Prosopopeia is a powerful literary device that gives human qualities to inanimate objects, animals, or abstract ideas, enhancing emotional connection and vivid imagery. By personifying elements within a narrative, writers enable readers to engage more deeply and intuitively with the text. Explore the article to discover how prosopopeia can transform your storytelling and captivate your audience.
Table of Comparison
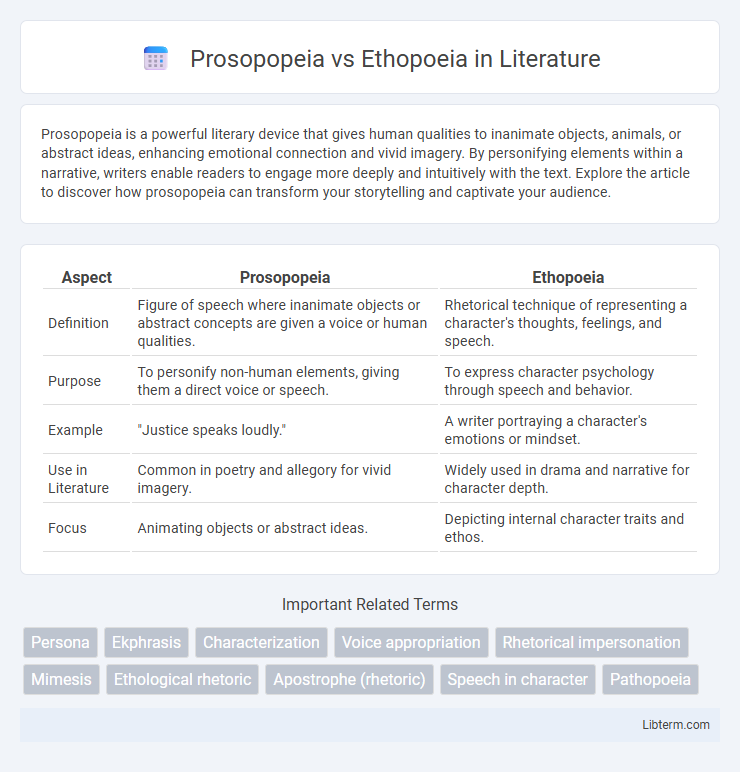
| Aspect | Prosopopeia | Ethopoeia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Figure of speech where inanimate objects or abstract concepts are given a voice or human qualities. | Rhetorical technique of representing a character's thoughts, feelings, and speech. |
| Purpose | To personify non-human elements, giving them a direct voice or speech. | To express character psychology through speech and behavior. |
| Example | "Justice speaks loudly." | A writer portraying a character's emotions or mindset. |
| Use in Literature | Common in poetry and allegory for vivid imagery. | Widely used in drama and narrative for character depth. |
| Focus | Animating objects or abstract ideas. | Depicting internal character traits and ethos. |
Introduction to Prosopopeia and Ethopoeia
Prosopopeia is a rhetorical device that attributes human characteristics or voices to abstract concepts, inanimate objects, or absent persons, enabling vivid and imaginative expression. Ethopoeia involves the imitation or representation of another person's character, speech, or behavior, often used to convey emotions or personalities authentically. Both techniques enhance narrative and persuasive effectiveness by giving life to intangible ideas or embodying individual identities in literature and speech.
Defining Prosopopeia: Origins and Usage
Prosopopeia is a rhetorical device originating from ancient Greek literature, where an absent or imaginary person, or a thing, is given a voice to speak or act, often to convey a message or evoke emotion. Rooted in classical speeches and poetry, prosopopeia allows authors to animate abstract concepts, deceased individuals, or inanimate objects, enhancing narrative depth and emotional resonance. Its usage spans various genres, including epic poetry, drama, and oratory, serving as a powerful tool to personify and dramatize ideas or entities.
Ethopoeia: Meaning and Historical Context
Ethopoeia refers to the rhetorical practice of impersonating or expressing the thoughts, feelings, and character of another person, often to persuade or illustrate a point in speech or writing. Rooted in classical Greek and Roman rhetoric, Ethopoeia was used by orators like Cicero and Demosthenes to embody an opponent's voice or adopt a character's persona, enhancing emotional appeal and credibility. Unlike Prosopopeia, which involves speaking as an absent or imaginary figure, Ethopoeia emphasizes adopting the moral and psychological traits of a specific individual for argumentative effect.
Key Differences Between Prosopopeia and Ethopoeia
Prosopopeia involves giving voice or speech to inanimate objects, abstract concepts, or absent/deceased persons, creating vivid personification in literature. Ethopoeia focuses specifically on imitating or representing the character, emotions, and speech of a living person, often used in rhetoric and drama to depict personality traits. The key difference lies in prosopopeia's broad application to non-living entities versus ethopoeia's targeted impersonation of individual human behavior and speech.
Rhetorical Functions of Prosopopeia
Prosopopeia functions primarily as a rhetorical device that personifies abstract concepts, inanimate objects, or absent individuals, enabling speakers and writers to imbue their arguments with emotional appeal and vivid imagery. This technique enhances persuasion by giving voice to entities that cannot speak for themselves, thereby creating a stronger emotional connection and emphasizing ethical or moral points. Unlike Ethopoeia, which involves adopting the character or emotions of a specific person to argue persuasively, Prosopopeia operates through imaginative personification to animate ideas and evoke empathy.
Ethopoeia in Classical and Modern Rhetoric
Ethopoeia, a rhetorical technique involving the impersonation of a character's thoughts and emotions, was extensively used in Classical rhetoric to create vivid and persuasive speeches by embodying the ethos of another person. In modern rhetoric, Ethopoeia adapts to digital and multimedia contexts, enhancing narrative engagement through personalized storytelling and character-driven discourse. While Prosopopeia emphasizes speaking as a personified object or abstract concept, Ethopoeia centers on reconstructing a specific individual's internal perspective and moral character to influence audience perception.
Literary Examples of Prosopopeia
Prosopopeia is a rhetorical device where an abstract concept, inanimate object, or absent person is given a human voice, as seen in Shakespeare's "Julius Caesar," where Caesar's ghost speaks to Brutus. This technique personifies entities to convey deeper emotional resonance, contrasting with Ethopoeia, which involves impersonating a specific character's traits or speech to express their thoughts and feelings, such as in Homer's epics. Prosopopeia enhances literary works by animating ideas, like Death or Justice, making intangible themes more vivid and engaging for readers.
Ethopoeia in Character Development
Ethopoeia plays a crucial role in character development by vividly portraying a character's inner emotions and moral qualities, making personalities more relatable and complex. Unlike prosopopeia, which involves personification or giving voice to inanimate objects or abstract ideas, ethopoeia centers on the psychological and ethical dimensions within speech or narrative. This technique enriches storytelling by deepening the audience's understanding of motivations and fostering emotional connections with characters.
Comparative Analysis: Effectiveness in Persuasion
Prosopopeia employs vivid personification by giving voice to abstract ideas or absent figures, enhancing emotional appeal and creating a strong connection with the audience. Ethopoeia focuses on imitating the character's speech and mannerisms, effectively establishing credibility and fostering empathy through authentic representation. Comparing effectiveness in persuasion, prosopopeia excels in dramatic impact and emotional engagement, while ethopoeia strengthens argumentation by providing realistic character-driven perspectives.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Prosopopeia and Ethopoeia
Choosing between prosopopeia and ethopoeia depends on the narrative purpose and desired emotional impact: prosopopeia animates inanimate objects or abstract concepts by giving them a voice, enhancing metaphorical depth, while ethopoeia embodies a character's thoughts and emotions to create vivid psychological portrayal. Employ prosopopeia to personify ideas for symbolic resonance, and select ethopoeia when aiming for intimate character insight and dynamic dialogue. Effective use hinges on aligning each technique with the story's thematic goals and audience engagement strategy.
Prosopopeia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com