Freedom embodies the power to make choices that align with your values and aspirations, fostering personal growth and fulfillment. It enables individuals to pursue opportunities without undue restrictions, shaping their own path in life. Explore how embracing freedom can transform your mindset and unlock endless possibilities throughout the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
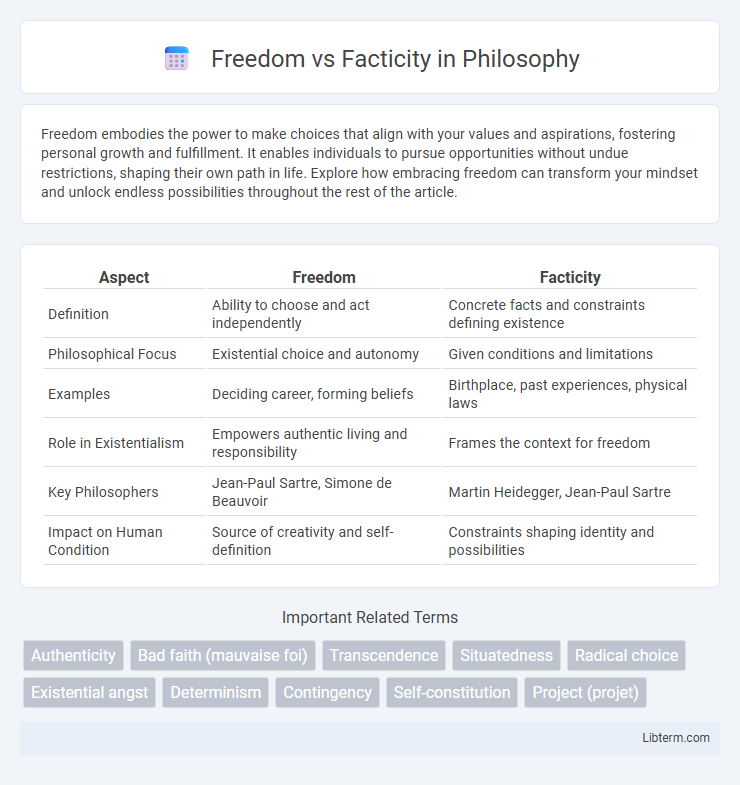
| Aspect | Freedom | Facticity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to choose and act independently | Concrete facts and constraints defining existence |
| Philosophical Focus | Existential choice and autonomy | Given conditions and limitations |
| Examples | Deciding career, forming beliefs | Birthplace, past experiences, physical laws |
| Role in Existentialism | Empowers authentic living and responsibility | Frames the context for freedom |
| Key Philosophers | Jean-Paul Sartre, Simone de Beauvoir | Martin Heidegger, Jean-Paul Sartre |
| Impact on Human Condition | Source of creativity and self-definition | Constraints shaping identity and possibilities |
Understanding Freedom: Definitions and Perspectives
Freedom encompasses the ability to make choices unconstrained by external forces, reflecting autonomy and self-determination in philosophical discourse. Perspectives on freedom range from existentialist views, emphasizing individual agency despite facticity--the unchangeable conditions of existence--to political theories prioritizing rights and liberties within societal frameworks. Understanding freedom involves analyzing its interplay with facticity, highlighting how humans navigate constraints while asserting personal freedom.
Facticity Explained: The Boundaries of Existence
Facticity refers to the concrete details and conditions that define an individual's existence, such as birthplace, social background, and historical context, which set the boundaries within which freedom operates. These innate and external constraints shape possibilities but do not eliminate the capacity for autonomous choice and self-definition. Understanding facticity is crucial to grasp how freedom is exercised within the limitations imposed by reality.
Philosophical Roots: Sartre, Heidegger, and Existentialism
Freedom vs facticity is central in existential philosophy, with Sartre emphasizing radical freedom as the foundation of human existence despite facticity's constraints like birth and social context. Heidegger explores facticity as "thrownness," highlighting how individuals are always situated in a specific world that shapes their possibilities but do not determine their freedom to choose. Existentialism broadly grapples with the tension between freedom and facticity, underscoring the individual's responsibility to create meaning within given circumstances.
The Tension Between Choice and Circumstance
Freedom involves the capacity to make choices independent of external constraints, while facticity represents the concrete conditions and limitations shaping those choices. The tension between choice and circumstance arises because individuals must navigate their actions within given contexts such as social, historical, and personal realities. This dynamic interplay reflects existentialist themes where human freedom is exercised against an unavoidable backdrop of facticity.
Freedom Within Limits: Navigating Human Constraints
Freedom within limits acknowledges that human autonomy operates under inherent constraints such as biology, social norms, and existential conditions. Navigating these boundaries requires accepting facticity while exercising agency to make meaningful choices within given circumstances. This balance between freedom and facticity forms the foundation of pragmatic human decision-making and authentic existence.
Facticity and Identity: Shaping Who We Are
Facticity encompasses the concrete details of our existence, such as birthplace, cultural background, and historical context, which anchor our identity in specific conditions beyond our control. These elements shape our self-perception and social roles by providing a framework within which freedom operates, limiting and enabling choices. Understanding facticity reveals how identity is constructed through the interplay of given circumstances and conscious decisions, emphasizing its role in defining who we are.
Social and Cultural Dimensions of Facticity
Facticity in social and cultural dimensions encompasses the historical, environmental, and societal conditions that shape individual existence and limit choices. Social roles, traditions, and collective norms represent concrete facticities that influence behavior and identity within specific cultural contexts. Understanding facticity highlights the tension between individual freedom and the constraints imposed by inherited social structures.
Authenticity: Overcoming Facticity Through Choice
Authenticity in existential philosophy demands recognizing facticity--the immutable conditions of existence such as past experiences, social background, and physical limitations--while actively exercising freedom through conscious choices. By embracing responsibility for decisions despite these constraints, individuals transcend deterministic aspects of facticity to create meaningful and self-defined lives. This dynamic interplay between freedom and facticity underscores the human capacity for authentic existence through deliberate choice.
Ethical Dilemmas: Responsibility Amid Facticity
Freedom exists within the constraints of facticity, where individuals face ethical dilemmas by navigating responsibilities shaped by their given circumstances. Responsibility amid facticity requires acknowledging limits imposed by social, historical, and personal conditions while exercising freedom to make morally significant choices. This interplay reveals that authentic ethical behavior arises from confronting facticity without denying the inherent freedom to act responsibly.
Freedom vs Facticity in Contemporary Life
Freedom in contemporary life is often challenged by facticity, which encompasses the unchangeable circumstances such as social conditions, historical context, and personal limitations. Individuals navigate these constraints while striving to assert autonomy and make meaningful choices, highlighting the tension between predetermined reality and self-determination. The dynamic interplay between freedom and facticity shapes ethical decisions, existential identity, and social interactions in modern societies.
Freedom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com