Symbolism plays a crucial role in conveying deeper meanings beyond the literal sense, allowing you to interpret complex ideas through images, signs, or motifs. Different cultures and contexts attribute unique significance to symbols, making them powerful tools in communication, literature, and art. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how symbols shape our understanding and expression.
Table of Comparison
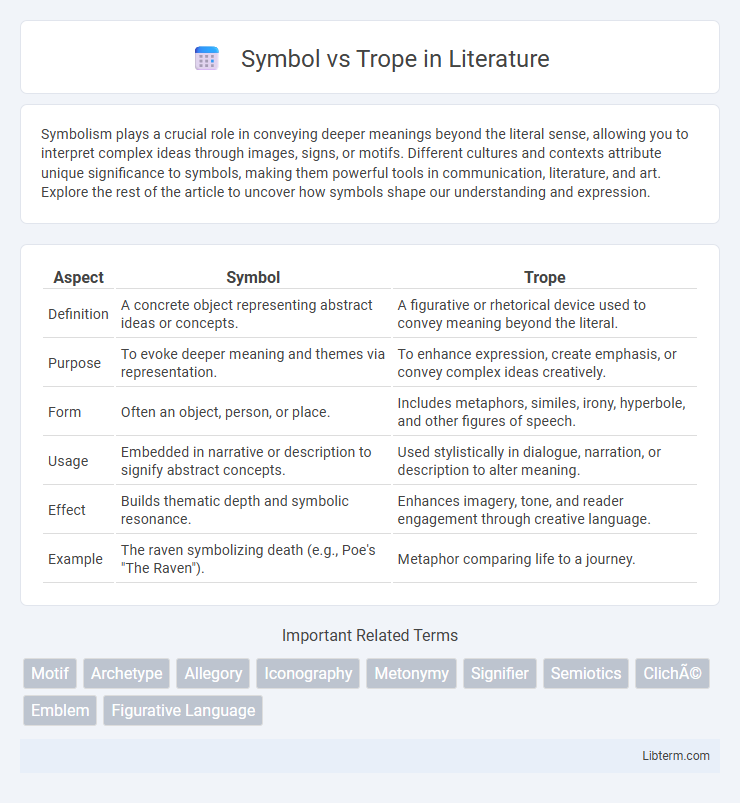
| Aspect | Symbol | Trope |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A concrete object representing abstract ideas or concepts. | A figurative or rhetorical device used to convey meaning beyond the literal. |
| Purpose | To evoke deeper meaning and themes via representation. | To enhance expression, create emphasis, or convey complex ideas creatively. |
| Form | Often an object, person, or place. | Includes metaphors, similes, irony, hyperbole, and other figures of speech. |
| Usage | Embedded in narrative or description to signify abstract concepts. | Used stylistically in dialogue, narration, or description to alter meaning. |
| Effect | Builds thematic depth and symbolic resonance. | Enhances imagery, tone, and reader engagement through creative language. |
| Example | The raven symbolizing death (e.g., Poe's "The Raven"). | Metaphor comparing life to a journey. |
Defining Symbols and Tropes
Symbols represent abstract ideas or concepts through concrete images, objects, or actions, serving as a bridge between the literal and the figurative in literature and art. Tropes involve the use of figurative language, such as metaphors, similes, or irony, to convey meanings that deviate from the literal interpretation of words or phrases. Understanding symbols involves recognizing their deeper thematic significance, while identifying tropes requires analyzing language patterns that create rhetorical or imaginative effects.
Historical Origins of Symbols and Tropes
Symbols have ancient origins, often rooted in early human communication systems like cave paintings and religious iconography, serving as visual representations imbued with collective meaning. Tropes emerged primarily in classical rhetoric, dating back to Ancient Greece and Rome, where figures of speech like metaphor and metonymy were formalized to enhance persuasive communication. The historical development of symbols emphasizes cultural and spiritual significance, while tropes evolved as linguistic tools for creative expression and argumentation.
Key Differences Between Symbols and Tropes
Symbols represent abstract ideas or concepts through a tangible object or image, often conveying deeper meaning beyond their literal sense. Tropes involve figurative language or literary devices like metaphors and irony, used to create an effect or convey nuanced meaning in communication. The key difference lies in symbols embodying concrete representations of abstract ideas, whereas tropes manipulate language and expression to evoke imagery or interpretation.
Functions of Symbols in Literature
Symbols in literature convey deeper meanings, representing abstract ideas or themes that extend beyond their literal sense, enriching narrative complexity. They function as tools for authors to evoke emotions, create connections, and reinforce motifs, often enhancing the reader's interpretive experience by embedding cultural or psychological significance. Unlike tropes, which are recurring literary devices or themes, symbols serve as multi-layered representations that invite analysis and personal interpretation.
Common Tropes in Popular Media
Common tropes in popular media include the "Hero's Journey," "Damsel in Distress," and "The Chosen One," serving as recognizable narrative patterns that guide audience expectations. Symbols, such as a red rose representing love or a broken mirror indicating fractured identity, convey deeper abstract meanings beyond their literal presence. Understanding the distinction between these recurring narrative devices and symbolic imagery enhances analysis of storytelling techniques and thematic depth.
How Symbols Enhance Storytelling
Symbols enhance storytelling by embedding deeper meanings that resonate emotionally and intellectually with audiences, creating layers of interpretation beyond the literal narrative. They invite readers to engage actively with the text, unlocking cultural, historical, or thematic significance that enriches understanding and connection. Unlike tropes that rely on conventional storytelling devices, symbols offer unique, personalized insights that deepen the story's impact and memorability.
The Role of Tropes in Shaping Genres
Tropes serve as foundational storytelling devices that define and differentiate genres by establishing recognizable patterns and expectations. In genres like horror, romance, or science fiction, specific tropes shape the narrative structure and audience anticipation, guiding emotional and thematic engagement. Unlike symbols, which carry deeper, often universal meanings, tropes function as genre-specific conventions that aid in world-building and character development.
Interplay of Symbols and Tropes in Narrative
Symbols and tropes function as fundamental narrative devices, where symbols represent deeper, often abstract meanings through concrete elements, while tropes serve as recognizable conventions or thematic motifs shaping story expectations. The interplay between symbols and tropes enriches storytelling by embedding layers of cultural or emotional significance within familiar narrative patterns, enhancing audience engagement and thematic resonance. This dynamic allows writers to subtly subvert or reinforce meanings, creating complexity and depth in character development and plot progression.
Recognizing Symbolism vs. Tropism in Analysis
Recognizing symbolism involves identifying objects, colors, or figures that represent broader abstract meanings beyond their literal sense, often conveying cultural or emotional significance. Tropism, particularly in literary analysis, refers to recurring motifs or themes that reveal underlying patterns or attitudes but do not carry the layered representational weight of symbols. Differentiating between symbolism and tropism improves interpretive accuracy by distinguishing between deep, often universal meanings and repetitive thematic elements.
Creating Impactful Stories with Symbols and Tropes
Symbols and tropes serve as powerful storytelling tools that create layers of meaning and emotional resonance within narratives. Using symbols--objects, colors, or motifs imbued with deeper significance--can subtly convey themes and evoke strong emotional responses from audiences. Tropes, as recurrent narrative devices or character archetypes, help structure stories and meet audience expectations, enhancing engagement and the overall impact of the story.
Symbol Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com