Authenticity is the quality of being genuine and true to oneself, reflecting honesty and integrity in actions and expressions. Embracing authenticity fosters deeper connections and builds trust in both personal and professional relationships. Discover how you can cultivate authenticity to enhance your life and interactions in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
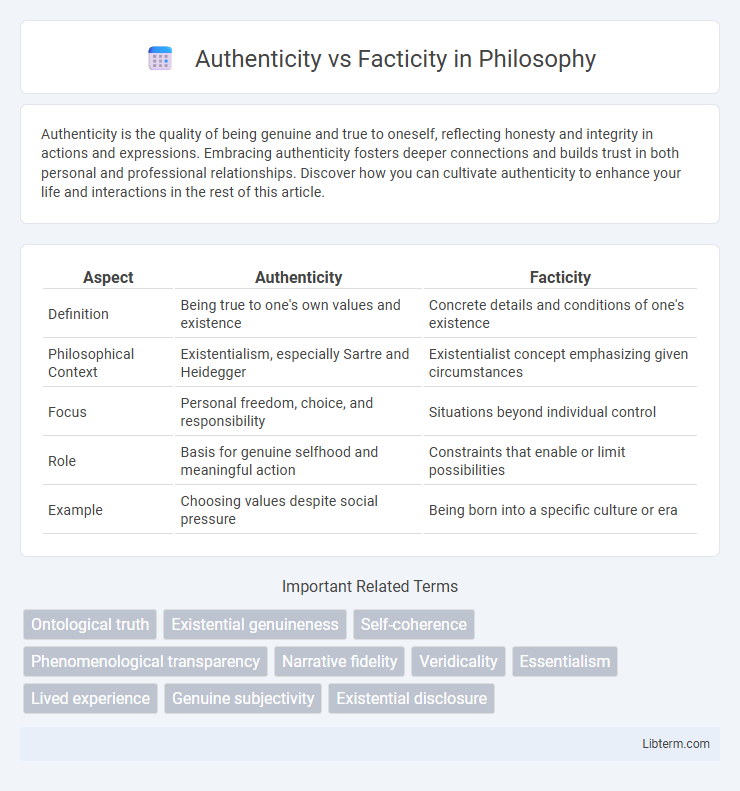
| Aspect | Authenticity | Facticity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Being true to one's own values and existence | Concrete details and conditions of one's existence |
| Philosophical Context | Existentialism, especially Sartre and Heidegger | Existentialist concept emphasizing given circumstances |
| Focus | Personal freedom, choice, and responsibility | Situations beyond individual control |
| Role | Basis for genuine selfhood and meaningful action | Constraints that enable or limit possibilities |
| Example | Choosing values despite social pressure | Being born into a specific culture or era |
Defining Authenticity and Facticity
Authenticity in existential philosophy refers to living in accordance with one's true self and values, embracing freedom and responsibility without self-deception. Facticity encompasses the concrete details of one's existence, such as birth, social conditions, and past choices, which set the context for authentic living. Defining authenticity requires recognizing how facticity shapes possibilities while maintaining personal agency in shaping one's identity.
Historical Roots of Authenticity
Authenticity, rooted in existential philosophy, draws heavily from Martin Heidegger's concept of "Eigentlichkeit," emphasizing an individual's genuine existence amidst societal pressures. Historical roots trace back to Kierkegaard's exploration of selfhood and the struggle against conformity, highlighting the tension between authentic being and facticity--the factual conditions and limitations one inherits. This foundational discourse underscores how authenticity challenges deterministic facts to affirm individual freedom and self-realization.
The Philosophical Origins of Facticity
Facticity originates from existentialist philosophy, particularly the works of Martin Heidegger and Jean-Paul Sartre, emphasizing the concrete details of individual existence that define one's situation. Heidegger introduced facticity as the "thrownness" (Geworfenheit) of humans into the world, highlighting how individuals find themselves embedded in pre-existing contexts beyond their control. This concept contrasts with authenticity by underscoring the unavoidable circumstances and conditions that shape human freedom and identity.
Authenticity in Modern Life
Authenticity in modern life emphasizes living in accordance with one's true self, values, and beliefs despite external pressures and societal expectations. It involves conscious self-reflection, embracing personal responsibility, and resisting conformity to maintain individual integrity. Prioritizing authenticity enhances psychological well-being and fosters genuine connections in increasingly complex and digitalized social environments.
Facticity and the Role of Truth
Facticity refers to the concrete details and conditions of a person's existence, including historical, social, and personal facts that shape experience and limit freedom. The role of truth in facticity highlights the importance of acknowledging these objective realities to achieve genuine self-understanding and authentic decision-making. Embracing facticity involves confronting the unchangeable aspects of life while interpreting them through an honest and truthful lens to foster existential authenticity.
Authenticity vs Facticity in Personal Identity
Authenticity in personal identity emphasizes living in accordance with one's true self, values, and beliefs, fostering a coherent and self-determined existence. Facticity refers to the concrete, given conditions of an individual's existence, such as historical context, social background, and physical limitations, which influence but do not determine identity. The tension between authenticity and facticity lies in balancing self-determined meaning with the unavoidable realities that shape an individual's identity over time.
Navigating Society: Authenticity or Facticity?
Navigating society requires balancing authenticity, the genuine expression of self, with facticity, the acceptance of social constraints and realities. Authenticity fosters individuality and meaningful relationships, while facticity acknowledges external conditions like culture, history, and social roles that shape identity. Successful social navigation harmonizes authentic selfhood with the practical necessities imposed by facticity to create adaptive and genuine interactions.
Authenticity, Facticity, and Moral Choices
Authenticity involves embracing one's true self and making moral choices aligned with personal values despite external pressures, while facticity refers to the concrete conditions and limitations that contextualize these choices. Understanding facticity helps individuals recognize the constraints imposed by history, culture, and circumstance, enabling more genuine and responsible ethical decisions. Moral choices emerge from the dynamic interplay between authenticity and facticity, highlighting the necessity of self-awareness within specific situational boundaries.
Challenges in Balancing Authenticity and Facticity
Balancing authenticity and facticity presents challenges such as navigating the tension between personal freedom and external constraints shaped by social, historical, and cultural contexts. Individuals often struggle to remain true to their authentic selves while acknowledging the factual realities of their existence, which can limit choices and influence identity formation. The conflict arises in integrating subjective experiences with objective circumstances without succumbing to self-deception or alienation.
The Future of Authenticity and Facticity in a Digital Age
The future of authenticity and facticity in a digital age hinges on the increasing integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain technology to verify identities and experiences. Digital platforms are evolving to prioritize transparent algorithms and verifiable data, which enhance genuine interactions and reduce misinformation. As virtual environments expand, maintaining authentic self-representation and acknowledging existential facts will become critical for ethical digital citizenship.
Authenticity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com