Glossolalia, commonly known as speaking in tongues, is a phenomenon where individuals vocalize speech-like sounds without recognizable meaning, often associated with religious practices. This spiritual expression can serve various purposes, including personal edification and communal worship, reflecting deep emotional or mystical experiences. Explore the following article to understand the origins, significance, and interpretations of glossolalia in diverse cultural contexts.
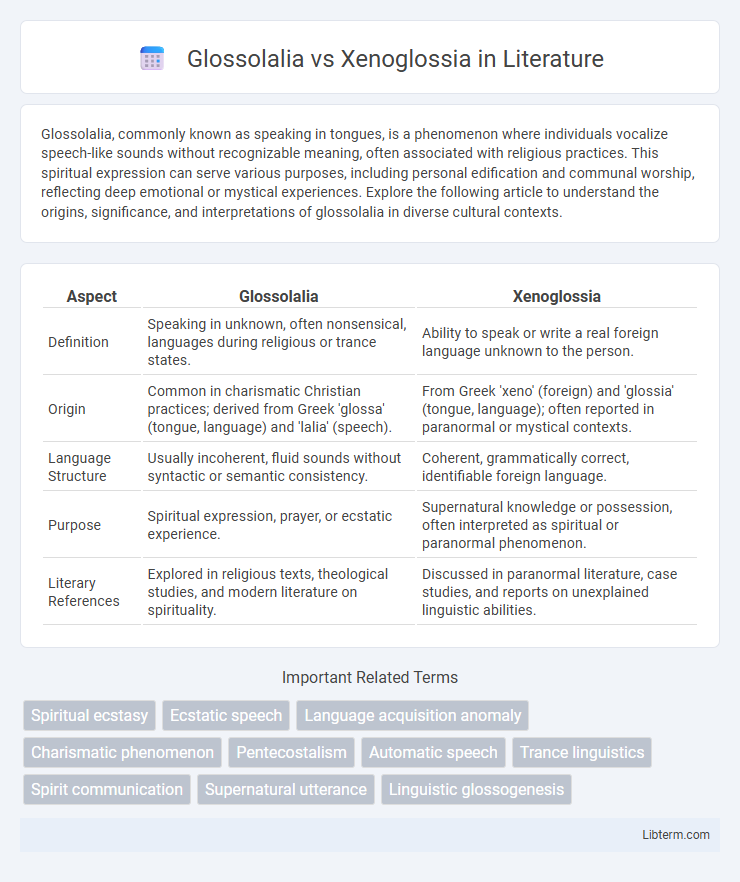
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Glossolalia | Xenoglossia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Speaking in unknown, often nonsensical, languages during religious or trance states. | Ability to speak or write a real foreign language unknown to the person. |
| Origin | Common in charismatic Christian practices; derived from Greek 'glossa' (tongue, language) and 'lalia' (speech). | From Greek 'xeno' (foreign) and 'glossia' (tongue, language); often reported in paranormal or mystical contexts. |
| Language Structure | Usually incoherent, fluid sounds without syntactic or semantic consistency. | Coherent, grammatically correct, identifiable foreign language. |
| Purpose | Spiritual expression, prayer, or ecstatic experience. | Supernatural knowledge or possession, often interpreted as spiritual or paranormal phenomenon. |
| Literary References | Explored in religious texts, theological studies, and modern literature on spirituality. | Discussed in paranormal literature, case studies, and reports on unexplained linguistic abilities. |
Understanding Glossolalia: Definition and Origins
Glossolalia, commonly known as speaking in tongues, refers to vocalizing fluent-sounding but unintelligible language typically during religious worship, whereas xenoglossia involves speaking or writing in a language unknown to the individual, often with verifiable linguistic structure. Glossolalia's origins trace back to early Christian practices described in the New Testament, with psychological and sociolinguistic studies linking it to altered states of consciousness and emotional expression. Understanding glossolalia requires examining its role in spiritual experiences and its distinction from xenoglossia's linguistic authenticity and cross-cultural manifestations.
What is Xenoglossia? Key Characteristics
Xenoglossia refers to the phenomenon where an individual suddenly speaks or writes a language previously unknown to them, often without any formal education or exposure. Key characteristics include spontaneous language production, lack of prior learning, and often appearing during trance-like or altered states of consciousness. This differs from glossolalia, which involves fluent but nonsensical speech that resembles language sounds rather than actual foreign languages.
Glossolalia in Religious and Spiritual Contexts
Glossolalia, commonly known as speaking in tongues, often occurs in Pentecostal and Charismatic Christian worship, where it is viewed as a divine spiritual gift facilitating direct communication with God. This phenomenon is characterized by fluent speech-like sounds without recognizable linguistic meaning, symbolizing spiritual ecstasy and connection to the Holy Spirit. In contrast, xenoglossia involves speaking in a foreign language unknown to the speaker, which is less common and typically regarded with skepticism in religious studies.
Xenoglossia: Documented Cases and Controversies
Xenoglossia refers to the phenomenon where individuals speak or write in a language unknown to them, distinct from glossolalia which involves speaking in unintelligible or ecstatic speech. Documented cases of xenoglossia, such as those reported in the work of psychiatrist Ian Stevenson, often occur in contexts of alleged past-life memories or trance states, sparking significant debate about their authenticity and possible explanations. Critics argue that xenoglossia can be attributed to cryptomnesia, subconscious memory recall, or fraud, while supporters cite these cases as evidence for paranormal or reincarnation phenomena, sustaining ongoing controversies within scientific and paranormal research communities.
Linguistic Features: Comparing Glossolalia and Xenoglossia
Glossolalia involves the production of fluent, speech-like sounds without recognizable meaning or consistent syntactic structure, often characterized by repetitive phonemes and intonation patterns similar to natural language but lacking semantic coherence. Xenoglossia, in contrast, entails the spontaneous or sudden use of a foreign language that the speaker has not consciously learned, exhibiting genuine grammatical rules, vocabulary, and syntax consistent with the target language. Linguistically, glossolalia is a non-structured vocalization primarily associated with emotional or spiritual expression, whereas xenoglossia reflects an actual, though unexplained, mastery of a specific linguistic system.
Psychological Perspectives on Glossolalia and Xenoglossia
Glossolalia, often described as speaking in tongues, is viewed by psychologists as a dissociative state linked to altered consciousness and emotional release, frequently occurring in religious or high-stress contexts. In contrast, xenoglossia involves the spontaneous utterance of a foreign language unknown to the speaker, which remains highly controversial and lacks robust empirical support in psychological literature. Research primarily emphasizes glossolalia's psychological mechanisms such as trance induction, cognitive dissociation, and social reinforcement rather than validating claims of genuine linguistic competence in xenoglossia.
Scientific Explanations and Skepticism
Glossolalia, often called speaking in tongues, is characterized by fluent, non-meaningful speech patterns studied as a psychological phenomenon involving altered states of consciousness and neural mechanisms related to language production. Xenoglossia, defined as the purported ability to speak or write a language previously unknown to the individual, lacks empirical support and is frequently explained by fraud, cryptomnesia, or subconscious language recall rather than paranormal causes. Scientific skepticism emphasizes the absence of verifiable linguistic competence in controlled settings for xenoglossia and interprets glossolalia through neurophysiological and cognitive frameworks without invoking supernatural explanations.
Cultural and Historical Significance of Both Phenomena
Glossolalia, often called speaking in tongues, holds a prominent place in Pentecostal and Charismatic Christian traditions, symbolizing spiritual gifting and divine connection, with roots tracing back to early Christian experiences documented in the New Testament. Xenoglossia, the phenomenon of speaking a language unknown to the speaker, has intrigued researchers and spiritualists alike, appearing in historical cases such as medieval mystics and trance channelers, often perceived as evidence of supernatural communication or past-life memories. Both phenomena reflect diverse cultural interpretations of language and spirituality, highlighting the intersection between linguistic expression and metaphysical beliefs across different societies and historical periods.
Debates: Supernatural Versus Natural Interpretations
Glossolalia, often termed "speaking in tongues," is debated as either a supernatural gift involving divine language or a psychological phenomenon linked to altered states of consciousness. Xenoglossia, where a person speaks an unknown foreign language, sparks discussions about its authenticity, with skeptics citing subconscious knowledge or fraud versus proponents claiming miraculous acquisition. The core debate contrasts natural scientific explanations such as neurology and cognitive psychology with supernatural interpretations rooted in spiritual experiences and religious texts.
Glossolalia vs. Xenoglossia: Main Differences Summarized
Glossolalia refers to speaking in fluent, speech-like but unintelligible sounds often considered a spiritual language, while xenoglossia involves the ability to speak or understand a foreign, real language unknown to the speaker. The main differences hinge on linguistic intelligibility, with glossolalia lacking semantic meaning recognizable to others and xenoglossia demonstrating genuine proficiency in an actual language. Glossolalia is typically linked to religious experiences, whereas xenoglossia often appears in paranormal or extraordinary claims of language acquisition.
Glossolalia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com