Dualism explores the idea that reality consists of two fundamental substances: mind and matter, which are distinct yet interact in complex ways. This philosophical view raises important questions about consciousness, identity, and the nature of existence that continue to influence debates in science and metaphysics. Dive deeper into this article to understand how dualism shapes our understanding of mind-body relationships and its implications for your worldview.
Table of Comparison
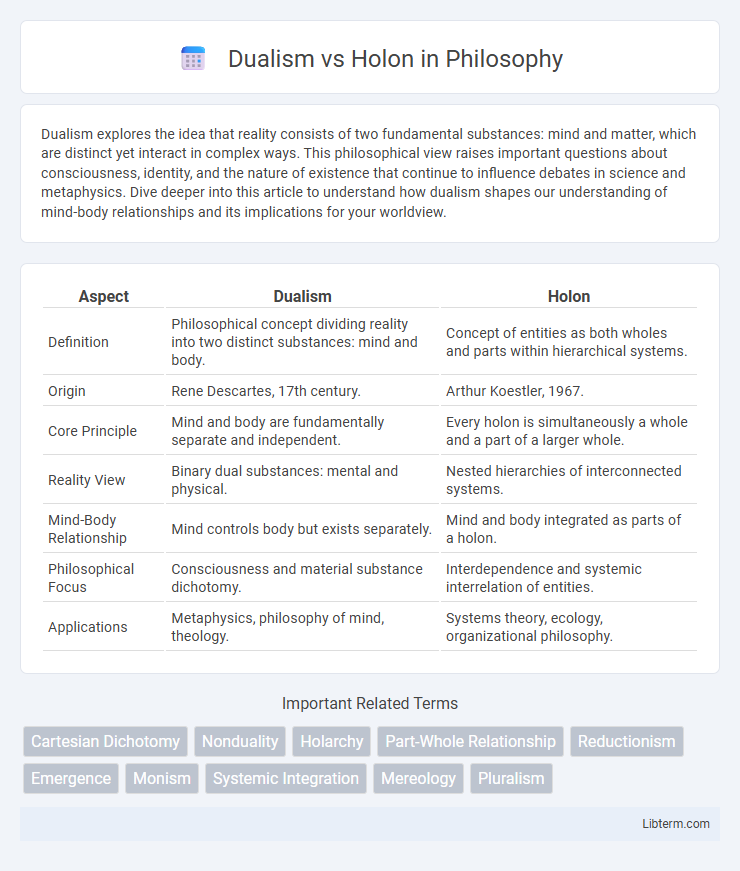
| Aspect | Dualism | Holon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophical concept dividing reality into two distinct substances: mind and body. | Concept of entities as both wholes and parts within hierarchical systems. |
| Origin | Rene Descartes, 17th century. | Arthur Koestler, 1967. |
| Core Principle | Mind and body are fundamentally separate and independent. | Every holon is simultaneously a whole and a part of a larger whole. |
| Reality View | Binary dual substances: mental and physical. | Nested hierarchies of interconnected systems. |
| Mind-Body Relationship | Mind controls body but exists separately. | Mind and body integrated as parts of a holon. |
| Philosophical Focus | Consciousness and material substance dichotomy. | Interdependence and systemic interrelation of entities. |
| Applications | Metaphysics, philosophy of mind, theology. | Systems theory, ecology, organizational philosophy. |
Introduction to Dualism and Holon
Dualism describes the philosophical concept that reality consists of two fundamental and often opposing components, such as mind and body or good and evil. Holon, introduced by Arthur Koestler, refers to an entity that is simultaneously a whole and a part of a larger system, emphasizing interconnectedness and hierarchical organization. Understanding these frameworks is essential for analyzing complex systems in philosophy, biology, and cognitive science.
Historical Perspectives on Dualism
Historical perspectives on dualism trace back to ancient philosophy, notably in Plato's theory of forms and Descartes' mind-body distinction, emphasizing the separation between mind and matter. This long-standing dichotomy has influenced metaphysics, psychology, and theology by framing reality as two fundamentally different substances. The dualistic framework contrasts with the holistic view of holons, which integrates parts within wholes, highlighting interconnectedness rather than division.
Origins and Evolution of Holon Theory
Holon theory, introduced by Arthur Koestler in the 1960s, emerged as a response to traditional dualism by proposing that entities function simultaneously as wholes and parts within larger systems. This evolutionary concept integrates hierarchical self-regulating systems, contrasting with the rigid binary nature of dualism by emphasizing the interconnectedness and interdependence of components in complex organizations. The development of holon theory has significantly influenced systems science, biology, and philosophy, fostering a holistic understanding of dynamic, multi-level structures.
Defining Dualism: Key Concepts
Dualism is a philosophical concept asserting the existence of two fundamental and distinct substances or realities, commonly identified as mind and body or spirit and matter. It emphasizes separation and opposition between these entities, suggesting they operate independently yet interactively within human experience. Key concepts include substance dualism, which posits two types of substance, and property dualism, which focuses on different properties of a single substance.
Understanding the Holon: Fundamentals
The concept of the holon, introduced by Arthur Koestler, defines entities as simultaneously wholes and parts within hierarchical systems, emphasizing interconnectedness and dynamic relationships. Unlike dualism, which separates mind and body into distinct categories, holon theory integrates these elements into a unified framework, highlighting emergent properties at each level. Understanding holons involves recognizing their autonomous yet interdependent nature, essential for analyzing complex biological, social, and ecological systems.
Dualism in Philosophy and Science
Dualism in philosophy posits the existence of two fundamentally distinct substances or realities, typically mind and body, which interact but remain separate. In science, dualism challenges materialist perspectives by asserting that mental phenomena cannot be fully explained by physical processes alone. This conceptual framework underpins debates in consciousness studies and cognitive science, emphasizing the epistemological divide between subjective experience and objective observation.
The Holon Approach in Systems Thinking
The Holon approach in systems thinking emphasizes that every element is simultaneously a whole and a part of a larger system, integrating both autonomy and interdependence. Unlike dualism, which separates entities into independent categories, holons highlight nested hierarchies where each level influences and is influenced by others, promoting a more dynamic and interconnected understanding of complex systems. This perspective enhances problem-solving by acknowledging multiple layers of reality and fostering collaboration across different system components.
Comparative Analysis: Dualism vs Holon
Dualism divides reality into two distinct and opposing entities, such as mind and body, emphasizing their separation and interaction, whereas the Holon concept introduces a unit that is simultaneously a whole and a part, promoting integration and systemic relationships. Dualism often leads to binary thinking and hierarchical structures, while Holon supports nested, interconnected systems that reflect complexity and interdependence. This comparative analysis highlights Dualism's focus on dichotomy against Holon's emphasis on unity and multiplicity within natural and social phenomena.
Implications for Consciousness and Reality
Dualism posits a fundamental separation between mind and body, suggesting consciousness exists independently from physical reality, which raises challenges in explaining their interaction and integration. Holon theory, emphasizing whole-part relationships, views consciousness and reality as nested, interconnected systems where each entity is both a whole and a part, fostering a more integrated understanding of mind-matter interdependence. This holistic perspective supports emergent properties of consciousness arising from complex, multi-level interactions within reality's hierarchical structure.
Future Directions: Integrative Theories
Future directions in integrative theories emphasize synthesizing dualism and holon frameworks to create comprehensive models of consciousness and reality. Research explores how dualistic mind-body distinctions can coexist with holonic hierarchical systems that view entities as nested wholes and parts simultaneously. Advancements in cognitive science, quantum physics, and systems theory support the development of unified paradigms, facilitating breakthroughs in understanding complex phenomena across biology, psychology, and philosophy.
Dualism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com