A physical stance involves understanding and predicting behavior by focusing on the physical structure and capabilities of an organism or system. This approach explains actions based on physical interactions and constraints rather than abstract reasoning or mental states. Discover how the physical stance influences various fields by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
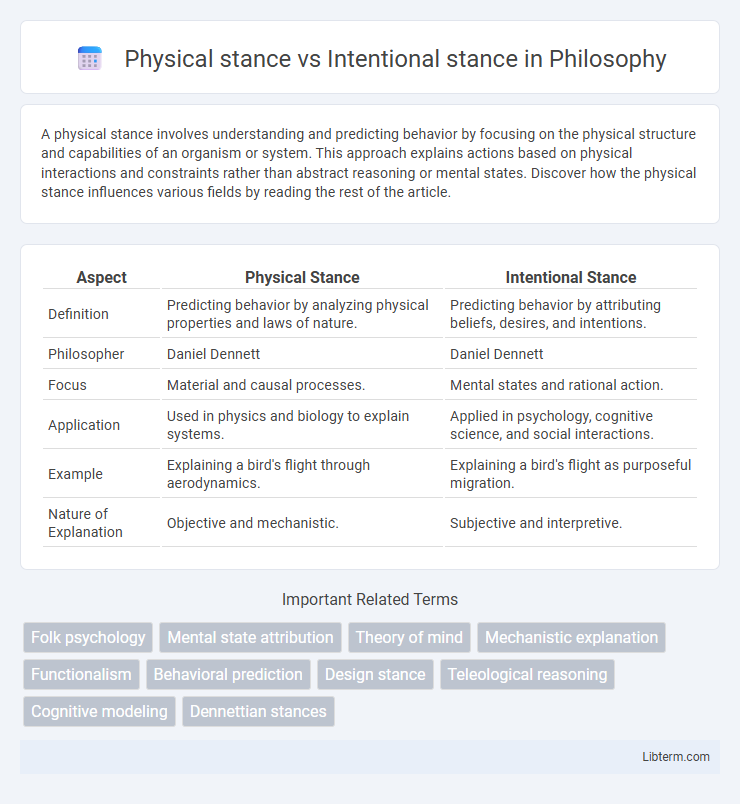
| Aspect | Physical Stance | Intentional Stance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Predicting behavior by analyzing physical properties and laws of nature. | Predicting behavior by attributing beliefs, desires, and intentions. |
| Philosopher | Daniel Dennett | Daniel Dennett |
| Focus | Material and causal processes. | Mental states and rational action. |
| Application | Used in physics and biology to explain systems. | Applied in psychology, cognitive science, and social interactions. |
| Example | Explaining a bird's flight through aerodynamics. | Explaining a bird's flight as purposeful migration. |
| Nature of Explanation | Objective and mechanistic. | Subjective and interpretive. |
Introduction to Physical and Intentional Stances
The physical stance involves predicting behavior based on the physical constitution and laws governing an entity's components, emphasizing mechanistic and scientific explanations. The intentional stance interprets behavior by attributing beliefs, desires, and rationality to an agent, treating it as a purposeful decision-maker. These stances provide distinct frameworks for understanding and predicting actions, essential in fields like cognitive science and artificial intelligence.
Defining the Physical Stance
The physical stance involves predicting and explaining behavior by analyzing an entity's physical properties and the laws of physics governing them. This approach relies on understanding mechanical processes, chemical interactions, and biological functions to determine outcomes without attributing mental states. Emphasizing observable, measurable phenomena, the physical stance contrasts with the intentional stance, which interprets behavior through beliefs, desires, and rationality.
Defining the Intentional Stance
The Intentional stance is a strategy described by philosopher Daniel Dennett, where one interprets the behavior of an entity by assuming it has beliefs, desires, and rationality, treating it as an agent with intentions. This approach differs from the Physical stance, which analyzes an entity purely through physical laws and mechanisms without attributing mental states. Using the Intentional stance facilitates prediction and explanation of complex behaviors in humans, animals, and even artificial intelligence by inferring purposeful actions.
Historical Context and Origins
The physical stance, rooted in classical physics and early behaviorism, interprets systems purely through their physical properties and causal laws, emphasizing observable phenomena and deterministic mechanisms. The intentional stance, introduced by philosopher Daniel Dennett in the late 20th century, represents a paradigm shift by attributing beliefs, desires, and rationality to agents for predictive purposes, advancing cognitive science and philosophy of mind. This conceptual evolution reflects the historical trajectory from mechanistic explanations to embracing mental states as heuristic tools in understanding complex systems.
Key Differences Between the Stances
The physical stance explains behavior by referencing an object's physical properties and laws of nature, emphasizing observable and measurable phenomena. The intentional stance interprets behavior by attributing beliefs, desires, and intentions to agents, focusing on predictive understanding through mental states. Key differences lie in the physical stance's reliance on mechanistic explanations versus the intentional stance's use of rational agent models.
Applying the Physical Stance in Analysis
Applying the Physical Stance in analysis involves understanding systems purely through their physical properties and mechanistic interactions, emphasizing cause-and-effect relationships governed by natural laws. This approach prioritizes observable data and predictive modeling based on the system's structural components, often used in fields like physics, engineering, and neuroscience. By focusing on tangible elements and dismissing assumptions about intentions or goals, the Physical Stance enables precise, objective explanations of behavior and outcomes.
Applying the Intentional Stance in Analysis
Applying the Intentional Stance in analysis involves interpreting an agent's behavior by attributing beliefs, desires, and rational choices to predict actions effectively. This approach, developed by philosopher Daniel Dennett, contrasts with the Physical Stance, which relies solely on underlying physical and biological mechanisms. Utilizing the Intentional Stance simplifies complex systems, enabling more efficient and accurate predictions in fields like artificial intelligence, cognitive science, and behavioral economics.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
The physical stance analyzes behavior through the laws of physics, such as predicting a ball's trajectory or a robot's mechanical movements. The intentional stance interprets actions by attributing beliefs and desires, seen in case studies of AI like DeepMind's AlphaGo, which models opponents' strategies as goal-driven agents. Real-world examples include diagnosing malfunctioning machinery via physical states, contrasted with understanding human social interactions by ascribing intentions.
Relevance in Philosophy and Cognitive Science
The physical stance emphasizes explaining behavior through physical properties and causal mechanisms, grounding analysis in observable phenomena and neural processes within philosophy and cognitive science. The intentional stance, by attributing beliefs, desires, and rationality to agents, provides a framework for predicting behavior based on mental state attributions and functional roles. This distinction is crucial for understanding different explanatory models in cognitive science and debates on the nature of mind in philosophy.
Implications and Future Directions
The physical stance, which interprets behavior through mechanical and biological processes, offers precise predictions but often falls short in explaining complex mental states, while the intentional stance treats entities as rational agents with beliefs and desires, enabling more flexible interaction models. Implications of integrating both stances suggest advancements in artificial intelligence, enhancing machines' abilities to predict human behavior and improve human-computer interactions. Future directions involve developing hybrid frameworks that leverage the explanatory power of the intentional stance and the empirical rigor of the physical stance to create more adaptive and context-aware AI systems.
Physical stance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com