Systemic thinking involves understanding complex systems by examining the interconnections and interactions among their components rather than viewing them in isolation. This approach helps identify underlying patterns and leverage points that drive system behavior, making it essential for effective problem-solving and decision-making in various fields. Discover how systemic thinking can transform your perspective and improve outcomes by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
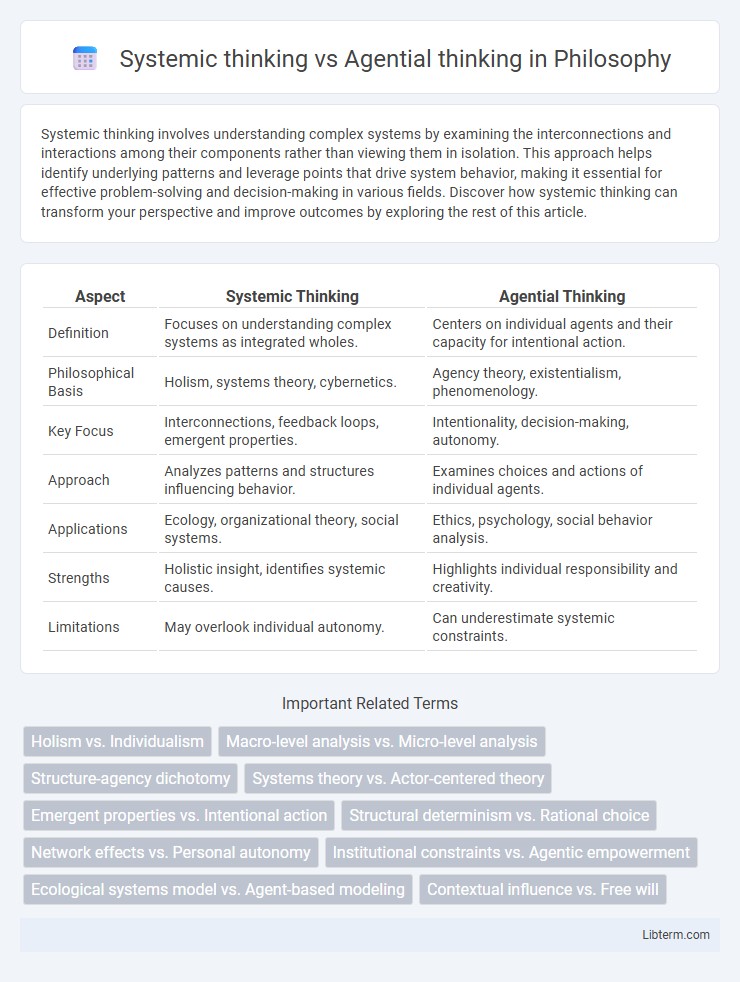
| Aspect | Systemic Thinking | Agential Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on understanding complex systems as integrated wholes. | Centers on individual agents and their capacity for intentional action. |
| Philosophical Basis | Holism, systems theory, cybernetics. | Agency theory, existentialism, phenomenology. |
| Key Focus | Interconnections, feedback loops, emergent properties. | Intentionality, decision-making, autonomy. |
| Approach | Analyzes patterns and structures influencing behavior. | Examines choices and actions of individual agents. |
| Applications | Ecology, organizational theory, social systems. | Ethics, psychology, social behavior analysis. |
| Strengths | Holistic insight, identifies systemic causes. | Highlights individual responsibility and creativity. |
| Limitations | May overlook individual autonomy. | Can underestimate systemic constraints. |
Introduction to Systemic and Agential Thinking
Systemic thinking emphasizes understanding complex systems by analyzing interactions and relationships between components within an entire system. Agential thinking centers on individual or collective agency, focusing on how decision-makers influence outcomes through intentional actions. Both approaches provide essential frameworks for addressing challenges by balancing structural context and human intervention.
Defining Systemic Thinking
Systemic thinking involves understanding complex systems by analyzing the interrelationships and patterns among components within a whole, emphasizing the dynamic interactions and feedback loops that influence system behavior. It prioritizes holistic perspectives, recognizing that changes in one part of the system can affect the entire structure, leading to emergent properties that cannot be predicted by examining individual elements alone. Key concepts include systems theory, causal loops, and holistic problem-solving, which contrast with agential thinking's focus on individual actors and decision-making.
Understanding Agential Thinking
Agential thinking centers on recognizing individual agents as autonomous decision-makers who influence outcomes within systems through intentional actions and choices. It emphasizes the capacity of individuals or entities to exercise agency, adapt strategies, and respond dynamically to changing environments. This mode of thinking contrasts with systemic thinking by highlighting personal accountability and the potential for innovation rather than solely focusing on structural factors and interdependencies.
Core Differences Between Systemic and Agential Approaches
Systemic thinking emphasizes understanding complex systems by analyzing interrelationships, patterns, and feedback loops, focusing on whole-system behavior rather than individual elements. Agential thinking centers on the capacity of individual agents to make autonomous decisions and enact change within a system based on their intentions and actions. The core difference lies in systemic thinking's holistic perspective versus agential thinking's focus on individual autonomy and agency within systemic contexts.
Benefits of Systemic Thinking in Problem-Solving
Systemic thinking enhances problem-solving by enabling a comprehensive understanding of complex systems and their interrelated components, which helps identify root causes rather than superficial symptoms. This approach promotes long-term solutions by considering the ripple effects of decisions across an entire system, leading to more sustainable outcomes. It also fosters collaboration among stakeholders by highlighting interconnectedness and encouraging holistic strategies that address multiple factors simultaneously.
Advantages of Agential Thinking in Decision-Making
Agential thinking empowers decision-makers by emphasizing individual agency, adaptability, and proactive problem-solving in complex environments. This approach enables swift responses to dynamic situations by focusing on personal influence and intentional actions rather than solely on systemic constraints. Agential thinking enhances innovation and accountability, fostering decisions that leverage unique insights and creative strategies for effective outcomes.
Real-World Examples: Systemic vs. Agential Thinking
Systemic thinking analyzes complex interactions within systems such as climate change models, where multiple environmental, social, and economic factors influence outcomes. Agential thinking emphasizes individual or organizational decision-making, as seen in entrepreneurial ventures where a founder's choices directly impact business success. Real-world examples highlight how systemic approaches address broad issues like urban planning, while agential thinking drives innovation through targeted actions.
Integrating Systemic and Agential Perspectives
Integrating systemic and agential perspectives enhances decision-making by combining the holistic understanding of interconnected systems with the active role of individual agents in shaping outcomes. Systemic thinking highlights patterns and feedback loops within complex environments, while agential thinking emphasizes human creativity, intentionality, and adaptive behavior. This integration fosters more robust strategies that account for both structural constraints and proactive interventions, improving organizational resilience and innovation.
Challenges in Applying Systemic and Agential Thinking
Applying systemic thinking presents challenges such as managing the complexity of interconnected components and anticipating emergent behaviors within dynamic environments. Agential thinking struggles with accounting for individual autonomy and unpredictable decision-making while integrating these actions into broader system-level analysis. Both approaches demand balancing detailed local actions with global systemic insights, often requiring advanced modeling tools and interdisciplinary expertise to effectively reconcile micro- and macro-level perspectives.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting between systemic thinking and agential thinking depends on the complexity of the problem and the desired outcome. Systemic thinking excels in understanding interconnected patterns and long-term impacts within ecosystems or organizations. Agential thinking is more effective for targeted actions and individual decision-making, emphasizing autonomy and adaptive behavior in dynamic environments.
Systemic thinking Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com