Gnosticism explores the belief that secret knowledge, or gnosis, enables spiritual awakening and liberation from the material world's illusions. This ancient philosophical and religious movement emphasizes the duality between the physical and the divine, offering profound insights into the nature of existence and human consciousness. Discover how Gnosticism can deepen your understanding of spirituality by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
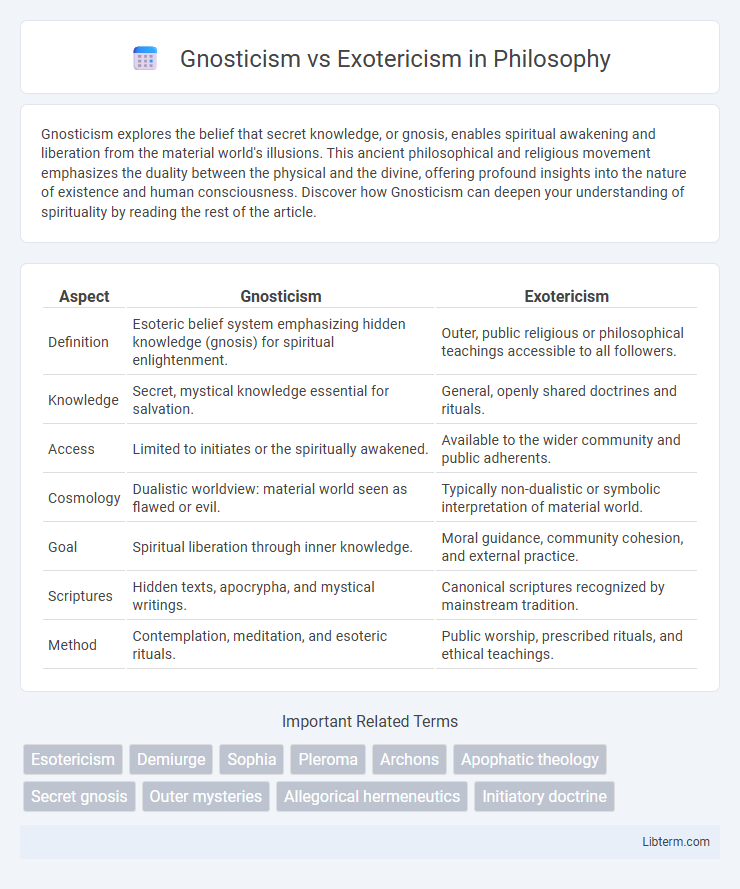
| Aspect | Gnosticism | Exotericism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Esoteric belief system emphasizing hidden knowledge (gnosis) for spiritual enlightenment. | Outer, public religious or philosophical teachings accessible to all followers. |
| Knowledge | Secret, mystical knowledge essential for salvation. | General, openly shared doctrines and rituals. |
| Access | Limited to initiates or the spiritually awakened. | Available to the wider community and public adherents. |
| Cosmology | Dualistic worldview: material world seen as flawed or evil. | Typically non-dualistic or symbolic interpretation of material world. |
| Goal | Spiritual liberation through inner knowledge. | Moral guidance, community cohesion, and external practice. |
| Scriptures | Hidden texts, apocrypha, and mystical writings. | Canonical scriptures recognized by mainstream tradition. |
| Method | Contemplation, meditation, and esoteric rituals. | Public worship, prescribed rituals, and ethical teachings. |
Understanding Gnosticism: Core Beliefs and Practices
Gnosticism centers on the pursuit of gnosis, a deep, esoteric knowledge that reveals the divine spark within and the illusionary nature of the material world, contrasting sharply with exoteric traditions that emphasize outward rituals and communal worship. Core beliefs include the dualistic view of existence, where the spiritual realm is seen as pure and the physical world as flawed or evil, created by a lesser deity known as the Demiurge. Gnostic practices often involve meditation, mystical experience, and personal revelation aimed at awakening the inner divine essence and transcending the limitations imposed by exoteric doctrines.
Defining Exotericism: Main Features and Traditions
Exotericism refers to knowledge and teachings that are openly accessible and intended for the general public, contrasting with the secretive and mystical nature of Gnosticism. Main features of exotericism include public rituals, codified doctrines, and ethical guidelines spread through established religious traditions such as Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism. These traditions emphasize communal worship, scripture study, and moral conduct, promoting spiritual understanding without the hidden or esoteric knowledge characteristic of Gnostic belief systems.
Historical Origins of Gnosticism and Exotericism
Gnosticism originated in the early centuries of the Common Era, emerging as a diverse set of religious movements emphasizing secret knowledge (gnosis) for spiritual salvation, often contrasting with orthodox Christian teachings. Exotericism, rooted in ancient philosophical traditions, refers to publicly accessible doctrines and practices designed for a broad audience, evolving alongside mainstream religious and philosophical systems. The historical divergence reflects differing approaches to knowledge transmission: Gnosticism's focus on hidden, mystical insight versus Exotericism's emphasis on communal, outward teachings.
Knowledge and Revelation: Esoteric vs. Exoteric Approaches
Gnosticism emphasizes hidden, mystical knowledge (gnosis) as the path to spiritual awakening, revealing divine truths accessible only through inner revelation and personal experience. Exotericism promotes open, accessible teachings intended for the general populace, focusing on prescribed doctrines and rituals conveyed openly by religious authorities. The esoteric Gnostic tradition prioritizes secret wisdom that transcends literal interpretation, while exoteric systems rely on communal understanding and external revelation for spiritual guidance.
The Role of Scriptures in Gnostic and Exoteric Faiths
In Gnosticism, scriptures are revered as esoteric texts containing hidden knowledge (gnosis) essential for spiritual awakening and liberation from the material world. Exoteric faiths emphasize scriptures as authoritative, communal guides for moral conduct and worship accessible to all believers. The divergent roles reflect Gnosticism's focus on inner enlightenment versus Exotericism's emphasis on outward religious practice and doctrinal orthodoxy.
Initiation and Secrecy: Contrasting Spiritual Pathways
Gnosticism emphasizes initiation as a transformative inner journey revealing hidden divine knowledge inaccessible to the unprepared, with secrecy protecting esoteric wisdom from misuse. Exotericism, by contrast, promotes accessible teachings and communal rituals designed for broader understanding, prioritizing public participation over hidden truths. This divergence underscores Gnosticism's focus on personal spiritual awakening through guarded mysteries, while Exotericism fosters inclusive practices rooted in outward religious expression.
Authority and Hierarchy in Gnostic and Exoteric Systems
Gnostic systems emphasize esoteric knowledge accessible primarily to an enlightened inner circle, establishing a hierarchical structure where spiritual authority is vested in those possessing hidden wisdom. In contrast, exoteric systems prioritize openly accessible teachings and uniform authority often centralized in institutionalized religious leadership, such as clerical hierarchies or councils. The divergence in authority dynamics reflects Gnosticism's focus on personal gnosis versus exotericism's emphasis on collective adherence to established doctrines.
Salvation and Enlightenment: Divergent Goals and Methods
Gnosticism emphasizes salvation through secret knowledge (gnosis) and inner enlightenment, seeking liberation from the material world's illusions by awakening the divine spark within. Exotericism promotes accessible, communal spiritual teachings and practices aimed at moral improvement and enlightenment through external rituals and doctrines. These divergent approaches highlight Gnosticism's focus on individual mystical insight versus Exotericism's emphasis on collective religious experience for achieving salvation and spiritual growth.
Influence on Modern Spirituality and Religious Thought
Gnosticism, with its emphasis on esoteric knowledge and inner spiritual awakening, profoundly shapes modern spirituality by encouraging personal mystical experiences and direct connection with the divine. Exotericism promotes accessible religious practices and communal rituals, influencing organized religion's role in society and fostering collective moral frameworks. The interplay between Gnostic inner exploration and exoteric communal traditions enriches contemporary spiritual discourse, blending individual enlightenment with established religious structures.
Comparative Analysis: Key Differences and Contemporary Relevance
Gnosticism emphasizes esoteric knowledge (gnosis) as a path to spiritual enlightenment, contrasting with Exotericism's focus on outward teachings accessible to the general population. Key differences include the hidden, mystical nature of Gnostic beliefs versus the public, doctrinal nature of Exoteric traditions. Contemporary relevance is seen in modern spirituality, where Gnosticism influences personalized, inner-directed practices, while Exotericism underpins established religious institutions and communal rituals.
Gnosticism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com