Rhetoric is the art of persuasive communication that strategically uses language to influence an audience's thoughts and emotions. Mastering rhetoric enhances your ability to craft compelling arguments and engage listeners effectively. Explore the rest of the article to discover techniques that will sharpen your rhetorical skills.
Table of Comparison
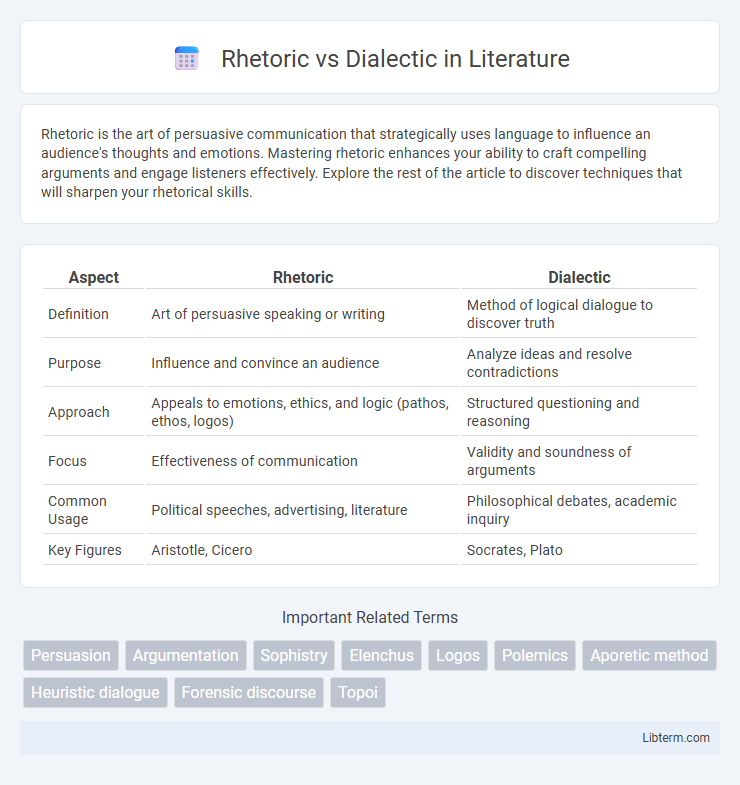
| Aspect | Rhetoric | Dialectic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art of persuasive speaking or writing | Method of logical dialogue to discover truth |
| Purpose | Influence and convince an audience | Analyze ideas and resolve contradictions |
| Approach | Appeals to emotions, ethics, and logic (pathos, ethos, logos) | Structured questioning and reasoning |
| Focus | Effectiveness of communication | Validity and soundness of arguments |
| Common Usage | Political speeches, advertising, literature | Philosophical debates, academic inquiry |
| Key Figures | Aristotle, Cicero | Socrates, Plato |
Introduction to Rhetoric and Dialectic
Rhetoric and dialectic serve distinct functions in persuasive communication, with rhetoric focusing on appeal to emotions and audience persuasion, while dialectic emphasizes logical reasoning and truth-seeking through structured dialogue. Aristotle's "Introduction to Rhetoric" identifies three artistic proofs--ethos, pathos, and logos--integral to effective persuasion. Dialectic, rooted in Socratic dialogue, systematically examines conflicting ideas to arrive at knowledge or resolution through question and answer exchanges.
Defining Rhetoric: Techniques and Purposes
Rhetoric involves the art of persuasive communication through strategic use of language, emphasizing ethos, pathos, and logos to influence audiences effectively. Techniques include rhetorical questions, repetition, and metaphor, crafted to appeal emotionally and ethically while structuring logical arguments. Its primary purpose is to shape opinions and motivate action in public speaking, advertising, and political discourse.
Understanding Dialectic: Methods and Goals
Dialectic is a structured method of dialogue aimed at discovering truth through reasoned arguments and critical questioning, often attributed to Socratic techniques. Its core goal is to achieve a deeper understanding and resolve contradictions by systematically examining beliefs and assumptions. Unlike rhetoric, which seeks to persuade an audience, dialectic prioritizes logical rigor and collaborative inquiry to refine concepts and uncover underlying principles.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Rhetoric originated in ancient Greece as the art of persuasive speaking, primarily developed by figures like Aristotle, who categorized it as a means to influence public opinion and decision-making. Dialectic, rooted in Socratic methods, focused on logical dialogue and critical questioning to discover truth through reasoned argumentation. Over time, rhetoric evolved into a tool for political and legal persuasion, while dialectic became foundational in philosophy and the scientific method.
Key Differences Between Rhetoric and Dialectic
Rhetoric focuses on persuasion through emotional appeal and stylistic techniques, aiming to influence an audience's beliefs or actions, while dialectic centers on logical reasoning and structured dialogue to uncover truth or resolve contradictions. Rhetoric often employs persuasive language and appeals to ethos, pathos, and logos, whereas dialectic relies on rigorous argumentation and questioning to refine ideas. The key difference lies in rhetoric's goal to convince and dialectic's pursuit of reaching irrefutable conclusions through critical examination.
Applications in Modern Communication
Rhetoric and dialectic serve distinct yet complementary roles in modern communication, where rhetoric emphasizes persuasive techniques tailored for public speaking, marketing, and media to influence audiences emotionally and cognitively. Dialectic underpins structured debate, critical thinking, and problem-solving frameworks, fostering deeper understanding through reasoned dialogue and examination of opposing viewpoints. Both methods enhance effective communication in fields such as law, politics, and education by balancing persuasion with logical analysis.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Each Approach
Rhetoric excels in persuasion by appealing to emotions and audience values, making it effective for influencing public opinion but risks prioritizing style over truth. Dialectic emphasizes logical reasoning and structured dialogue, fostering critical thinking and clarity but can be less accessible and slower in reaching consensus. Each method complements the other; rhetoric energizes and motivates, while dialectic ensures rigor and depth in argumentation.
Rhetoric and Dialectic in Education
Rhetoric in education emphasizes persuasive communication, critical for developing students' public speaking and argumentation skills. Dialectic fosters structured dialogue and inquiry, promoting deeper understanding and analytical thinking through reasoned debate. Both methods complement each other by enhancing cognitive abilities and effective expression in diverse learning environments.
Interplay and Overlap in Discourse
Rhetoric and dialectic intersect in discourse through their mutual aim of persuasion, where rhetoric emphasizes emotional appeal and audience engagement while dialectic prioritizes logical argumentation and critical questioning. Both methods employ techniques such as questioning, refutation, and structured reasoning to shape understanding and influence conclusions. This interplay allows speakers to adapt strategies for effective communication, blending persuasive rhetoric with dialectical analysis to enhance clarity and impact.
Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Communication
Effective communication requires selecting rhetoric when the goal is to persuade and appeal to emotions, leveraging storytelling and stylistic devices to influence an audience. Dialectic suits structured dialogue and critical reasoning, emphasizing logical argumentation and systematic questioning to uncover truth and resolve disagreements. Understanding the context and desired outcome guides the choice between rhetoric's persuasive power and dialectic's analytical clarity for impactful interactions.
Rhetoric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com