Sensation refers to the process by which our sensory organs detect stimuli from the environment and transmit this information to the brain for interpretation. This fundamental mechanism enables you to perceive the world around you through sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell. Explore the rest of the article to understand how sensation shapes your daily experiences and interactions.
Table of Comparison
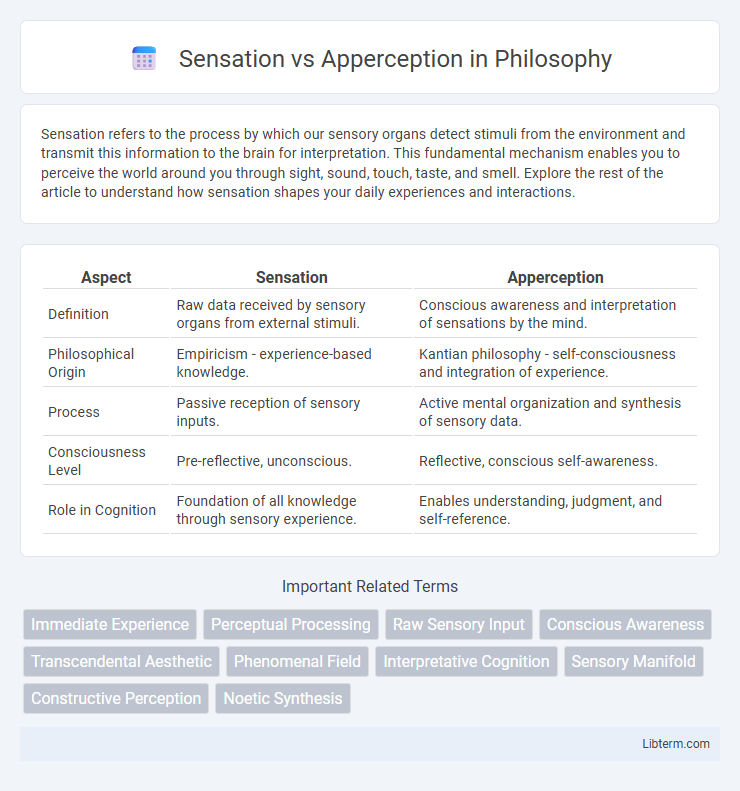
| Aspect | Sensation | Apperception |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw data received by sensory organs from external stimuli. | Conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations by the mind. |
| Philosophical Origin | Empiricism - experience-based knowledge. | Kantian philosophy - self-consciousness and integration of experience. |
| Process | Passive reception of sensory inputs. | Active mental organization and synthesis of sensory data. |
| Consciousness Level | Pre-reflective, unconscious. | Reflective, conscious self-awareness. |
| Role in Cognition | Foundation of all knowledge through sensory experience. | Enables understanding, judgment, and self-reference. |
Introduction to Sensation and Apperception
Sensation involves the initial detection of stimuli through sensory organs, converting physical signals into neural impulses. Apperception integrates these sensory inputs with past experiences, allowing meaningful interpretation and conscious awareness. Understanding the distinction between sensation as raw data input and apperception as cognitive processing is crucial in fields like psychology and neuroscience.
Defining Sensation: The Basics of Sensory Input
Sensation refers to the initial process of detecting and encoding environmental stimuli through sensory receptors, such as photoreceptors in the eyes or mechanoreceptors in the skin, converting physical energy into neural signals. This raw sensory input represents the basic data collected by the nervous system before any interpretation or understanding occurs. Sensory input forms the foundation of perception, providing the essential information required for apperception, where the brain organizes and interprets these signals into meaningful experiences.
Understanding Apperception: Interpreting Experiences
Apperception involves the active process of interpreting sensory input by integrating past knowledge, experiences, and cognitive frameworks to create meaningful understanding. Unlike mere sensation, which is the raw detection of stimuli, apperception transforms these sensations into organized perceptions by assigning context and significance. This higher-level cognitive function enables individuals to comprehend and respond effectively to their environment through informed interpretation.
Key Differences Between Sensation and Apperception
Sensation refers to the process of detecting and encoding raw sensory stimuli from the environment through sensory organs, while apperception involves the conscious interpretation and organization of these sensory inputs based on prior knowledge and experiences. Sensation is primarily a passive and physiological response to external stimuli, whereas apperception is an active cognitive function that integrates perception with memory and understanding. Key differences include the level of awareness, with sensation being unconscious and apperception requiring conscious attention, and the role of higher mental processes in apperception that shape how sensory information is meaningfully perceived.
The Role of the Brain in Sensation and Apperception
The brain plays a crucial role in transforming raw sensory input into meaningful experiences by integrating sensation and apperception. Sensation involves the detection of stimuli through sensory receptors, whereas apperception is the brain's active interpretation and organization of these sensory signals into coherent perceptions. Neural processes in the cerebral cortex, particularly in areas such as the occipital and parietal lobes, facilitate the synthesis of sensory data with past experiences to enable conscious awareness and understanding.
Sensation and Apperception in Psychological Theories
Sensation refers to the initial process of detecting and encoding environmental stimuli through sensory organs, serving as the raw data for perception. Apperception involves the higher-level cognitive process where these sensory inputs are integrated with past experiences, knowledge, and expectations to create meaningful understanding. Psychological theories such as those from Wilhelm Wundt and Johann Friedrich Herbart emphasize apperception as essential for conscious awareness and cognitive processing beyond mere sensory registration.
Real-life Examples of Sensation vs Apperception
Sensation involves the raw data received through sensory organs, such as feeling the heat from a stove or hearing a siren, while apperception is the mind's interpretation and meaningful understanding of these sensations, like recognizing the stove as hot and dangerous or the siren as an emergency alert. For example, a person touching a surface senses temperature variations, but apperception allows them to identify if the surface is safely warm or too hot to touch. In auditory scenarios, sensation detects sound waves, whereas apperception enables distinguishing between music, speech, or noise based on past experiences and cognitive processing.
The Importance of Apperception in Learning and Development
Apperception enhances learning by integrating new sensory information with prior knowledge, enabling deeper understanding and meaningful connections. This cognitive process supports critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to apply learned concepts across contexts, fostering advanced developmental outcomes. Emphasizing apperception in education facilitates active engagement, promoting lifelong cognitive growth beyond mere sensory perception.
Sensation and Apperception in Art and Perception
Sensation in art refers to the raw data received through sensory organs, such as the visual stimuli of colors and shapes, which form the foundation of perception. Apperception involves the mind's active interpretation and organization of these sensory inputs, allowing the viewer to comprehend and assign meaning to artistic elements. The interplay between sensation and apperception shapes how art is experienced, transforming mere sensory impressions into complex aesthetic understanding.
Concluding Thoughts: Bridging Sensation and Apperception
Sensation provides the raw data input from the environment, while apperception involves the mind's active organization and interpretation of these sensory signals. Bridging sensation and apperception reveals how perception is a dynamic process where sensory information is not merely received but comprehended in the context of prior knowledge and experience. Understanding this connection enhances insights into cognitive processing and the subjective nature of human experience.
Sensation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com