Dialogism explores how meaning is created through the interaction of different voices and perspectives within a text, emphasizing the dynamic and relational nature of language. It highlights the importance of understanding context, cultural influences, and the interplay between speakers to fully grasp communication. Discover how dialogism transforms language and meaning in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
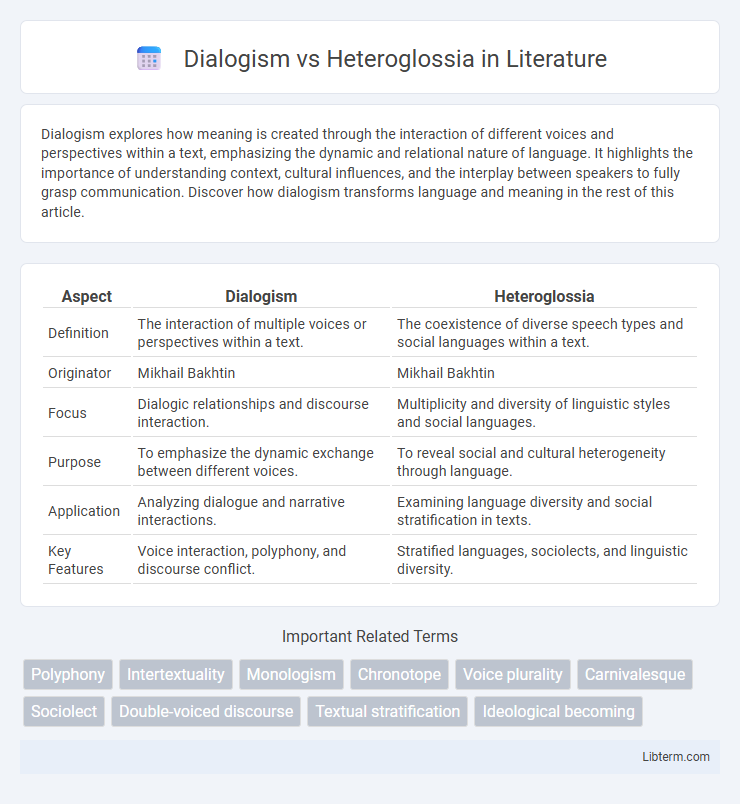
| Aspect | Dialogism | Heteroglossia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The interaction of multiple voices or perspectives within a text. | The coexistence of diverse speech types and social languages within a text. |
| Originator | Mikhail Bakhtin | Mikhail Bakhtin |
| Focus | Dialogic relationships and discourse interaction. | Multiplicity and diversity of linguistic styles and social languages. |
| Purpose | To emphasize the dynamic exchange between different voices. | To reveal social and cultural heterogeneity through language. |
| Application | Analyzing dialogue and narrative interactions. | Examining language diversity and social stratification in texts. |
| Key Features | Voice interaction, polyphony, and discourse conflict. | Stratified languages, sociolects, and linguistic diversity. |
Understanding Dialogism: A Foundational Concept
Dialogism, a concept introduced by Mikhail Bakhtin, refers to the continuous interaction and exchange between diverse voices and perspectives within a text or discourse. It emphasizes the dynamic, multifaceted nature of meaning-making, where no single viewpoint dominates but instead coexists and contests with others. Understanding dialogism involves recognizing the intrinsic interconnectedness of voices that shape narrative complexity and social discourse.
Defining Heteroglossia in Literary Theory
Heteroglossia in literary theory refers to the coexistence of multiple voices, languages, or social dialects within a single text, highlighting the diversity and multiplicity of meaning. Unlike dialogism, which emphasizes the interactive relationship between these voices, heteroglossia focuses on the stratification of speech types that reflect different social and ideological perspectives. This concept, introduced by Mikhail Bakhtin, reveals how literature conveys complex social realities through the interplay of various linguistic expressions.
Dialogism vs Heteroglossia: Key Differences
Dialogism refers to the interaction of multiple voices or perspectives within a text, emphasizing the dynamic exchange between different viewpoints. Heteroglossia specifically highlights the presence of diverse social languages and linguistic varieties that coexist and interact within a single narrative. Key differences include dialogism's broader focus on interactive dialogue and conflict between voices, while heteroglossia centers on the coexistence of varied speech types reflecting social diversity.
Historical Origins: Bakhtin’s Contributions
Mikhail Bakhtin introduced the concepts of dialogism and heteroglossia as foundational elements in literary theory and linguistics, emphasizing the dynamic interaction between multiple voices within a text. Dialogism refers to the ongoing interaction and negotiation of meanings between different voices or perspectives, reflecting the social and ideological diversity inherent in language. Heteroglossia highlights the coexistence of distinct socio-ideological languages within a single textual or spoken context, showcasing the historical and social stratifications embedded in language use.
The Role of Voice and Perspective
Dialogism emphasizes the interaction of multiple voices, highlighting the dynamic interplay of perspectives within a text that challenges a singular, authoritative voice. Heteroglossia refers to the coexistence of diverse speech types and social languages in literature, enriching narrative complexity by showcasing varied ideological and social viewpoints. Both concepts underscore the critical role of voice and perspective in shaping meaning, revealing how language reflects and constructs diverse realities.
Language Diversity in Texts
Dialogism emphasizes the interactive presence of multiple voices within a text, reflecting diverse perspectives and social contexts, while heteroglossia highlights the coexistence of different language varieties, dialects, and speech types that reveal cultural and social diversity. Language diversity in texts enriches meaning by incorporating varied linguistic codes and sociolects, challenging a monologic or single-voice interpretation. This interplay showcases how texts function as dynamic sites of ideological and linguistic plurality, enhancing interpretive complexity and cultural representation.
Dialogism in Modern Literary Analysis
Dialogism in modern literary analysis emphasizes the interaction of multiple voices and perspectives within a text, revealing the dynamic interplay of social, cultural, and ideological discourses. It highlights how texts are not monologic but constantly engage with and respond to other texts, contexts, and interpretations, fostering a multi-dimensional understanding of meaning. This approach deepens the analysis of narrative complexity and authorial intent, making it a crucial tool in contemporary literary studies.
Heteroglossia and Social Context
Heteroglossia refers to the presence of multiple voices, languages, or social dialects within a single text, reflecting diverse social contexts and power dynamics. It emphasizes how language varies according to different social groups, ideologies, and historical backgrounds, making texts socially and culturally layered. Unlike dialogism, which highlights interaction between voices, heteroglossia underscores the social stratification embedded in language diversity.
Applications in Multicultural Literature
Dialogism in multicultural literature emphasizes the interaction of diverse voices and perspectives, fostering a dynamic exchange that reflects cultural plurality. Heteroglossia highlights the coexistence of multiple languages, dialects, and social registers within a text, enhancing authenticity and cultural depth. Together, these concepts enrich narratives by representing complex identities and challenging monolithic cultural norms.
Dialogism & Heteroglossia in Contemporary Discourse
Dialogism and heteroglossia are key concepts in contemporary discourse analysis, reflecting the dynamic interplay of multiple voices and perspectives within communication. Dialogism emphasizes the ongoing interaction and negotiation between utterances, highlighting how meaning is co-constructed in social contexts. Heteroglossia complements this by showcasing the coexistence of diverse linguistic styles and socio-cultural voices, enriching the complexity and depth of modern discursive practices.
Dialogism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com