Synecdoche is a figure of speech where a part represents the whole or vice versa, enhancing imagery and meaning in communication. Understanding how this literary device works can improve your writing and comprehension of texts by highlighting the intricate relationship between language and thought. Explore the rest of the article to discover examples and practical uses of synecdoche in everyday language.
Table of Comparison
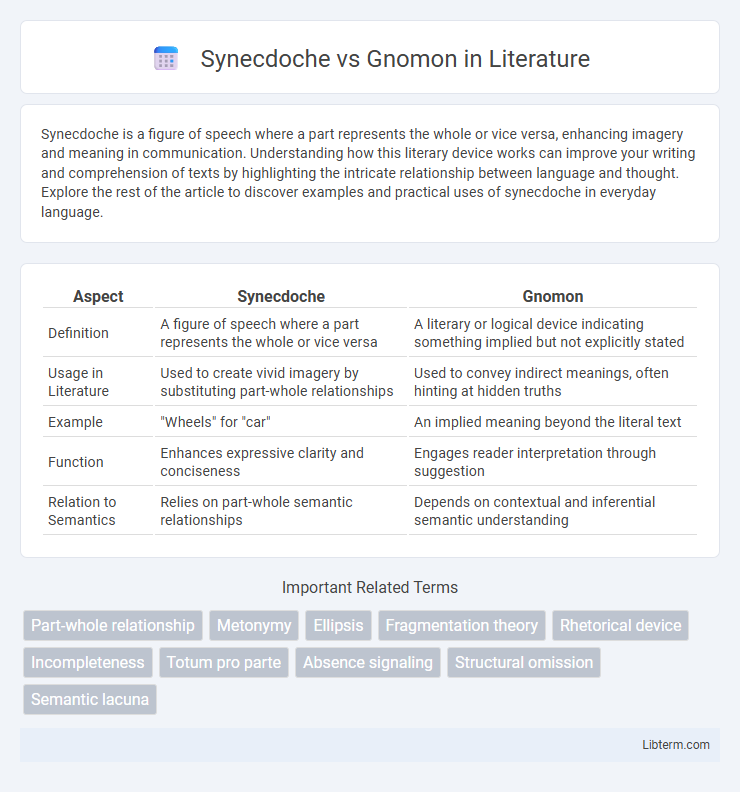
| Aspect | Synecdoche | Gnomon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A figure of speech where a part represents the whole or vice versa | A literary or logical device indicating something implied but not explicitly stated |
| Usage in Literature | Used to create vivid imagery by substituting part-whole relationships | Used to convey indirect meanings, often hinting at hidden truths |
| Example | "Wheels" for "car" | An implied meaning beyond the literal text |
| Function | Enhances expressive clarity and conciseness | Engages reader interpretation through suggestion |
| Relation to Semantics | Relies on part-whole semantic relationships | Depends on contextual and inferential semantic understanding |
Understanding Synecdoche: Definition and Origins
Synecdoche is a figure of speech in which a part represents the whole or the whole represents a part, often used in literature and rhetoric to create vivid imagery and concise expression. Its origins trace back to ancient Greek rhetoric, where it was defined as a form of metonymy that highlights a particular aspect to imply a broader concept. Understanding synecdoche involves recognizing its function as a linguistic device that connects specific elements to their larger contexts, enriching meaning through this semantic association.
What is Gnomon? A Conceptual Overview
Gnomon is a geometric and conceptual figure representing a shape formed by removing a smaller similar figure from a larger one, often seen in ancient Greek mathematics and arts to illustrate growth and proportion. This concept extends beyond geometry into philosophical and literary contexts, symbolizing the idea of a part that reveals the whole or an element that facilitates understanding of a greater structure. Unlike synecdoche, which uses a part to represent the whole in language, gnomon emphasizes spatial and proportional relationships to convey meaning and insight.
Historical Roots: Synecdoche in Literature and Art
Synecdoche, rooted in ancient Greek rhetoric, has been a critical device in literature and art since classical antiquity, symbolizing part-whole relationships to convey complex meanings succinctly. Early examples appear in Homeric epics and Aristophanes' plays, where specific parts represent entire entities, influencing later artistic and literary traditions. This rhetorical figure evolved through medieval allegories and Renaissance art, underscoring cultural narratives by visually and textually emphasizing significant components as metaphors for broader human experiences.
Gnomon in Mathematics and Symbolism
Gnomon in mathematics refers to a figure formed by removing a similar parallelogram from a corner of a larger parallelogram, often used to illustrate geometric progressions and number theory. Symbolically, the gnomon represents growth and transformation, embodying the concept of extension from a basic form into more complex structures. Unlike synecdoche, which is a figure of speech representing a part for the whole or vice versa, the gnomon has precise geometric and symbolic significance deeply rooted in mathematical patterns and philosophical ideas.
Synecdoche vs. Gnomon: Key Differences
Synecdoche represents a figure of speech where a part of something is used to refer to the whole or vice versa, such as "wheels" to mean a car, highlighting a relationship of inclusion. Gnomon, in contrast, originates from geometry and metaphors, symbolizing that which reveals or points to something greater, often signifying something that when added to a shape, forms a new similar figure. The key difference lies in synecdoche's linguistic role in substitution within language, while gnomon serves as a conceptual or visual tool emphasizing growth or addition in mathematical and symbolic contexts.
Applications of Synecdoche in Language
Synecdoche is widely applied in language to create vivid imagery by using a part to represent the whole or vice versa, enhancing expression and clarity. Common examples include referring to "wheels" to mean a car or "sails" to indicate a ship, making communication more efficient and engaging. This figure of speech is prevalent in literature, marketing, and everyday conversation, enriching narrative depth and emotional resonance.
Interpretations of Gnomon Across Disciplines
Gnomon, a geometric figure that subtracts a smaller shape from a larger one, is interpreted differently across disciplines; in mathematics, it represents a fundamental tool for understanding number patterns and figurate numbers, while in art and design, it symbolizes growth and transformation through its evolving form. In literature and philosophy, the gnomon is viewed as a metaphor for incompleteness and the process of self-realization, contrasting with synecdoche's role as a figure of speech where a part represents the whole. This multifaceted interpretation highlights the gnomon's unique ability to bridge abstract mathematical concepts and symbolic meaning across various fields.
Real-world Examples: Synecdoche and Gnomon in Use
Synecdoche appears in everyday language when parts represent wholes, such as referring to a car as "wheels" or calling workers "hands." Gnomons serve as metaphoric tools in problem-solving and design, symbolizing growth or direction, exemplified in architectural elements that indicate time or orientation like sundials. In literature and rhetoric, synecdoche enhances vivid imagery by using tangible parts, while gnomons inspire insights through their geometric and philosophical implications.
Theoretical Implications compared: Synecdoche and Gnomon
Synecdoche and gnomon both serve as foundational figures of speech in linguistics and philosophy, with synecdoche representing a part to signify the whole and gnomon embodying a shape that reveals absence through its presence, impacting semiotic theory differently. Synecdoche's theoretical implications revolve around comprehension through relational substitution and metonymic cognition, while gnomon challenges ontological assumptions by emphasizing negation and absence in meaning construction. Their comparative study enriches understanding of semantic representation, bridging the gap between presence (synecdoche) and absence (gnomon) in language interpretation and cognitive modeling.
Choosing the Right Device: When to Use Synecdoche or Gnomon
Synecdoche effectively captures part-whole relationships, making it ideal for highlighting specific components of a larger concept in storytelling or rhetoric. Gnomon excels in indicating growth or change by visually representing what is added or missing, often used in mathematical or philosophical contexts. Choosing the right device depends on whether the emphasis is on representing a part as a whole (synecdoche) or illustrating incremental development or absence (gnomon).
Synecdoche Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com