Subordination is a grammatical structure that links dependent clauses to independent clauses, showing the relationship between ideas and clarifying sentence meaning. It enhances writing by adding depth and complexity, helping Your communication become more precise and nuanced. Explore the rest of the article to learn how effective use of subordination can improve your writing skills.
Table of Comparison
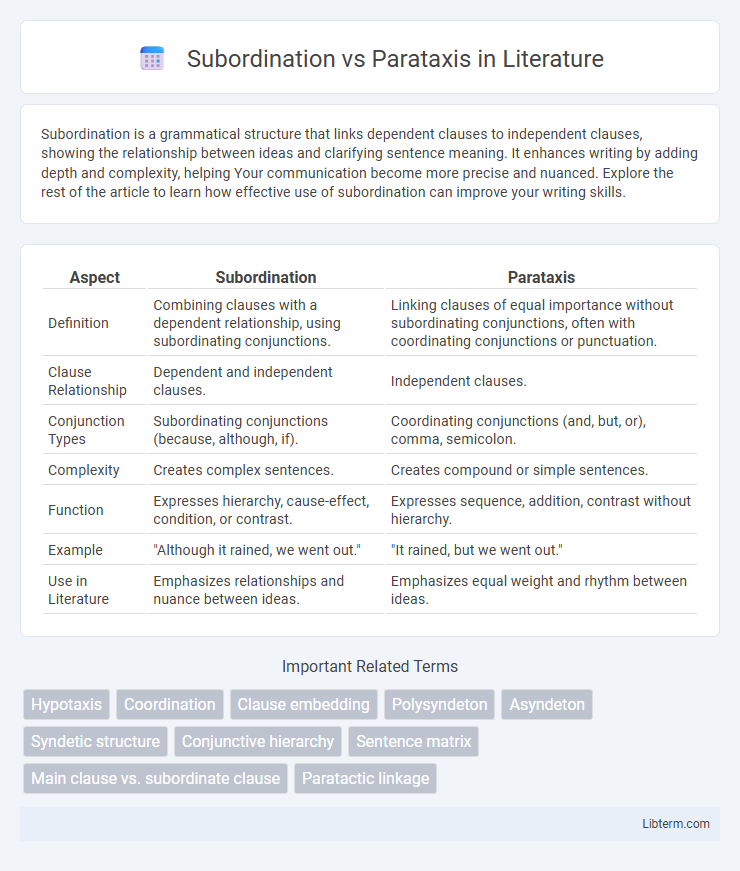
| Aspect | Subordination | Parataxis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining clauses with a dependent relationship, using subordinating conjunctions. | Linking clauses of equal importance without subordinating conjunctions, often with coordinating conjunctions or punctuation. |
| Clause Relationship | Dependent and independent clauses. | Independent clauses. |
| Conjunction Types | Subordinating conjunctions (because, although, if). | Coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or), comma, semicolon. |
| Complexity | Creates complex sentences. | Creates compound or simple sentences. |
| Function | Expresses hierarchy, cause-effect, condition, or contrast. | Expresses sequence, addition, contrast without hierarchy. |
| Example | "Although it rained, we went out." | "It rained, but we went out." |
| Use in Literature | Emphasizes relationships and nuance between ideas. | Emphasizes equal weight and rhythm between ideas. |
Understanding Subordination and Parataxis
Subordination involves linking clauses where one is dependent on the other, establishing a hierarchy of ideas that clarifies relationships like cause, time, or condition. Parataxis places clauses or phrases side by side without explicit connectors, creating equal emphasis and often a more direct, fragmented effect in writing. Mastering the distinction enhances sentence variety and clarity, improving the effectiveness of communication in both formal and creative contexts.
Key Differences Between Subordination and Parataxis
Subordination involves linking clauses where one depends on the other, creating a hierarchy with main and subordinate clauses, often using subordinating conjunctions like "because," "although," or "while." Parataxis places clauses or phrases side by side without indicating dependency, typically using coordinating conjunctions such as "and," "but," or simply juxtaposition. The key difference lies in the syntactic relationship: subordination emphasizes dependence and hierarchy, whereas parataxis expresses coordination and equality between clauses.
Historical Development of Subordination and Parataxis
The historical development of subordination traces back to Latin and Ancient Greek, where complex sentence structures allowed meaning to be embedded within dependent clauses, enhancing syntactic hierarchy and semantic precision. Parataxis, prevalent in early oral traditions and classical rhetoric, relies on juxtaposition of simple, independent clauses without explicit connective markers, reflecting a more direct and linear narrative style. Over time, the evolution from parataxis to subordination paralleled the growth of written language and linguistic complexity, facilitating nuanced expression of temporal, causal, and conditional relationships.
The Role of Syntax in Meaning Construction
Subordination structures meaning by embedding dependent clauses within independent ones, creating hierarchical relationships that clarify complex ideas and emphasize causal or temporal connections. Parataxis arranges clauses side-by-side without explicit syntactic dependence, allowing for equal emphasis and a more open, flexible interpretation of relationships between ideas. The role of syntax in meaning construction lies in guiding readers through these structural choices, shaping how information is prioritized and understood within a text.
Advantages of Subordination in Writing
Subordination enhances writing clarity by establishing clear relationships between ideas, allowing complex thoughts to be expressed with precision. It improves sentence coherence, guiding readers through primary and supporting information efficiently. This technique also creates varied sentence structures, making the text more engaging and easier to follow.
Benefits of Parataxis for Clarity and Impact
Parataxis enhances clarity by presenting ideas in simple, direct phrases or sentences without complex subordination, making the message easily accessible and immediately understandable. This technique allows each clause to stand independently, which can intensify the impact through repetition, rhythm, and equal emphasis on each point. In comparison to subordination, parataxis minimizes ambiguity and cognitive load, facilitating rapid comprehension and a stronger emotional or rhetorical effect.
Common Examples of Subordination and Parataxis
Subordination commonly appears in sentences like "Although she was tired, she finished her work," where one clause depends on the other. Parataxis involves placing clauses or phrases side-by-side without explicit dependency, as in "She was tired, she finished her work." Examples of subordination include using conjunctions like because, although, and since, while parataxis often employs simple coordination with and, but, or commas separating independent clauses.
Subordination and Parataxis in Literary Styles
Subordination in literary styles creates complex sentences where main clauses are emphasized while subordinate clauses provide additional context or detail, enhancing narrative depth and clarity. Parataxis features the placement of clauses or phrases side by side without subordinating conjunctions, producing a more direct, rhythmic, and impactful effect often seen in modernist and minimalist prose. Authors like James Joyce utilize parataxis to convey stream-of-consciousness experiences, whereas classic literature frequently employs subordination to build elaborate descriptions and causal relationships.
Tips for Using Subordination and Parataxis Effectively
Using subordination effectively involves clearly establishing the relationship between ideas by placing less important information in dependent clauses, which enhances clarity and precision in complex sentences. Parataxis shines in creating emphasis and rhythm by placing clauses or phrases of equal importance side by side without conjunctions, making statements more direct and impactful. Balancing subordination and parataxis can improve writing by matching sentence structure to the desired tone and complexity, with subordination providing depth and parataxis delivering straightforwardness.
Choosing Between Subordination and Parataxis in Your Writing
Choosing between subordination and parataxis in your writing depends on the clarity and emphasis you want to achieve; subordination effectively highlights the relationship between ideas by making one clause dependent on another, which is ideal for showing cause, condition, or contrast. Parataxis involves placing clauses or phrases side by side with equal importance, creating a straightforward, impactful style that suits descriptive or narrative contexts. Balancing these structures enhances readability and allows precise control over the flow and nuance of information in complex or simple sentences.
Subordination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com