themes within data, providing a rich and detailed account of the dataset. It involves coding data systematically, categorizing related codes into themes that capture important aspects relevant to the research question. This approach emphasizes understanding the meanings and insights embedded in textual data, contrasting with Diachronic Analysis, which examines change and development across time.
Understanding Diachronic Analysis
Diachronic Analysis examines changes and developments in language, culture, or texts over time, emphasizing temporal progression and historical context. This method contrasts with Thematic Analysis, which identifies and analyzes recurring themes within data regardless of temporal order. Understanding Diachronic Analysis involves recognizing how shifts in meaning, usage, or structure occur sequentially, providing insights into transformation and continuity across periods.
Key Differences Between Thematic and Diachronic Analysis
Thematic analysis identifies patterns and themes within qualitative data to interpret meaning across a dataset, emphasizing content and recurring concepts. In contrast, diachronic analysis examines changes and developments over time, focusing on temporal sequences and evolution. Key differences include thematic analysis's cross-sectional approach versus diachronic analysis's longitudinal perspective, highlighting variation in emphasis on content versus historical progression.
Methodologies in Thematic Analysis
Thematic Analysis employs a systematic approach to identify, analyze, and report patterns or themes within qualitative data, emphasizing coding phases such as familiarization, generating initial codes, searching for themes, reviewing themes, defining and naming themes, and producing the final report. Researchers use either inductive or deductive coding strategies to extract meaningful themes that capture the essence of the dataset, often supported by software tools like NVivo or ATLAS.ti for data organization and retrieval. This methodology contrasts with Diachronic Analysis, which focuses on the temporal evolution of language or phenomena, analyzing changes over time rather than thematic patterns within static datasets.
Techniques Used in Diachronic Analysis
Diachronic analysis employs techniques such as longitudinal data collection, time-series analysis, and historical context evaluation to study changes and developments over time in linguistic, cultural, or social phenomena. This method contrasts with thematic analysis, which focuses on identifying patterns and themes within a dataset at a single point in time. Techniques in diachronic analysis often include comparative text analysis across different time periods and tracking linguistic evolution or cultural shifts through archival records and chronological datasets.
Applications of Thematic Analysis in Research
Thematic Analysis is widely applied in qualitative research to identify, analyze, and report patterns or themes within data, enabling researchers to interpret complex textual information across disciplines such as psychology, sociology, and education. This method is particularly effective for exploring participants' experiences, perceptions, and social phenomena by providing a flexible yet rigorous framework for coding and categorizing data. Unlike Diachronic Analysis, which examines changes over time, Thematic Analysis emphasizes the extraction of significant themes within a single time frame, facilitating the synthesis of rich, detailed insights from interviews, focus groups, and archival materials.
Applications of Diachronic Analysis in Research
Diachronic analysis examines changes and developments in data, language, or phenomena over time, making it essential for historical linguistics, sociocultural research, and evolutionary studies. Researchers apply diachronic analysis to track linguistic shifts, cultural transformations, and technological advancements by comparing data across different time periods. This approach uncovers temporal patterns, facilitating deeper understanding of progression and causality in various academic fields.
Strengths and Limitations of Both Approaches
Thematic Analysis excels in identifying patterns and themes across qualitative data, providing rich, detailed insights and flexibility across research contexts, but it may overlook temporal changes and sequence in data. Diachronic Analysis focuses on the evolution and development of phenomena over time, offering a dynamic perspective on change and historical context, though it can be time-consuming and less effective for identifying broader thematic patterns. Combining both approaches can offset their limitations by addressing thematic content while capturing temporal dynamics.
Choosing the Right Analytical Method for Your Study
Selecting between thematic analysis and diachronic analysis depends on your study's focus and research questions. Thematic analysis is ideal for identifying patterns and themes within qualitative data to explore meanings and experiences, while diachronic analysis examines changes and developments over time, emphasizing temporal evolution. Researchers should prioritize thematic analysis for understanding static concepts and diachronic analysis for studies emphasizing historical progression or transformation.
Thematic Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com