Allegory is a literary device that conveys hidden meanings through symbolic figures and actions, often reflecting moral, political, or spiritual lessons. This technique allows authors to explore complex ideas in a nuanced and engaging way, enriching the reader's understanding beyond the surface narrative. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how allegory can transform your reading experience and interpretation skills.
Table of Comparison
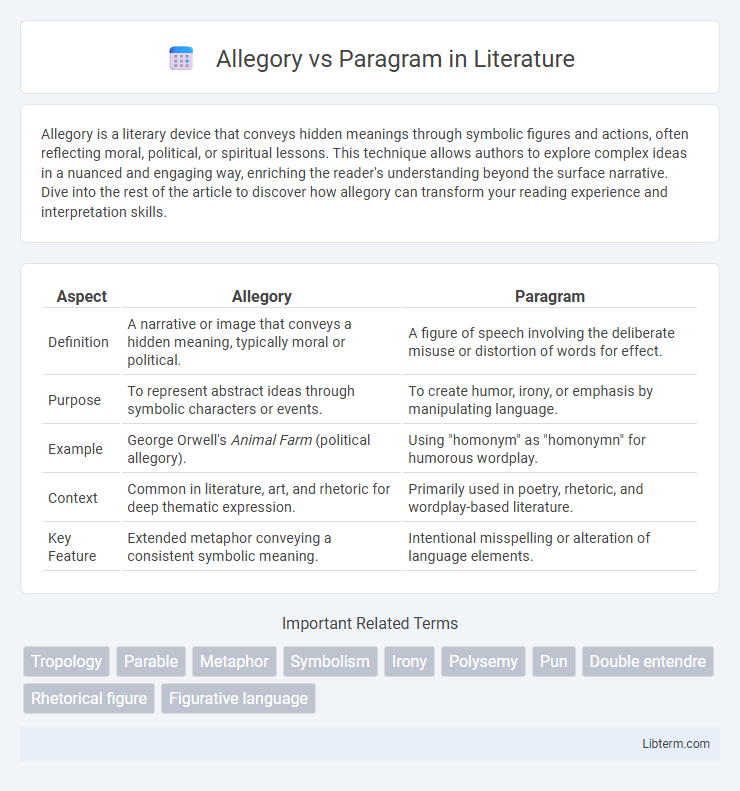
| Aspect | Allegory | Paragram |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A narrative or image that conveys a hidden meaning, typically moral or political. | A figure of speech involving the deliberate misuse or distortion of words for effect. |
| Purpose | To represent abstract ideas through symbolic characters or events. | To create humor, irony, or emphasis by manipulating language. |
| Example | George Orwell's Animal Farm (political allegory). | Using "homonym" as "homonymn" for humorous wordplay. |
| Context | Common in literature, art, and rhetoric for deep thematic expression. | Primarily used in poetry, rhetoric, and wordplay-based literature. |
| Key Feature | Extended metaphor conveying a consistent symbolic meaning. | Intentional misspelling or alteration of language elements. |
Introduction to Allegory and Paragram
Allegory is a narrative technique that uses symbolic figures, actions, or events to convey deeper moral, spiritual, or political meanings beyond the literal story. Paragram, a less common literary device, involves intentional wordplay or a pun to create a double meaning, often enhancing meaning through linguistic creativity. Understanding allegory emphasizes interpretation of extended metaphors, whereas paragram highlights playful manipulation of language within texts.
Defining Allegory: Key Concepts
Allegory is a narrative or visual representation that uses symbolic figures, actions, or imagery to convey complex ideas and moral lessons beyond the literal meaning. It operates through a sustained metaphor, where characters and events correspond to abstract concepts or historical realities. Understanding allegory involves recognizing its dual-layered storytelling, blending surface plots with deeper philosophical or ethical messages.
Understanding Paragram: Core Principles
Paragram hinges on the strategic substitution of words or phrases to create new meanings, often playing on phonetic and semantic similarities. This technique transforms the original message through wordplay, enabling layered interpretations and enhancing linguistic creativity. Understanding paragram requires recognizing how subtle shifts in language structure can generate humor, irony, or critical commentary.
Historical Origins of Allegory
Allegory originated in ancient Greek literature, notably in the works of Plato, who used symbolic narratives to convey philosophical ideas beyond the literal meaning. This technique evolved through Roman and medieval periods, where allegorical interpretation became central to biblical exegesis and moral storytelling. The historical foundation of allegory is deeply rooted in its use as a method for exploring complex concepts through layered symbolism and personification.
Evolution of Paragram in Literature
Paragram, initially a linguistic play on words involving deliberate misuse or substitution of letters, evolved in literature from a simple rhetorical device to a complex tool for nuanced expression and satire. Its progression is marked by its integration into poetic and prose works, where authors manipulated paragrams to enrich meaning, challenge readers, and engage in wordplay that transcends mere phonetic alteration. This evolution reflects a broader literary trend toward embracing ambiguity and multiplicity of interpretation, distinguishing paragram as a dynamic element in the interplay between language and meaning.
Major Differences Between Allegory and Paragram
Allegory is an extended metaphor where characters, events, and settings symbolically represent abstract ideas or moral qualities, often conveying a deeper meaning throughout a narrative. Paragram, by contrast, involves a playful or deliberate misuse of words, such as puns or word substitutions, to create humor or clever effects without a hidden symbolic message. The major difference lies in allegory's purpose to communicate complex concepts through symbolic storytelling, whereas paragram focuses on linguistic creativity and wordplay without inherent symbolic depth.
Functions and Purpose in Texts
Allegory functions as a complex narrative device where characters and events represent broader moral, political, or spiritual meanings, enabling multilayered interpretation beyond the literal story. Paragram operates as a linguistic play on words, often used for humor, satire, or to emphasize meaning through deliberate misuse or alteration of terms, enhancing textual engagement and irony. Both devices serve distinct purposes: allegory deepens thematic exploration and moral instruction, while paragram intensifies rhetorical impact and reader amusement.
Examples of Allegory in Classic Works
Classic works such as George Orwell's "Animal Farm" exemplify allegory by using farm animals to symbolize the Russian Revolution and its political implications. John Bunyan's "The Pilgrim's Progress" serves as a renowned allegory portraying the spiritual journey of a Christian toward salvation through characters and events symbolizing virtues and vices. Dante Alighieri's "Divine Comedy" presents a layered allegory of the soul's journey through Hell, Purgatory, and Heaven, representing moral and theological themes central to medieval Christian belief.
Notable Uses of Paragram in Modern Contexts
Paragrams are frequently employed in modern advertising and branding to create memorable, playful word substitutions that engage audiences and enhance recall. Notable examples include clever product names like "Froot Loops" and pun-based slogans that leverage phonetic similarities for humor and impact. These strategic uses of paragrammatic wordplay contribute to consumer recognition and marketing effectiveness in contemporary media.
Choosing Between Allegory and Paragram in Writing
Choosing between allegory and paragram in writing depends on the intended depth and complexity of the message. Allegory conveys layered, symbolic meaning suited for exploring moral, political, or philosophical themes, while paragram emphasizes wordplay and linguistic creativity to engage readers through subtle language shifts. Writers aiming for profound thematic impact often prefer allegory, whereas those seeking to highlight linguistic wit and nuanced expression may opt for paragram.
Allegory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com