Realism focuses on depicting life and society accurately, emphasizing everyday experiences and authentic characters. This literary and artistic movement rejects romanticized or idealized portrayals, aiming instead for truth and objectivity. Discover how realism shapes narratives and influences your interpretation of art and literature in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
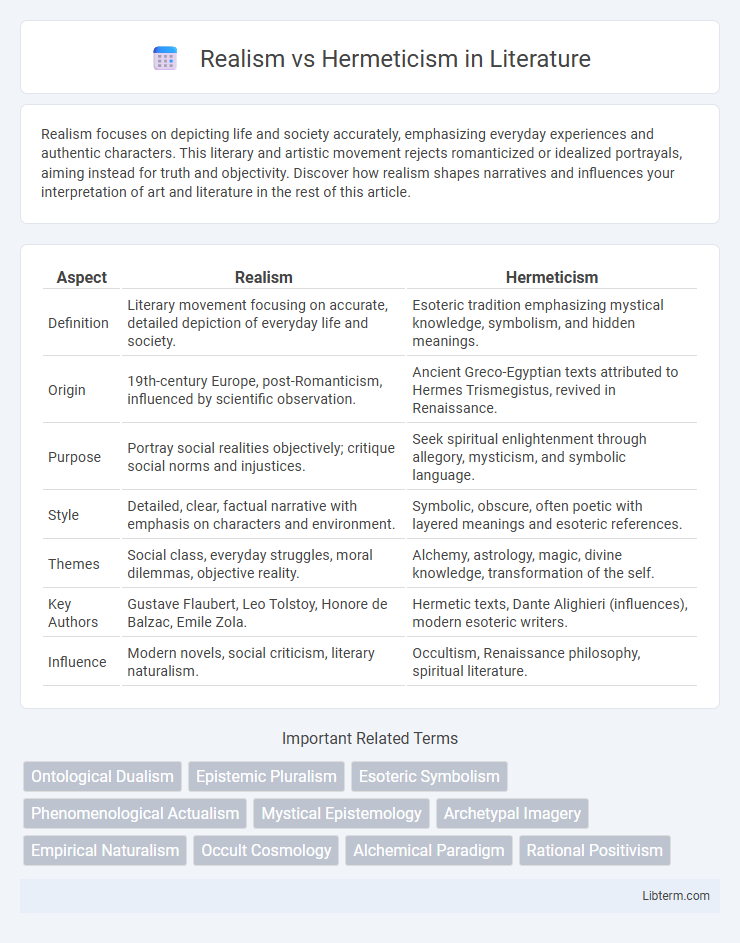
| Aspect | Realism | Hermeticism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Literary movement focusing on accurate, detailed depiction of everyday life and society. | Esoteric tradition emphasizing mystical knowledge, symbolism, and hidden meanings. |
| Origin | 19th-century Europe, post-Romanticism, influenced by scientific observation. | Ancient Greco-Egyptian texts attributed to Hermes Trismegistus, revived in Renaissance. |
| Purpose | Portray social realities objectively; critique social norms and injustices. | Seek spiritual enlightenment through allegory, mysticism, and symbolic language. |
| Style | Detailed, clear, factual narrative with emphasis on characters and environment. | Symbolic, obscure, often poetic with layered meanings and esoteric references. |
| Themes | Social class, everyday struggles, moral dilemmas, objective reality. | Alchemy, astrology, magic, divine knowledge, transformation of the self. |
| Key Authors | Gustave Flaubert, Leo Tolstoy, Honore de Balzac, Emile Zola. | Hermetic texts, Dante Alighieri (influences), modern esoteric writers. |
| Influence | Modern novels, social criticism, literary naturalism. | Occultism, Renaissance philosophy, spiritual literature. |
Introduction to Realism and Hermeticism
Realism in philosophy asserts that external reality exists independently of human perception, emphasizing objective truth and empirical evidence. Hermeticism, rooted in ancient spiritual traditions, explores esoteric knowledge and the interconnectedness of the cosmos through symbolic and mystical interpretation. Both frameworks offer contrasting approaches to understanding reality, with Realism grounded in observable phenomena and Hermeticism focusing on hidden meanings and spiritual insights.
Historical Origins and Development
Realism originated in Ancient Greek philosophy, notably with Plato and Aristotle emphasizing objective reality and the existence of universal forms independent of perception. Hermeticism traces back to Hellenistic Egypt, rooted in the Corpus Hermeticum, blending Greek, Egyptian, and mystical traditions centered around esoteric knowledge and spiritual transformation. The development of Realism influenced medieval Scholasticism while Hermeticism shaped Renaissance occultism and alchemical thought, reflecting distinct approaches to knowledge and reality.
Core Philosophical Principles
Realism centers on the belief that reality exists independently of human perception, asserting that objects, facts, and truths have an objective existence discoverable through reason and empirical observation. Hermeticism emphasizes spiritual knowledge and the interconnectedness of the universe, advocating that hidden truths about reality can be revealed through esoteric wisdom and symbolic interpretation. The core philosophical divide lies in Realism's commitment to external, measurable reality versus Hermeticism's focus on inner, mystical understanding and metaphysical correspondences.
Realism: Key Concepts and Thinkers
Realism emphasizes objective reality and the pursuit of knowledge through empirical observation and rational analysis, rejecting metaphysical speculation. Key thinkers include Aristotle, who laid the foundation for scientific realism by asserting that universals exist independently of the mind, and Thomas Aquinas, who integrated Aristotelian realism into Christian theology. Modern realists like Roy Bhaskar advocate for critical realism, which acknowledges the existence of an objective reality while recognizing the complexity of social phenomena.
Hermeticism: Foundational Texts and Teachings
Hermeticism centers on foundational texts such as the Corpus Hermeticum and the Emerald Tablet, which emphasize esoteric knowledge, spiritual transformation, and the unity of the cosmos. Its teachings promote the principle of "As above, so below," highlighting the correspondence between the macrocosm and microcosm. Hermetic philosophy advocates for inner enlightenment through alchemy, astrology, and theurgy, contrasting with the empirical focus of Realism.
Comparing Worldviews: Reality and Perception
Realism posits that reality exists independently of human perception, emphasizing objective truths and the external world's concrete nature, while Hermeticism centers on the interconnectedness between the cosmos and individual consciousness, asserting that reality is shaped by spiritual insights and subjective experiences. In Realism, knowledge is derived through empirical observation and logical analysis, contrasting with Hermeticism's reliance on esoteric wisdom and symbolic interpretation to access hidden truths. These differing worldviews highlight a fundamental division: Realism's focus on material existence versus Hermeticism's emphasis on metaphysical and mystical dimensions of reality and perception.
Influence on Art, Science, and Literature
Realism's influence on art emphasized accurate, detailed depictions of everyday life, shaping scientific observation by prioritizing empirical evidence and inspiring literature grounded in social conditions and human psychology. Hermeticism impacted art through symbolic and mystical imagery, fostering scientific exploration of alchemy and esoteric knowledge while enriching literature with allegorical and metaphysical themes. Both movements deeply influenced cultural expressions, with Realism promoting objective representation and Hermeticism encouraging introspective and hidden meanings.
Realism and Hermeticism in Modern Thought
Realism in modern thought emphasizes the existence of an objective reality independent of perception, shaping scientific inquiry and epistemology by asserting that truth corresponds to observable phenomena. Hermeticism, rooted in esoteric traditions and mystical knowledge, influences contemporary spirituality and alternative philosophies by promoting personal transformation through hidden wisdom and symbolic interpretation. The tension between realism's empirical approach and hermeticism's metaphysical insights reflects ongoing debates about the nature of truth and knowledge in modern intellectual discourse.
Intersections and Divergences
Realism emphasizes the objective existence of reality independent of perception, while Hermeticism centers on esoteric knowledge and the interconnectedness of the cosmos through symbolic understanding. Both explore the nature of truth, but Realism relies on empirical evidence and external observation, whereas Hermeticism prioritizes mystical experience and inner transformation. Their divergence lies in methodology--Realism seeks knowledge through scientific inquiry, whereas Hermeticism embraces spiritual insight and metaphysical principles.
Conclusion: Bridging or Dividing Perspectives
Realism and Hermeticism represent fundamentally different worldviews, with Realism emphasizing observable, objective reality and Hermeticism focusing on esoteric knowledge and spiritual transformation. Bridging these perspectives requires acknowledging the complementary roles of empirical evidence and metaphysical insight in understanding existence. The dialogue between them can either deepen intellectual divides or enrich philosophical discourse by integrating material and mystical dimensions.
Realism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com