Epenthesis is the phonological process where an extra sound is inserted within a word, often to make pronunciation easier or to conform to a language's phonotactic rules. This phenomenon can occur in various languages and affects both consonants and vowels, altering the word's original form without changing its meaning. Explore the rest of the article to understand how epenthesis influences language patterns and why it matters for your linguistic insights.
Table of Comparison
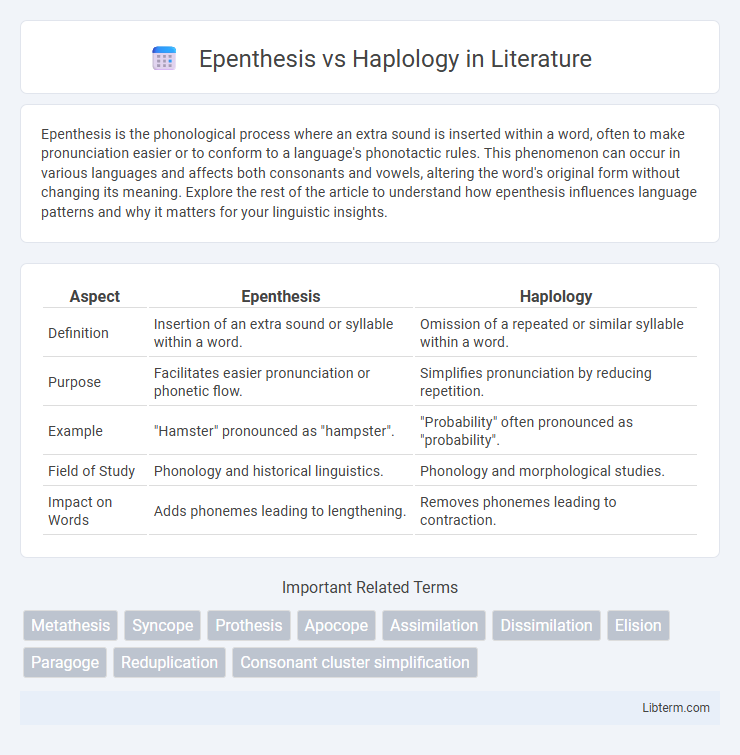
| Aspect | Epenthesis | Haplology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insertion of an extra sound or syllable within a word. | Omission of a repeated or similar syllable within a word. |
| Purpose | Facilitates easier pronunciation or phonetic flow. | Simplifies pronunciation by reducing repetition. |
| Example | "Hamster" pronounced as "hampster". | "Probability" often pronounced as "probability". |
| Field of Study | Phonology and historical linguistics. | Phonology and morphological studies. |
| Impact on Words | Adds phonemes leading to lengthening. | Removes phonemes leading to contraction. |
Introduction to Epenthesis and Haplology
Epenthesis refers to the phonological process where an extra sound is inserted within a word, often to ease pronunciation or preserve syllable structure, such as in "athlete" pronounced as "ath-e-lete." Haplology is the omission of one syllable when two similar syllables occur consecutively, streamlining speech, as seen in "library" pronounced as "libry." Both processes reflect natural language evolution aimed at optimizing speech efficiency and clarity.
Defining Epenthesis: Meaning and Function
Epenthesis is the phonological process of inserting an extra sound, usually a vowel or consonant, within a word to facilitate easier pronunciation or maintain syllable structure. This insertion often occurs to break up difficult consonant clusters or to conform to a language's phonotactic rules, enhancing speaker fluency and listener comprehension. Understanding epenthesis is crucial for analyzing language evolution, speech patterns, and phonetic adaptation across different linguistic contexts.
Understanding Haplology: Concept and Examples
Haplology is the linguistic phenomenon where a repeated or similar syllable or sound is omitted within a word to simplify pronunciation, such as "probly" instead of "probably." It contrasts with epenthesis, which involves the insertion of an extra sound or syllable, like the added "t" in "length" pronounced as "leng-th." Understanding haplology highlights how language efficiency drives phonetic changes, evident in everyday speech and historical language evolution.
Historical Evolution of Epenthesis in Languages
Epenthesis, the historical insertion of sounds into words, evolved to simplify pronunciation and distinguish meanings across languages, prominently shaping phonological development in Indo-European and Semitic language families. Linguistic records show epenthetic vowels often emerged in consonant clusters to enhance phonotactic constraints, as seen in Old English and Ancient Greek. Contrastingly, haplology eliminates redundant sounds, streamlining speech by reducing syllabic complexity, but epenthesis introduces complexity to resolve articulation challenges over time.
Haplology Across Different Language Families
Haplology, a phonological process where a syllable is omitted to simplify pronunciation, occurs across various language families including Indo-European, Afroasiatic, and Austronesian. In languages like English and Spanish, haplology reduces repetitive sounds in rapid speech, such as "probably" pronounced as "probly." Understanding haplology enhances insights into language evolution and speech patterns by highlighting natural tendencies toward efficiency and ease of articulation.
Linguistic Mechanisms Behind Epenthesis
Epenthesis involves the insertion of an extra sound or syllable within a word to facilitate smoother pronunciation, often triggered by the difficulty of transitioning between certain phonemes. This linguistic mechanism contrasts with haplology, where a sound or syllable is omitted to simplify a word's structure. Epenthesis enhances phonotactic constraints and contributes to language evolution by resolving consonant clusters or vowel hiatuses that hinder fluent speech.
Causes and Triggers of Haplology
Haplology occurs when speakers simplify word pronunciation by omitting a syllable, typically triggered by repetitive or similar adjacent syllables that cause difficulty in articulation. Causes of haplology include phonetic redundancy, ease of speech, and fast or casual speech patterns that favor efficiency in verbal communication. This contrasts with epenthesis, which involves the insertion of an extra sound to break up difficult consonant clusters or to ease pronunciation.
Phonological Impact of Epenthesis vs Haplology
Epenthesis involves the addition of one or more sounds within a word, which alters the phonological structure by increasing the segmental count and potentially easing articulation or preserving syllable patterns. Haplology results in the omission of one or more sounds, typically reducing phonemic complexity and promoting faster, more efficient speech production by eliminating redundant syllables. The phonological impact of epenthesis often enhances syllable weight and rhythmic stability, whereas haplology simplifies phonotactic patterns and diminishes syllable count, affecting prosodic and morphophonemic patterns differently.
Real-World Examples: Epenthesis and Haplology in Action
Epenthesis occurs in English when a vowel is inserted to break up difficult consonant clusters, as seen in the pronunciation of "athlete" often rendered as /'ael.@.thli/. Haplology involves the omission of one syllable in repeated sounds, such as the word "probably" frequently pronounced as /'prab.li/. These phonological processes illustrate how speakers simplify speech for ease of articulation in everyday language use.
Conclusion: Comparing Epenthesis and Haplology
Epenthesis involves the insertion of an extra sound within a word to ease pronunciation, while haplology refers to the omission of a syllable when similar consecutive sounds occur. Both processes influence language evolution by altering word forms and improving phonetic fluency. Understanding these phonological phenomena highlights their complementary roles in streamlining speech and shaping linguistic change.
Epenthesis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com