Satirical writing uses humor, irony, and exaggeration to expose and criticize societal flaws or human vices. This style often challenges norms and provokes thought by highlighting absurdities in politics, culture, or everyday life. Discover how mastering satire can sharpen your wit and deepen your understanding by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
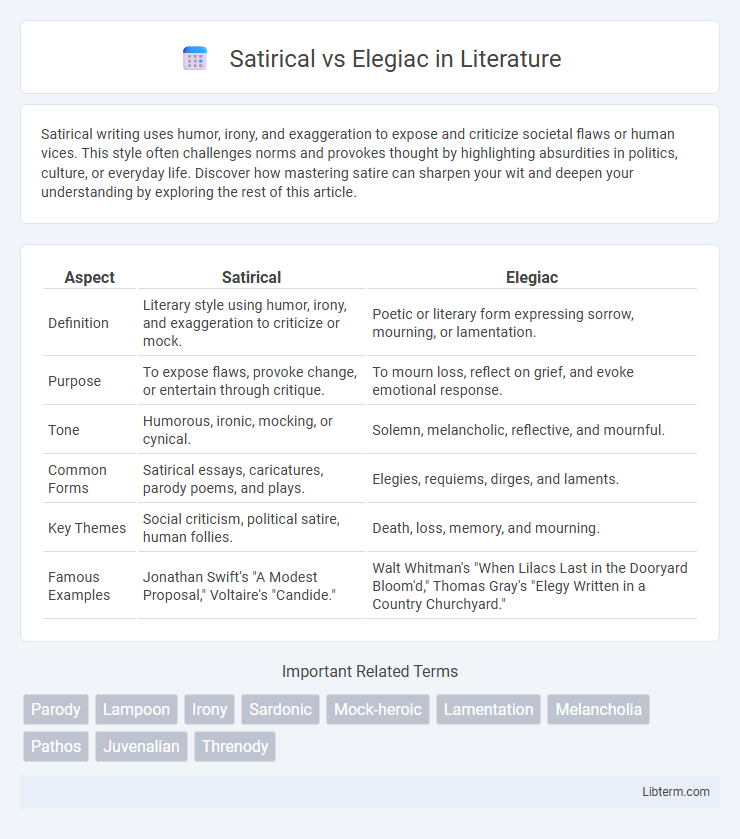
| Aspect | Satirical | Elegiac |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary style using humor, irony, and exaggeration to criticize or mock. | Poetic or literary form expressing sorrow, mourning, or lamentation. |
| Purpose | To expose flaws, provoke change, or entertain through critique. | To mourn loss, reflect on grief, and evoke emotional response. |
| Tone | Humorous, ironic, mocking, or cynical. | Solemn, melancholic, reflective, and mournful. |
| Common Forms | Satirical essays, caricatures, parody poems, and plays. | Elegies, requiems, dirges, and laments. |
| Key Themes | Social criticism, political satire, human follies. | Death, loss, memory, and mourning. |
| Famous Examples | Jonathan Swift's "A Modest Proposal," Voltaire's "Candide." | Walt Whitman's "When Lilacs Last in the Dooryard Bloom'd," Thomas Gray's "Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard." |
Defining Satirical and Elegiac Tones
Satirical tone employs humor, irony, and exaggeration to criticize or mock human vices and societal flaws, aiming to provoke change or highlight absurdities. Elegiac tone conveys a somber, reflective mood often associated with mourning or loss, expressing sorrow and lamentation in a melancholic style. Both tones serve distinct emotional and rhetorical purposes, shaping the reader's response through their unique stylistic elements.
Historical Origins of Satire and Elegy
Satire originated in ancient Rome as a literary genre aimed at criticizing societal flaws and human vices through humor and irony, with early practitioners like Horace and Juvenal shaping its form. Elegy, rooted in ancient Greek lyric poetry, began as a mournful expression of loss and lamentation, often performed with a rhythmic couplet known as the elegiac couplet. Both forms evolved to reflect cultural attitudes: satire targeting public morality and political corruption, while elegy centered on personal grief and reflection.
Key Characteristics of Satirical Writing
Satirical writing employs humor, irony, and exaggeration to criticize or mock societal flaws, aiming to provoke thought and encourage change. It often targets politics, social norms, or human vices with wit and sarcasm, using devices such as parody and caricature to highlight absurdities. Unlike elegiac writing, which expresses sorrow or mourning, satire is intentionally provocative and engaging, blending entertainment with sharp social commentary.
Key Elements of Elegiac Expression
Elegiac expression features a somber tone, reflective mood, and themes of loss, mourning, or longing, often conveyed through rhythmic and melancholic language. Key elements include sorrowful imagery, personal or universal grief, and a focus on memory or lamentation. Contrasting with satirical works that critique through humor and irony, elegiac texts evoke empathy and contemplation.
Satirical Devices and Techniques
Satirical literature employs devices such as irony, parody, exaggeration, and wit to criticize and expose societal flaws, often using humor to provoke reflection. Techniques like understatement, sarcasm, and caricature highlight contradictions and absurdities in human behavior or institutions. These tools enable satire to engage readers by blending entertainment with incisive social commentary.
The Emotional Impact of Elegiac Works
Elegiac works evoke profound feelings of sorrow and reflection by mourning loss and celebrating memories, creating a deeply emotional resonance with readers. Unlike satirical texts that provoke humor or criticism through irony and wit, elegiac poetry and prose emphasize solemnity and introspection, fostering empathy and catharsis. This emotional impact strengthens the connection between the audience and the subject, often leading to a shared experience of grief and remembrance.
Prominent Satirists and Elegists
Prominent satirists such as Jonathan Swift and Mark Twain employed wit and irony to critique societal flaws, using humor as a powerful tool for social commentary. Elegists like John Keats and W. H. Auden are renowned for their poignant, mournful poetry that reflects on loss and mortality with deep emotional resonance. The distinction lies in satire's aim to provoke change through ridicule, while elegy solemnly honors and mourns the deceased.
Satirical vs Elegiac: Purpose and Audience
Satirical literature aims to criticize and provoke change by using humor, irony, and exaggeration, targeting audiences who appreciate wit and social commentary. Elegiac works express sorrow and mourning, often commemorating loss, appealing to readers seeking emotional reflection and catharsis. The purpose of satire is to challenge societal flaws, while elegy focuses on honoring memories and evoking empathy.
Blending Satirical and Elegiac Styles
Blending satirical and elegiac styles creates a powerful literary contrast where irony and humor intertwine with solemn reflection, enhancing emotional depth and intellectual engagement. Satirical elements critique societal flaws and human follies through wit, while elegiac tones evoke mourning and nostalgia for loss, collectively enriching narrative complexity. This fusion allows writers to address serious themes with both levity and pathos, resonating profoundly with readers by balancing critique with compassion.
Modern Relevance of Satirical and Elegiac Forms
Satirical literature in modern media remains a powerful tool for social critique, using humor and irony to expose flaws in politics, culture, and human behavior. Elegiac forms continue to resonate deeply by expressing sorrow and reflection in response to contemporary losses, such as climate change and social justice struggles. Both genres adapt dynamically, shaping public discourse through emotional engagement and critical perspective in 21st-century art and communication.
Satirical Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com