Aboutness refers to the central theme or main subject that a text or piece of content is focused on, helping readers quickly grasp its core meaning. Understanding aboutness enhances your ability to identify relevant information and improve comprehension in research or communication. Explore the rest of the article to learn how aboutness influences effective reading and content analysis.
Table of Comparison
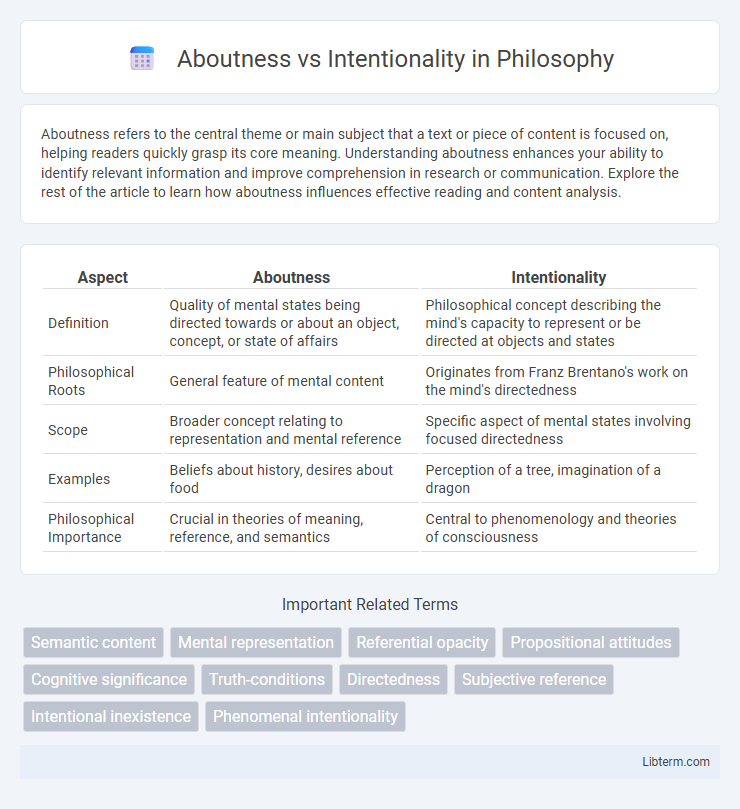
| Aspect | Aboutness | Intentionality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Quality of mental states being directed towards or about an object, concept, or state of affairs | Philosophical concept describing the mind's capacity to represent or be directed at objects and states |
| Philosophical Roots | General feature of mental content | Originates from Franz Brentano's work on the mind's directedness |
| Scope | Broader concept relating to representation and mental reference | Specific aspect of mental states involving focused directedness |
| Examples | Beliefs about history, desires about food | Perception of a tree, imagination of a dragon |
| Philosophical Importance | Crucial in theories of meaning, reference, and semantics | Central to phenomenology and theories of consciousness |
Defining Aboutness: Core Concepts
Aboutness refers to the semantic relationship between a piece of information and its subject matter, indicating what an expression or content is "about." Core concepts include reference, where linguistic elements point to specific entities, and content relevance, which measures the degree to which the information pertains to the intended topic. Understanding aboutness is essential for fields like information retrieval and natural language processing to ensure accurate interpretation and meaningful context extraction.
Understanding Intentionality in Philosophy
Intentionality in philosophy refers to the capacity of the mind to represent objects, properties, or states of affairs, highlighting the directedness of mental states toward something beyond themselves. It is a fundamental concept in phenomenology and the philosophy of mind, distinguishing mental phenomena from physical events by their "aboutness," yet emphasizing that intentionality involves a purposeful and meaningful relation to its object. Understanding intentionality clarifies how beliefs, desires, and perceptions are inherently structured to be about things, shaping discussions on consciousness, language, and meaning.
Historical Origins of Aboutness and Intentionality
Aboutness and intentionality trace their historical origins to classical philosophy, notably in the works of Brentano, who redefined intentionality as the mind's capacity to be directed toward objects or states of affairs. Medieval scholastic philosophers further developed aboutness through theories of reference and representation in language, emphasizing the relationship between mental states and meanings. These foundational ideas influenced modern analytic philosophy and cognitive science, shaping contemporary understandings of mental content, reference, and semantic relationships.
Key Differences Between Aboutness and Intentionality
Aboutness refers to the inherent quality of a representation or expression that makes it relate to or be about a particular subject matter. Intentionality is the mental capacity or directedness of thoughts and consciousness towards objects, states, or concepts, emphasizing the purposeful aspect of mental phenomena. Key differences include that aboutness concerns the content or reference of information, while intentionality focuses on the cognitive direction and purposefulness of mental states.
Aboutness in Linguistics and Semantics
Aboutness in linguistics and semantics refers to the property of a text, utterance, or discourse that indicates what it is primarily concerned with or describes. This concept plays a crucial role in information retrieval and text summarization by enabling systems to identify the main topic or subject matter based on semantic content and context. Understanding aboutness supports the accurate interpretation of meaning and relevance within communication, facilitating better alignment between language input and conceptual knowledge.
Intentionality in Philosophy of Mind
Intentionality in the philosophy of mind refers to the capacity of mental states to be about, represent, or stand for objects and states of affairs in the world. It is a fundamental feature distinguishing mental phenomena, enabling thoughts, beliefs, desires, and perceptions to have content directed toward something beyond themselves. Philosophers like Franz Brentano emphasized intentionality as the mark of the mental, contrasting it with mere physical processes that lack this property.
The Role of Reference and Meaning
Aboutness in linguistics refers to the relationship between a text or discourse and its subject matter, emphasizing the reference to entities, concepts, or situations in the world. Intentionality, rooted in philosophy of mind, concerns the capacity of mental states to be directed toward or about something, highlighting the purposeful nature of meaning and thought. The role of reference and meaning intertwines these concepts by grounding aboutness in the explicit linkage between language and its referents, while intentionality underscores the cognitive orientation toward these referents, reflecting how meaning is constructed through both linguistic reference and mental focus.
Cognitive Science Perspectives on Aboutness
In cognitive science, aboutness refers to the capacity of mental states to represent or be directed towards objects, properties, or states of affairs in the world, highlighting representational content and semantic relations. Intentionality, often used interchangeably yet distinct, emphasizes the mind's inherent directedness or "aboutness" towards something, grounding mental phenomena in directed reference and goal-oriented cognitive processes. Key theories insist that aboutness involves the interpretative frameworks by which cognitive agents attribute meaning, whereas intentionality pertains to the underlying mechanisms enabling such directed representation in reasoning, perception, and belief systems.
Practical Implications in Artificial Intelligence
Aboutness in artificial intelligence refers to the capacity of systems to represent or be about real-world entities, enabling accurate knowledge representation and retrieval. Intentionality involves an AI's ability to ascribe purpose or goals to actions, crucial for decision-making and autonomous behavior. Practical implications in AI systems include improving natural language understanding, enhancing contextual relevance in information retrieval, and enabling goal-directed interactions in autonomous agents.
Debates and Future Directions in Semantic Theory
Debates on aboutness versus intentionality in semantic theory center on whether meaning primarily derives from an entity's relational focus or its mental representational content, shaping divergent models of linguistic interpretation. Recent research explores integrating cognitive science insights with formal semantics to reconcile these perspectives, emphasizing the dynamic interplay between context and meaning. Future directions aim to develop hybrid frameworks that capture both the referential scope of aboutness and the mental states underpinning intentionality, advancing computational linguistics and natural language understanding.
Aboutness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com