The preface offers a glimpse into the author's inspiration and the context behind the creation of the book, highlighting key themes and objectives. It sets the tone for what readers can anticipate, enhancing understanding and engagement. Explore the rest of the article to discover the full story behind this compelling narrative.
Table of Comparison
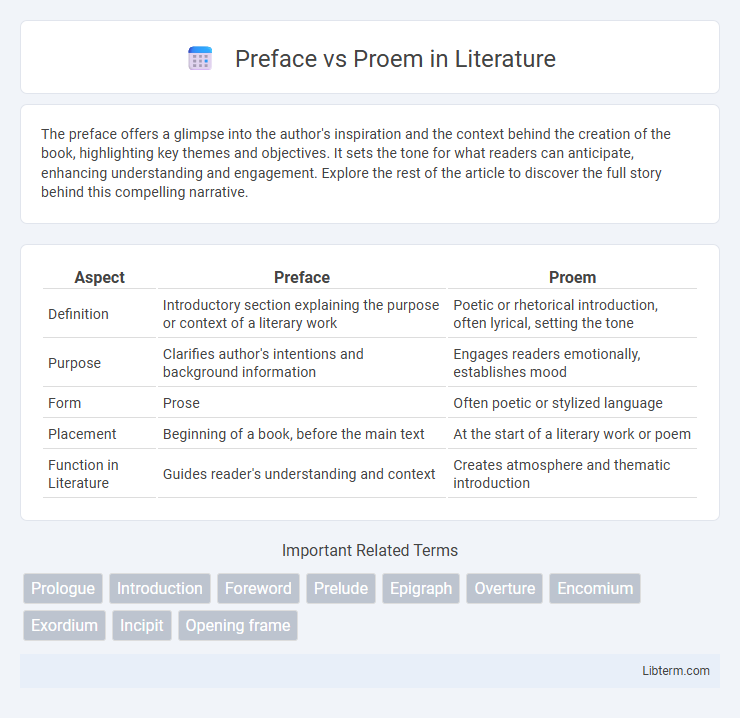
| Aspect | Preface | Proem |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introductory section explaining the purpose or context of a literary work | Poetic or rhetorical introduction, often lyrical, setting the tone |
| Purpose | Clarifies author's intentions and background information | Engages readers emotionally, establishes mood |
| Form | Prose | Often poetic or stylized language |
| Placement | Beginning of a book, before the main text | At the start of a literary work or poem |
| Function in Literature | Guides reader's understanding and context | Creates atmosphere and thematic introduction |
Introduction to Preface and Proem
A Preface serves as an introductory statement by the author, explaining the purpose, scope, and background of the work, often including acknowledgments and insights into the writing process. A Proem, traditionally a brief prelude or opening passage, functions as a poetic or rhetorical introduction designed to set the tone or theme for the text. Both elements serve to orient the reader, but the Preface is more informational and personalized, while the Proem emphasizes stylistic and thematic framing.
Defining Preface: Purpose and Features
A preface serves as an author's introduction to a book, explaining the purpose, scope, and context of the work, often including acknowledgments and the genesis of the text. It provides readers with insight into the author's intentions and the background behind the writing, establishing a connection before the main content. Unlike a proem, which is typically a poetic or rhetorical introduction, a preface is more straightforward and informative, focusing on purpose and features relevant to the work's creation.
What is a Proem? Meaning and Usage
A proem is an introductory section or preamble of a literary work, often serving to outline the theme or purpose and set the tone for the text. Unlike a preface, which usually provides background information or the author's intent, a proem often functions as a poetic or rhetorical invocation directly linked to the content's essence. Common in classical literature and epic poetry, proems succinctly engage readers by framing the narrative or argument with thematic significance.
Historical Origins of Preface and Proem
The historical origins of the preface trace back to ancient manuscripts where authors introduced their work and its purpose to readers, establishing context and credibility. The proem, derived from the Greek word "prooimion," served as a formal opening in classical literature, often poetic or rhetorical, designed to capture attention and set the tone. Both elements evolved distinctly within literary traditions, with the preface becoming more explanatory and the proem maintaining a ceremonial, stylistic introduction in early texts.
Structural Differences Between Preface and Proem
The preface typically serves as an introductory section written by the author, explaining the purpose, scope, and background of the entire work and often includes acknowledgments. In contrast, the proem functions as a literary or poetic introduction, setting the tone or theme without detailed explanations, commonly found in classical or epic literature. Structurally, the preface is prose-oriented and formal, while the proem is more concise and stylistically aligned with the work's genre or narrative style.
Literary Functions: Preface vs Proem
A preface serves as an introductory statement by the author, providing context, purpose, and background to the work, often reflecting on the writing process or intentions. A proem, distinct in classical literature, functions as a poetic or rhetorical introduction that sets the thematic tone and engages the audience through artistic expression. Both elements guide the reader's interpretation but differ in formality and literary device usage, with the preface more expository and the proem more evocative.
Examples of Prefaces in Classic Literature
Prefaces in classic literature often serve as a direct communication from the author, such as Victor Hugo's preface to *Cromwell*, where he outlines his literary manifesto and sets the tone for Romanticism. Another prominent example is Mary Shelley's preface to *Frankenstein*, where she explains the novel's inspiration and thematic intentions, providing crucial context for readers. These prefaces differ from proems by explicitly framing the work's purpose and guiding the audience's interpretation before the narrative begins.
Notable Proems in Historical Texts
Notable proems in historical texts serve as concise introductions that establish the thematic framework and rhetorical tone, often reflecting the author's philosophical or scholarly intent. Unlike prefaces, which provide contextual background and authorial explanations, proems emphasize literary artistry and thematic resonance, as seen in works like Plato's dialogues or Cicero's speeches. These proems not only set the stage for the main discourse but also engage readers through poetic or philosophical expressions that highlight the text's significance.
Choosing Between Preface and Proem
Choosing between a preface and a proem depends on the author's intent and the work's structure. A preface typically provides context, background information, or acknowledgments related to the book's creation and purpose. In contrast, a proem serves as an introductory poem or thematic prelude that sets the tone and mood, often used in literary or poetic works.
Conclusion: Preface and Proem in Modern Writing
Preface and proem serve distinct roles in modern writing: a preface typically offers context, author intentions, and acknowledgments, while a proem acts as an introductory passage to engage readers stylistically. Contemporary authors increasingly use prefaces to provide critical insights and situate the work within broader literary or historical frameworks. The conclusion highlights the evolving function of these sections in shaping reader expectations and deepening understanding of the text's purpose.
Preface Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com